Contents of the case

Media
Initial data
Whole works
- /01 Placement in the TOP-5 key categories
- /02 Expansion of the site structure
- /03 Expansion of the semantic core
- /04 Setting up SEO filters
- /05 Increasing the conversion rate of the site
Main problems and strategy
At the stage of getting the site up and running, it had a very simple first-level structure. That is, the website had only the main categories where all the products were. But such a structure did not cover all queries that we could rank for and that would be thematically relevant. Since the site was not ranked for almost any queries, it was necessary to create the correct hierarchy of categories, subcategories and SEO filters as a basis for further promotion.
That is why the main focus of work at the first stage was the correct structure. And there was another task, but it concerned more content managers, which affected the structure – this is the correct filling of filter attributes for the formation of SEO filter pages.
Next, we have already started working with the external reference profile and basic usability. Google ranking should have been improved due to strong external signals, good behavioral factors and high conversion rates.
There was no emphasis on technical optimization due to the specifics of the admin, as it has a closed code. The most we can do in such conditions is to fix all the critical problems, and then switch to the content and reference component.
What was done
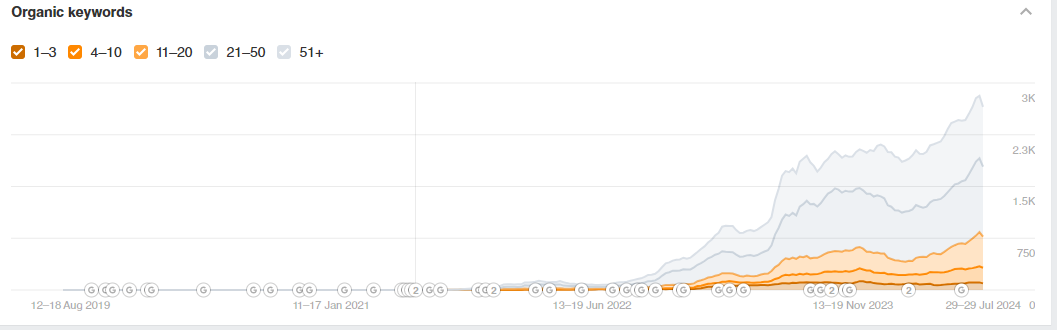
Semantics
The site was almost “scratch” and without a normal structure to hone in on all the relevant niche keywords. But there was a problem in that, having a closed code, it was not possible to conveniently generate pages for categories, etc., through the admin. Therefore, the pages were created manually: a full cluster of semantics was collected by category, the irrelevant semantics were discarded by the site’s products, the necessary semantics were clustered by subcategory and separately for products of this category. And so, we moved through each separate category.
In the course of work, the range of the site was expanded, and along the way new subcategories were added, on which semantics were collected, and pages were optimized.
After the main categories and subcategories have been created, it’s time to work with SEO filters. When filling categories and updating data in products, lists of attributes were collected for product groups of the category so that content managers could correctly write in the admin. This was necessary in order to create SEO filter pages in a semi-automatic mode. These pages were unique with meta tags and content so that Google would not count them as duplicates.
Content
Content for categories and subcategories was created on the basis of collected semantics and analysis of competitors’ texts for each individual cluster.
That is, after analyzing the texts of competitors, we knew the required average size, the percentage of nausea of keys, the approximate structure of the future text and other parameters. Combining this with the collected semantics, detailed TK of the copywriter for writing texts was created.
Expanding the structure
For the site, the expansion of the structure was a necessity, since we would not have been able to advance for the basic categories of HF requests alone. In order to be able to compete in commercial publishing with larger online stores and aggregators, we needed to create a large number of pages in order to at least come close to the smallest of competitors in terms of the number of unique pages on the site.
The second direction of expanding the structure was the implementation of the so-called SEO filter. This is when product filter pages become landing pages for relevant groups of queries. This is how it was possible to work out broader semantics and at the same time not to make a third level of nesting physically in the form of a subcategory.
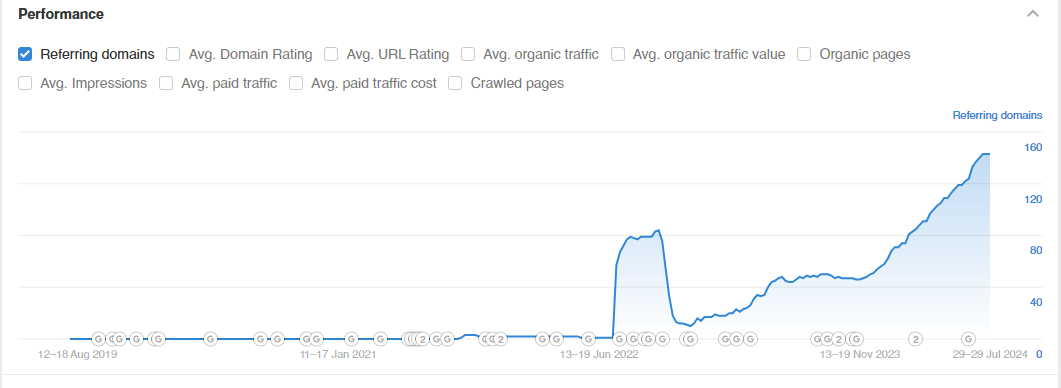
Referral profile
After analyzing the referral profiles of the site and TOP competitors, they formed a strategy for recruiting the referral mass of the site.
As mentioned above, the referral profile of the site was not pumped, so we started very smoothly, so that everything looked as natural as possible, and Google did not think that the referral profile was purchased.
For this, anchor links with thematic texts from technically high-quality sites were used. Also, crowd links and links from various directories, blogs, etc. were used to dilute the link profile.
All for the sole purpose of gaining reference weight and doing it as naturally as possible.
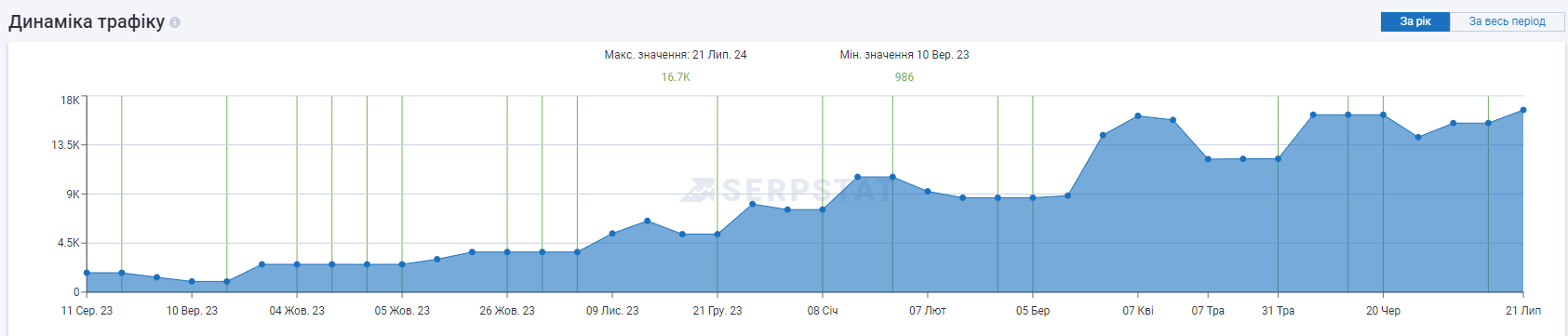
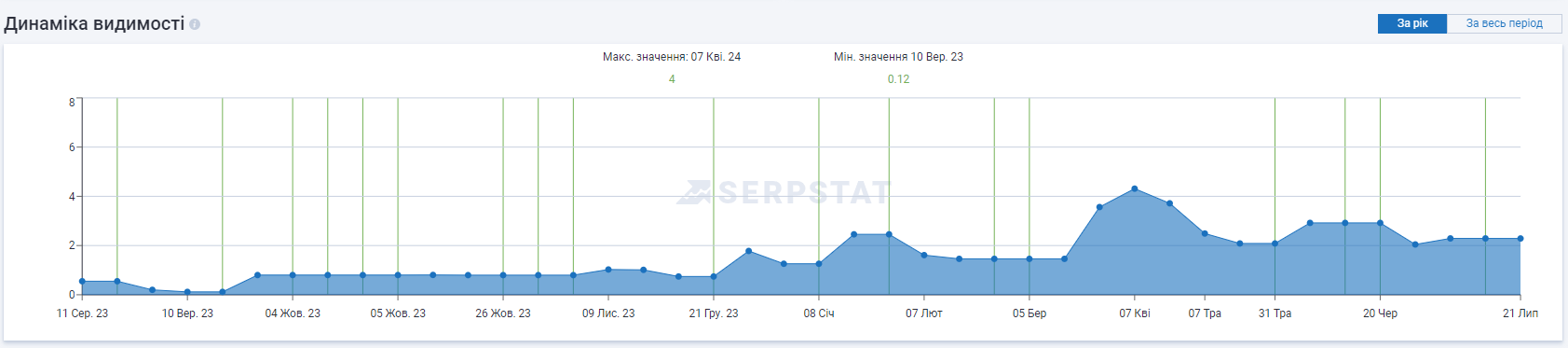
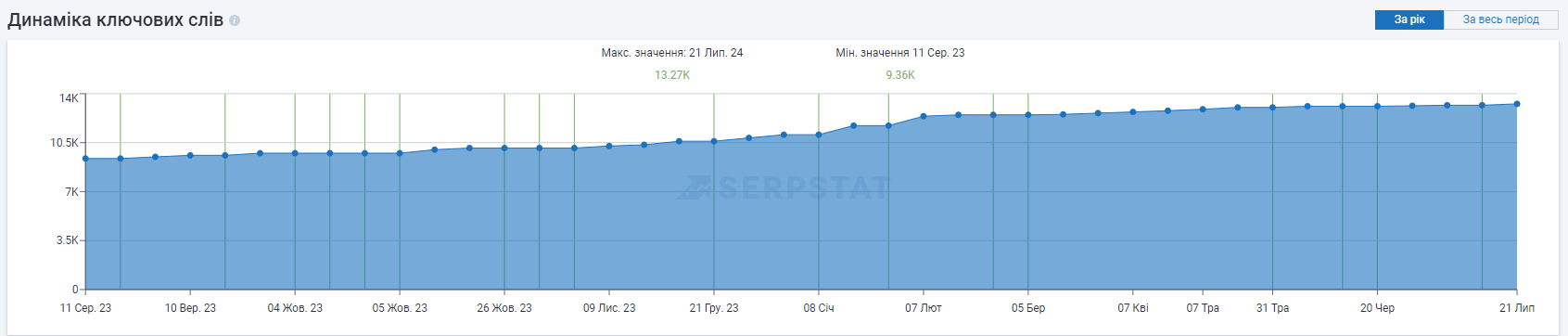
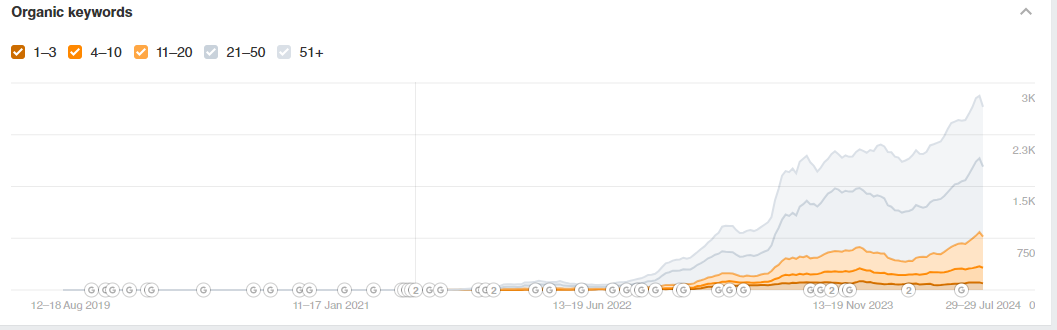
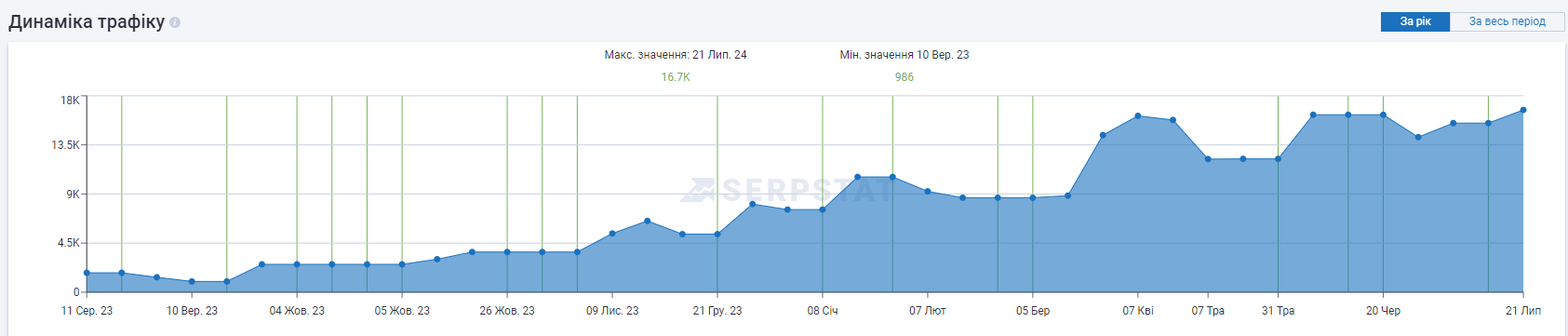
Results
| Options | At the beginning of work | After 10 months | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic traffic | |||
| Organic traffic | 986 | 19812 | +2001% |
| Site visibility | |||
| Site visibility | 0 | 2.29 | +229% |
| Key requests | |||
| Key requests | 3285 | 13270 | +402% |