Content of the article

In 2025, the rapid development of digital technologies and the mobile Internet creates new challenges and opportunities for businesses. More and more tasks – from work to shopping and communication – are performed from smartphones, and the majority of web traffic is generated by mobile devices. Users expect quick access to relevant content, and traditional navigation with a redirect to the main page of an app or website often leads to a loss of visitors and a decrease in conversion. In such conditions, businesses need solutions that minimize obstacles and immediately guide users to the necessary information.
In this article, we will take a closer look at the use of deep links in a business context. In particular, the technical principles of their work and the main types, the role of deep links in marketing strategies for attracting and retaining customers. We will also discuss practical approaches to implementing deeplinks in business processes and how deeplinks can optimize user experience and increase the effectiveness of digital marketing.
What is a deeplink?
A deeplink is a regular web link that does not lead to the main page of a website or application, but directly to a specific section or product. Instead of forcing the user to search for the desired content on their own, a deeplink takes them to the desired screen or page. As marketer Neil Patel explains, this is «a detail that can dramatically improve the user experience of your app.» On mobile devices, devices first check if the app is installed: if so, the deeplink immediately opens the desired section of the app, if not, it redirects the user, for example, to the AppStore or website.
Why is deeplink important for business?
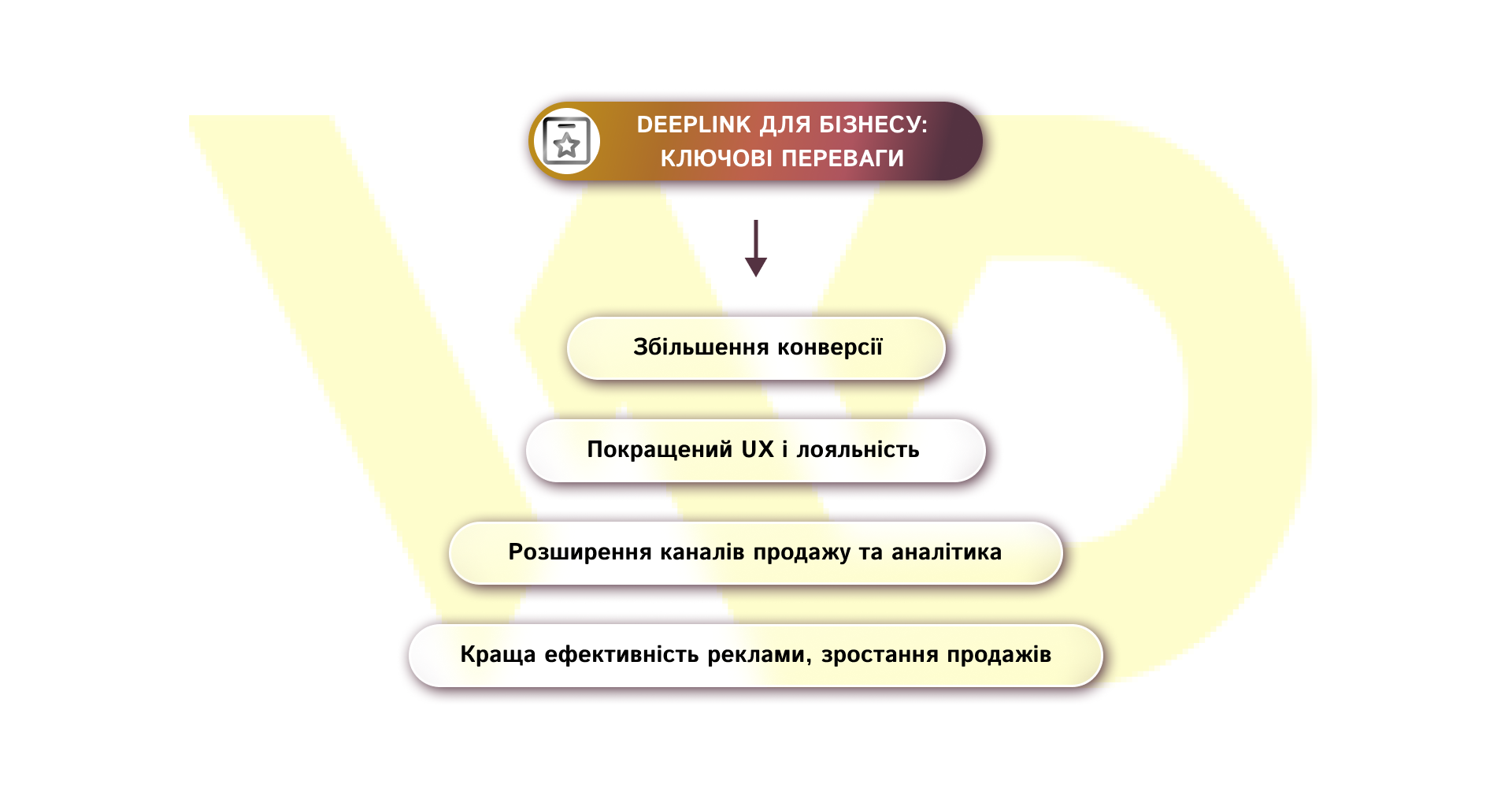
Implementing deeplinks dramatically optimizes the path from the first interaction with an ad or message to the desired user action, reducing it to a minimum number of steps. This allows businesses to achieve significantly higher conversion and retention rates: users who are redirected through deeplinks remain active in the app twice as often a month after the first installation and make purchases with greater regularity.
Deferred deeplinks are especially effective, as they redirect a new user to the app store first and automatically open the desired content after installation. This approach increases customer retention by one-third within the first 30 days and makes the first contact with the product almost three times faster than with standard links.
In addition to increasing the conversion rate and speeding up the user journey, deep links significantly increase the average revenue per user. As a result of deep link integration, ARPU (Average Revenue Per User) can increase by more than 100%, because the user is immediately taken to the section with the maximum readiness for action – whether it is a purchase, filling out an application, or interacting with promotional content.
As a result, businesses get not only a quantitative increase in sales, but also a qualitative improvement in customer interaction. Deeplinks create a sense of personalized service, reduce the cost of acquisition, increase loyalty, and allow you to make the most of your advertising budget across all channels – from email and SMS to QR codes and social media.
Main types of deeplinks
There are several types of deeplinks, depending on the goals and scenario.
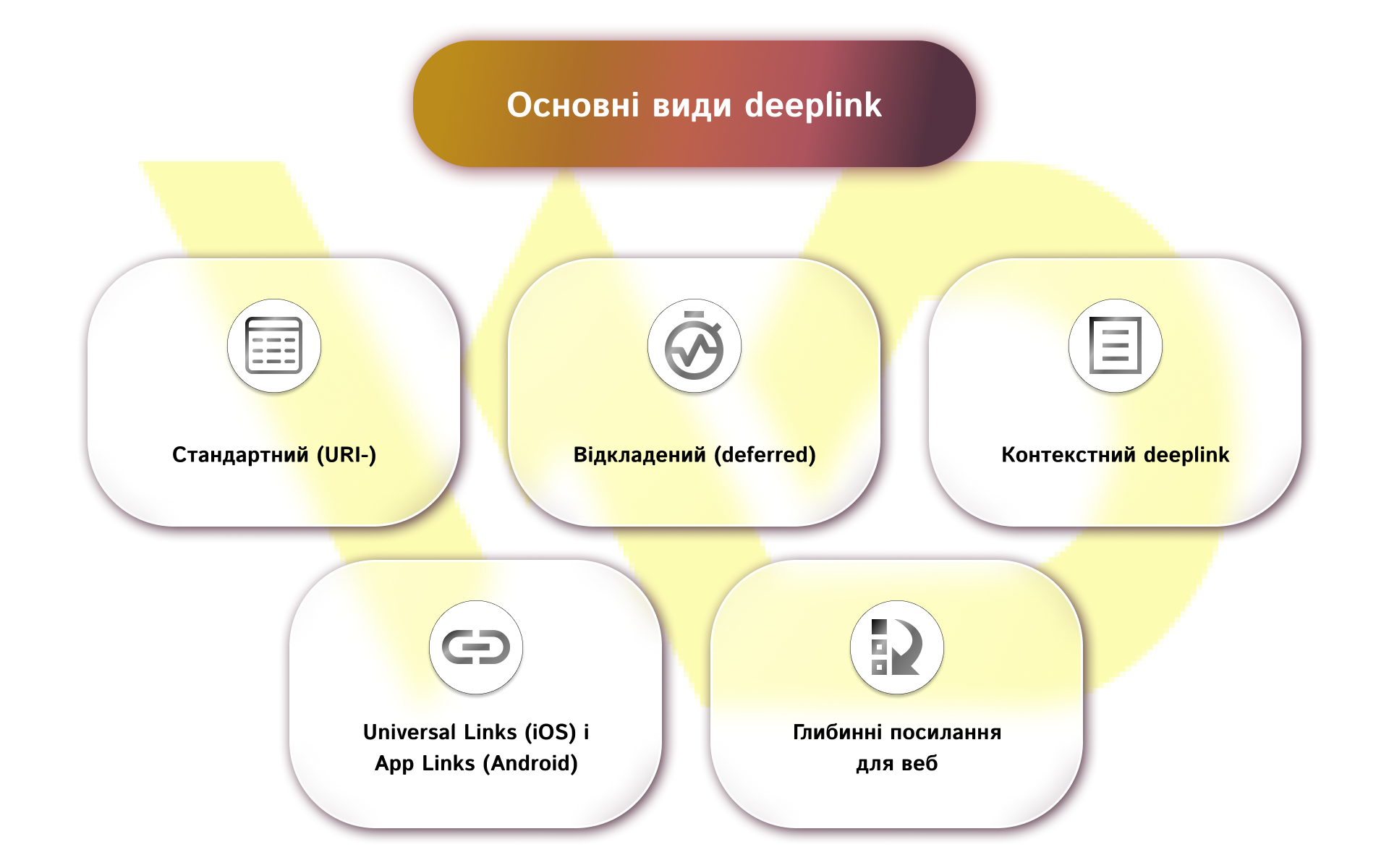
- Standard (URI-) deeplink.
Opens a specific section of a mobile app only if the user has already installed it on their device. For example, a clothing store sends a push notification with a URI-deeplink that instantly opens the card of a particular jacket in the app: the user sees the product, price, and the «Buy» button without any additional transitions. If the app is not available, the link simply doesn’t work or displays an error message, which is why this approach is best suited for already interested customers with the app pre-installed.
- Deferred deeplink.
Solves the problem of new users. When clicking on such a link, if the application is not installed, the user is first directed to the store (App Store or Google Play). After installing and launching the app for the first time, the user is automatically directed to the section or promotional offer that was announced. Imagine you see an ad banner with a new coffee recipe: a deferred deeplink will download the coffee shop’s app and then immediately open the cooking instructions – as if you were already a customer.
- Contextual deeplink.
Not only leads to the right place in the app, but also transmits additional data about the user or campaign. For example, a marketing platform launches an email campaign with a contextual link that indicates that the recipient is a member of a VIP program. After clicking on the link and opening the app, the user sees a personalized page with discounts and bonuses customized for their status. This enhances the sense of individual approach and increases the likelihood of activating a promotional code.
- Universal Links (iOS) and App Links (Android).
They use the built-in mechanisms of operating systems that automatically determine: if the application is installed, the transition takes place within it, if not, the web version of the required page or the page for downloading the application opens. This approach guarantees safe and reliable data transfer, prevents incorrect triggering, and provides a single universal URL for all platforms.
- Deep links for the web.
They are used when you need to lead the user directly to certain content on the website, bypassing the main page. For example, an advertising banner on a third-party portal can contain a URL that immediately opens an overview of the latest product catalog, rather than the brand’s main page. This is ideal for quick promotional transitions and increases the effectiveness of online campaigns.
Each of these types of deeplinks serves its own purpose: from quickly returning loyal customers to attracting new audiences and creating personalized in-app journeys. By using the right deeplink format, businesses can increase conversion and loyalty, and users get the most convenient way to the right content.
Technical implementation of Deeplink
To successfully integrate deeplinks into your app or website, you need to take a number of steps: set up a service provider (Branch, Firebase Dynamic Links, or your own backend), make changes to mobile clients (Android/iOS), and organize testing. Let us consider each approach in detail.
Using Branch
Getting started with Branch is quite simple: after creating an account on the Branch.io platform and registering a new project, you will receive unique Branch Key and Branch Secret keys. The next step is to install the SDK in your Android or iOS application: add the io.branch.sdk.android:library dependency to the Gradle file for Android, and add the Branch pod to Info.plist (iOS). Then, in the Android manifest, you specify the URI scheme (android:scheme=«yourapp») and the host (android:host=«open») so that the operating system recognizes deep link calls. In the Branch web console, you create a link by specifying the parameters of the target content and additional metadata, such as product ID or UTM tags for analytics. When the application is launched, the SDK intercepts the session, passes the built-in parameters to the handler, and you get access to the data that is embedded in the link.
Customization through Firebase Dynamic Links
Firebase Dynamic Links integrates as part of the Firebase ecosystem and is especially convenient if you already use Google analytics and other services. First, in the Firebase console, you need to register a domain for dynamic links (for example, xyz.page.link), add SHA certificates for Android and Associated Domains for iOS. After that, you install the SDK via Gradle or CocoaPods, and you can start generating links. In the Firebase console, you specify the target URL (for example, https://yourdomain.com/product/123), prefix domain, and configure Android/iOS settings. For small campaigns, it’s enough to create links manually in the interface, but if you need hundreds or thousands of unique deeplinks, you can programmatically generate short links using the createDynamicLink() method on Android or a similar API on iOS. When the app receives an intent, it checks if it contains getDynamicLink() data and processes the parameters to open the desired screen.
Own server and custom URI schemes
If you want to have full control over the redirect logic and data, you can implement deeplink through your own backend. To do this, you create an endpoint on the server, for example /dl/{token}, where {token} is a unique identifier corresponding to a certain content. When the user clicks on the link https://yourdomain.com/dl/abc123, the server checks the validity of the token, generates a 302 redirect to the URI scheme of the mobile application (myapp://product/123) or to the web version of the page if the application is not installed. In the mobile client, the AndroidManifest.xml and Info.plist for iOS configure the processing of the custom URI scheme (myapp://) so that the operating system launches the desired activity or controller with the parameters. It’s important to take care of security: tokens should have a limited lifespan, be verified on the server, and protected from abuse.
Testing and verification
After integrating any of the approaches, you need to conduct comprehensive testing on real devices and emulators. Make sure that standard deeplinks work for the installed applications and that deferred deeplinks are correctly redirected first to the app store and then to the target content. Use Branch’s debugging tools (Liveview), Firebase Dynamic Links logs, and HTTP clients (curl, Postman) to check server redirects. Don’t forget to test Universal Links/App Links on different OS versions and in different browsers, as the processing rules may differ.
Thus, the implementation of deeplink requires the coordination of settings between the backend, mobile clients, and analytical platforms, but it allows you to achieve the smoothest and most personalized experience for users and increase the effectiveness of business campaigns.
Success metrics
To evaluate the effectiveness of deeplink integration, it is important to look beyond the number of clicks. Deeplinks affect several key business metrics that together form a holistic picture of campaign performance. Here are the main metrics to track:

A comprehensive approach to evaluating the effectiveness of deeplink campaigns allows you to adapt your strategy, strengthen successful channels, and target your audience more accurately. This ensures sustainable growth not only in digital performance but also in overall business efficiency.
Risks and limitations
Despite the significant advantages, the implementation of deeplink is not a universal solution without drawbacks. To avoid unpleasant consequences, businesses should consider a number of technical and strategic limitations.
First, compatibility between platforms. Deep links behave differently in Android, iOS, and web environments. For example, simple URI schemes may not work on iOS without a special Universal Links configuration. If you don’t ensure proper adaptation for each OS, the link may not open or redirect the user to a generic page – negating the efforts of the marketing campaign.
Secondly, security and access control. In some cases, deeplinks can lead to sections that should be restricted (for example, pages with personal data or paid content). If the authentication is not properly configured, the user will either not see the content or will encounter an error, which will worsen the user experience.
Another limitation is dependence on third-party platforms. Using services such as Branch or Firebase Dynamic Links involves storing some data outside your infrastructure. This can create privacy risks or increase costs when scaling up. In addition, any malfunctions in the third-party tool directly affect the quality of the user experience.
It is also worth considering the complexity of customization and support. The implementation of deeplink often requires the involvement of developers, updating the structure of the mobile application, and setting up analytics. Without proper technical support, deeplinks can become a source of confusion or even lead to the loss of customers.
Special attention should be paid to performance tracking. If a campaign does not have clearly defined parameters (tags, events, traffic sources), you will not be able to accurately measure its effectiveness and ROI, which negates the benefits of a personalized approach.
A balanced implementation of deeplink involves not only technical implementation but also strategic planning. Taking into account the risks, you will be able to better prepare the infrastructure, adapt the promotion channels, and ensure stable operation at all points of interaction with the customer.
Examples of use
In different industries and communication channels, deep links help shorten the path to the desired action. Let’s look at some of the most common scenarios for their use.
E-commerce and retail
Companies take users directly to a specific product or promotional page. For example, in an ad with a holiday sale, the button leads directly to the offer section within the mobile app or to for the corresponding product. This is more convenient than opening the home page, where the customer will have to search for the desired product again.
Affiliate and partner marketing
Bloggers and partners use deep links on social networks and websites: when a reader clicks, they are sent directly to the store’s mobile app. Without a deeplink, there is a very high chance that the customer will get «lost» along the route.
Push notifications and email campaigns
When recovering an abandoned cart or re-engaging, it’s important to minimize the steps: clicking on a message takes the user directly to a full cart or to an unfinished task. OneSignal and CleverTap emphasize that deep links in push or emails «take users directly to the appropriate screen,» which significantly increases the likelihood of completing a purchase or returning to the app.
Social networks and advertising on them
If your audience uses mobile applications (Instagram, Facebook, TikTok, etc.), a simple URL link often opens in the internal browser and requires extra actions. Deep links «understand» that you are on a social network and redirect you directly to a native app or to the mobile web based on the context. This reduces the outflow of customers from the path to purchase.
QR codes and offline channels
Even in print ads, you can insert a QR code containing a deeplink. By scanning such a QR code, the customer is taken not just to the website, but immediately to the section of the app or mobile site that corresponds to the promotion. At the same time, the data on scanning the code is recorded, so you can track the effectiveness of offline campaigns.
Each of these scenarios illustrates: deeplink will make the user’s path the shortest and most convenient. Ignoring this technology in 2025 means letting your competitors get ahead. Stay convenient for your customers and they will reward you with loyalty and sales growth.






 13/08/2025
13/08/2025  1620
1620



