Content of the article
- /01 What is an NDA and what are its main types?
- /02 When and with whom to sign an NDA: 10 specific business scenarios
- /03 Key elements of an NDA: what must be specified and why
- /04 How to negotiate an NDA when presenting an idea to an investor or potential partner
- /05 What to do if the NDA is breached: operational steps and legal options
- /06 Organizational and technical measures alongside NDA


Nowadays, when knowledge, technologies, customer bases and business processes make up a significant part of the value of companies, the risk of losing an idea or leaking commercial information directly affects the profitability and competitiveness of a business. The World Intellectual Property Organization explains that trade secret management and a systematic approach to its protection is a key element of business strategy in today’s environment.
In this article, we will consider what an NDA is and what types of NDAs there are, when it is worth entering into an NDA, and what are the mandatory elements of the agreement. We will also analyze an important point: actions in case of suspected violations and organizational measures that complement the NDA.
What is an NDA and what are its main types?
According to the international definition, an NDA (Non-Disclosure Agreement) is a written agreement between two or more parties that sets out what information is considered confidential, what obligations are imposed on the recipient of such information, and what consequences will result in the event of its disclosure.
Types of non-disclosure agreements
There are 3 types of NDAs, which we will consider below.
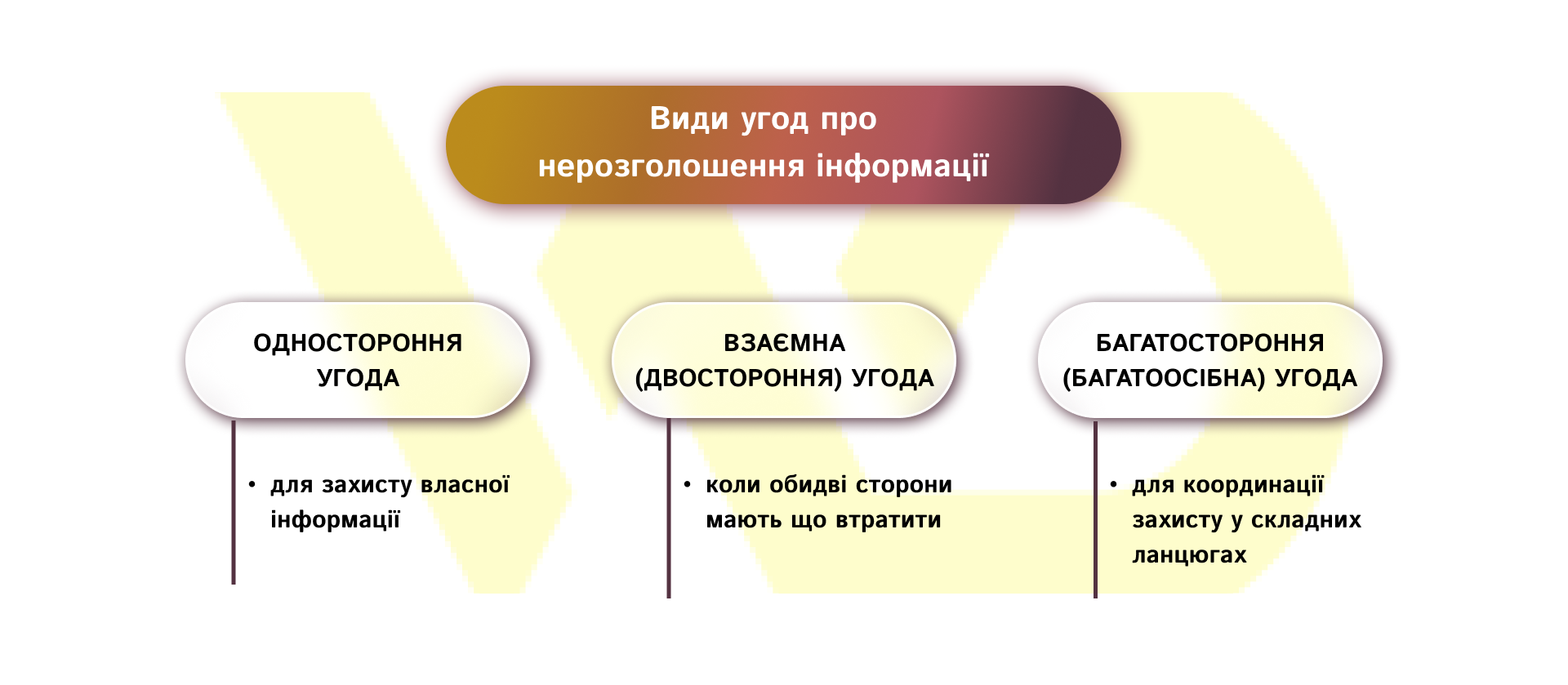
- Unilateral agreement.
This is an agreement under which only one party transfers confidential information, and the other party undertakes not to disclose or use it beyond the permitted purposes. This format is usually used in the «information owner – recipient» relationship. For example: a technology owner demonstrates a prototype to a potential manufacturer – a company passes details of a business process to a consultant – an employer gives access to a customer base to a new employee.
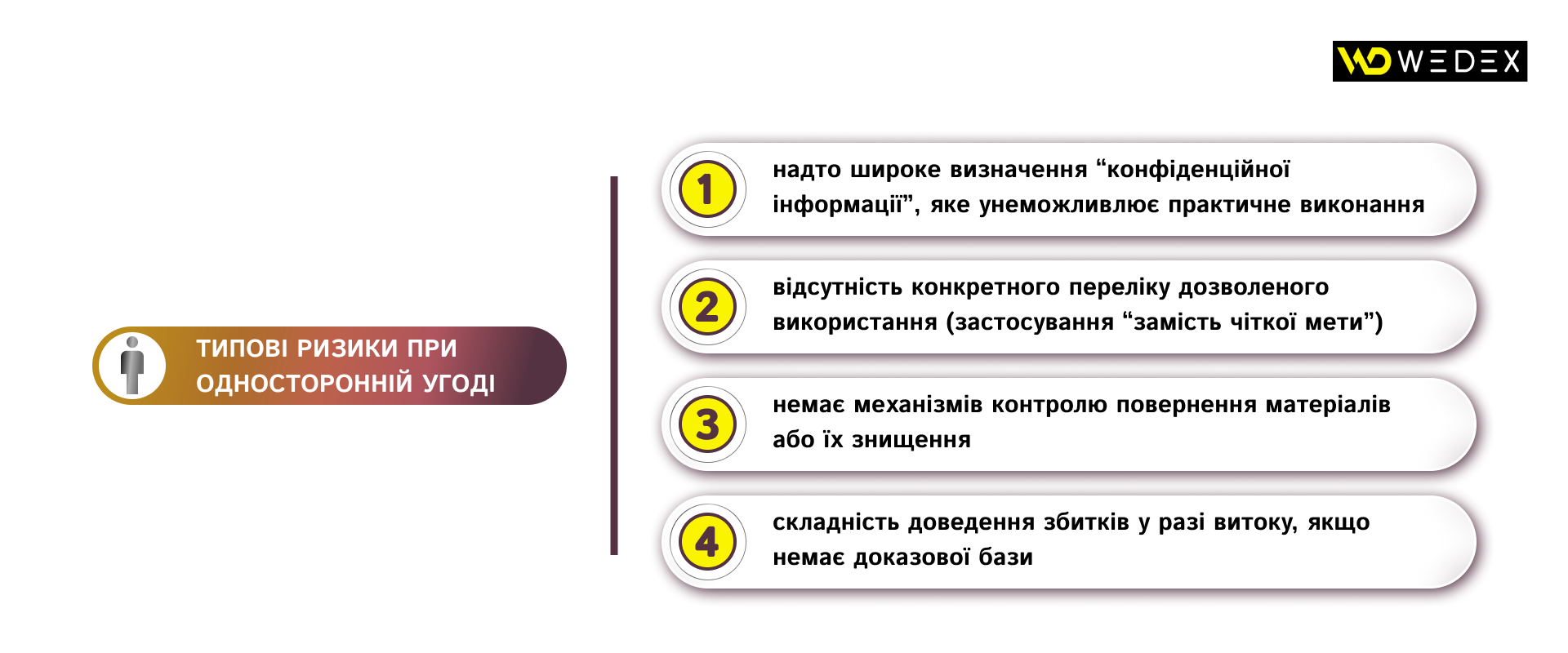
It is advisable to choose this type when only one of the parties transmits confidential information and the recipient does not plan to disclose its own secrets in return. Before entering into a unilateral agreement, it is important to clearly define the list of documents and data, the purpose of providing information, the terms of confidentiality and the procedure for returning or destroying materials – otherwise, too general wording makes the agreement ineffective in practice. If there is a possibility that the recipient will also disclose its own confidential information as part of the cooperation, or if the exchange of information is to be bilateral, it is better to consider concluding a bilateral agreement.
- Reciprocal (bilateral) agreement.
This is an agreement in which both parties simultaneously disclose confidential information to each other and undertake to keep it, not to use it for other than authorized purposes and not to disclose it to third parties. This format is used in negotiation processes and joint projects. For example: two companies exchange technical documentation when preparing a joint development – potential partners share financial forecasts and business plans when negotiating licensing terms – a company and a supplier exchange information about production facilities to prepare a joint contract.

A mutual agreement is suitable if both parties plan to actively exchange information and need mutual protection: in joint development, preparation of license agreements, integration of business processes, or in preliminary negotiations where each party has something to lose. In such cases, it is important to separate categories of confidential information («Party A information», «Party B information»), agree on a single procedure for the return or destruction of materials, and provide mechanisms to prevent «cross-contamination» of information.
- Multilateral (multi-party) agreement.
This is an agreement concluded between three or more parties and establishes general rules for the exchange and protection of confidential information between all participants at the same time. This format is used in complex projects and alliances. For example: a consortium of companies is carrying out a joint research project and needs uniform rules for sharing results – a customer and several contractors are integrating systems and need to agree on the procedure for processing technical data.
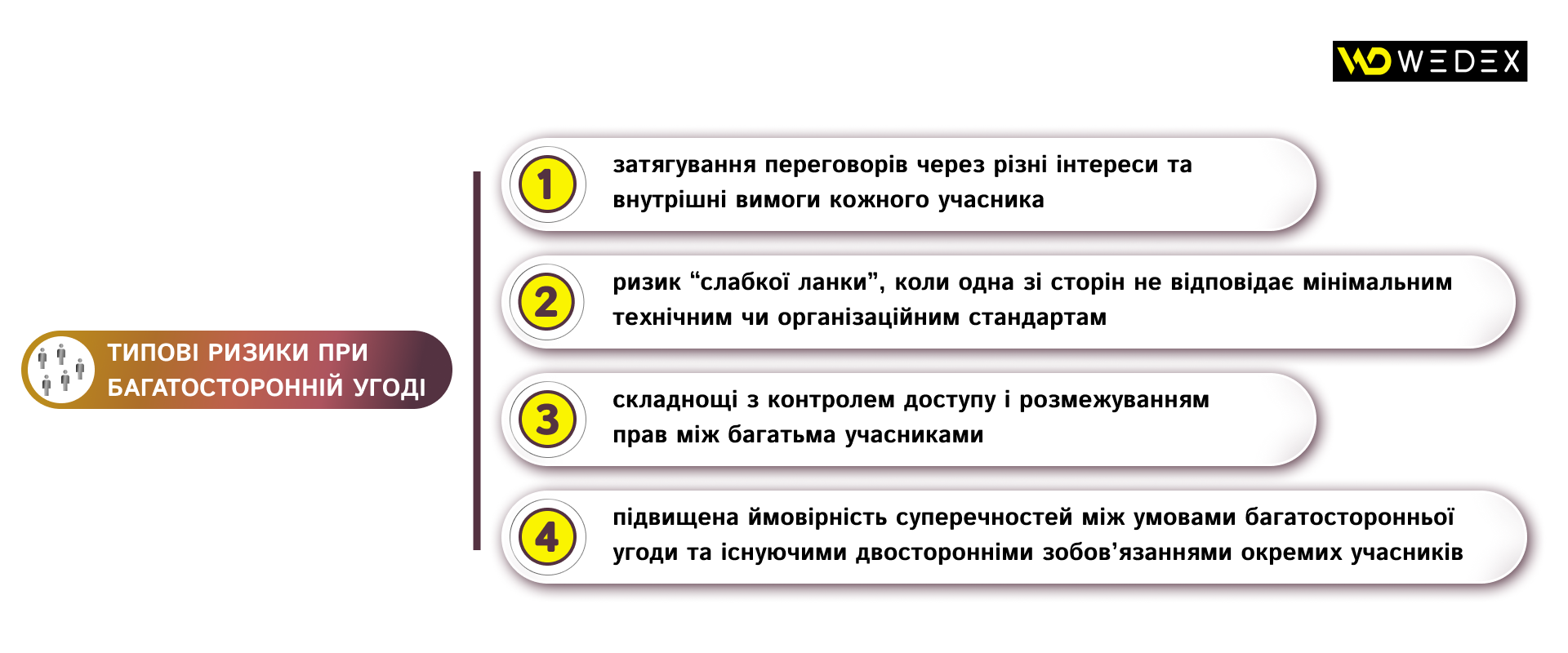
A multi-party agreement is appropriate when the number of participants makes it impractical to conclude a large number of pairwise agreements and a single, consistent protection policy is required within the project. At the same time, consider
- clear definition of roles: who is the discloser or recipient in each specific exchange episode;
- minimum technical and organizational requirements for all participants, such as encryption, labeling, access restrictions;
- a procedure for notification and joint action in the event of a breach.
When choosing a type, it is important to formulate the terms and conditions in a way that is realistic and enforceable in practice.
When and with whom to sign an NDA: 10 specific business scenarios
Signing a non-disclosure agreement is a serious and, in many cases, necessary step for long-term mutually beneficial cooperation. So let’s take a look at 10 typical business situations in which it is advisable to ask a partner to sign an NDA:
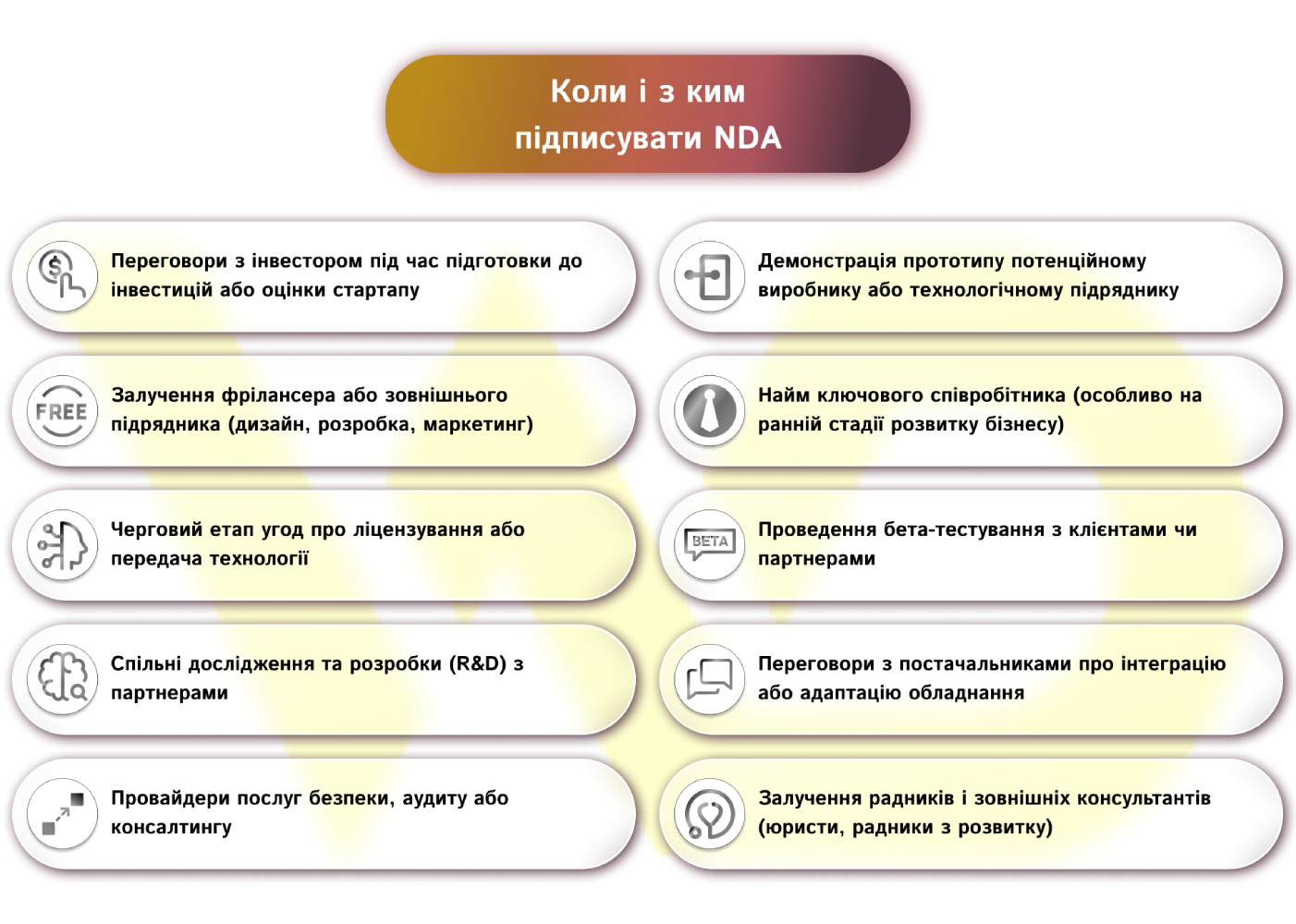
- Negotiations with an investor when preparing for an investment or evaluating a startup.
During the negotiations, when the startup demonstrates its business model and financial forecasts, the NDA should explicitly state that the transfer is «for the purpose of investment evaluation only.» It is also imperative to list key documents, such as a business plan, financial statements, and a demo version, and set restrictions on the further use of materials. This will allow you to maintain control over the information without blocking the investment attraction process itself.
- Demonstrate the prototype to a potential manufacturer or technology contractor.
In this case, a unilateral agreement that clearly specifies the list of drawings, specifications and samples will be effective. The purpose of the transfer («assessment of technological capability») and the procedure for returning or destroying samples after the inspection is completed should be specified separately to avoid the risk of unauthorized copying.
- Hiring a freelancer or external contractor (design, development, marketing).
In the contract, combine the elements of the NDA with provisions on the procedure for transferring rights to the work result and the obligation to return the source materials. This way, you will simultaneously protect trade secrets and regulate the ownership of the final product.
- Hiring a key employee (especially at an early stage of business development).
In addition to the NDA, it is advisable to integrate provisions on restrictions on the use of information into the employment contract or a separate non-competition agreement. However, excessive breadth of wording should be avoided: describe specific categories of data and reasonable timeframes for the obligations to be in effect so that the document is practically applicable in the event of a dispute.
- The next step in licensing or technology transfer agreements.
If both parties are simultaneously disclosing technical and commercial details, choose a mutual NDA with annexes that distinguish between «Party A information» and «Party B information» and specify a mechanism for dividing rights to the results of joint work to reduce the risk of further disputes.
- Conduct beta testing with clients or partners.
Agree on an NDA that combines the legal regime and technical access restrictions. In other words, fix what data testers can see, what rights to feedback are transferred to the manufacturer, and what is the procedure for working with error logs. This way, feedback will not turn into a leak of commercial information.
- Joint research and development (R&D) with partners.
Mutual or multilateral NDAs should provide not only for an information exchange regime, but also a clear procedure for determining and distributing rights to intellectual results, commercialization terms, and financial distribution. This helps to avoid conflicts after development is completed.
- Negotiations with suppliers on the integration or adaptation of equipment.
It is useful to specify in the contract what technical information is critical and to introduce requirements for labeling documents and restrictions on working with copies. In this way, you will reduce the risk of unauthorized use of design solutions.
- Security, audit, or consulting service providers.
Before starting work, conclude an NDA with data processing requirements (encryption, secure transmission channels) and obligations to keep the results of inspections confidential. Such steps ensure legal protection and technical reliability at the same time.
- Engage advisors and external consultants (lawyers, development advisors).
At the initial contact, you should limit yourself to a brief «teaser» of information, and only share full business models, financial scenarios, and strategy details after signing an NDA. The agreement should clearly state the purpose of using the information and the terms of confidentiality.
Each of the above scenarios illustrates one simple point: the effectiveness of an NDA depends not on its existence as such, but on the specifics – the correct definition of information, the adequacy of terms and control procedures. An agreement can work as a practical tool for protecting business values, but if it is illiterate, it creates the illusion of security and complicates partnerships.
Key elements of an NDA: what must be specified and why
For a non-disclosure agreement to be effective, it is important to clearly state several basic provisions. They not only define the boundaries of confidentiality, but also help to avoid legal gaps in case of disputes. Each clause has its own risks that should be considered in advance.
- Parties to the agreement: full details of each party to the agreement so that there is no doubt who is responsible for the obligations.
|
Risk |
Minimization |
|
If the data is incomplete or incorrect, the fact of signing can be challenged. |
Check official documents (registration data, passport information, EDRPOU codes). |
- Define confidential information: a clear list or criteria of what is considered to be secret data.
|
Risk |
Minimization |
|
Too general wording will lead to difficulties in proving the fact of disclosure. |
Describe the categories as specifically as possible – «financial statements for 2025», «product prototypes», «customer list». |
- Purpose of use: why the information is provided, to what extent it can be used.
|
Risk |
Minimization |
|
Without this, you can use the data for third-party projects and avoid liability. |
Specify a single purpose of cooperation («market analysis», «preparation of a commercial offer») and prohibit use in other contexts. |
- The term of the agreement: how long the parties are obliged to keep the secret – during the cooperation and after its completion.
|
Risk |
Minimization |
|
If the term is not defined, the data may become «open» after the end of the agreement. |
Specify a specific period, for example, «4 years after the end of cooperation». |
- Exceptions: data that is not subject to an NDA (e.g., already publicly available or legally obtained from a third party).
|
Risk |
Minimization |
|
Without exceptions, you may find yourself in a situation where even publicly available information is formally subject to an NDA. |
Clearly define the boundaries to avoid excessive restrictions and potential litigation. |
- Liability for violations: specific consequences, such as fines, damages, or other sanctions.
|
Risk |
Minimization |
|
Without prescribed sanctions, it will be time-consuming and expensive to prove the amount of damage in court. |
Fix fixed amounts of compensation or a mechanism for calculating them. |
- Dispute resolution procedure: which court or arbitration will consider the case in case of a conflict.
|
Risk |
Minimization |
|
The absence of this clause will complicate the process of protecting rights and delay litigation. |
Determine the jurisdiction in advance (for example, a commercial court in Kyiv or international arbitration). |
- Data return or destruction: a procedure after the end of cooperation to avoid unwanted storage of materials.
|
Risk |
Minimization |
|
If documents remain with the former partner, they may be used in the future. |
Provide for the obligation to return all copies or confirm destruction within a specified time frame. |
A well-written NDA balances the interests of the parties: on the one hand, it protects the business from leakage, and on the other hand, it does not restrict the partners in their legitimate and predictable work.
Practical checklist and short template wording
Below is a set of working wording for the key clauses of the NDA. They will help to avoid overly general or vague descriptions, which in real cases become a weak point in court or contractual disputes.
|
NDA element |
Wording (phrase) |
Why it is so |
|
Definition of «confidential information» |
«Confidential information is understood by the parties to mean any data expressly labeled as «confidential», whether transmitted in written, oral or electronic form, including business plans, financial statements, technical materials and commercial strategies». |
The specific list and labeling helps to avoid situations where ordinary business data is recognized as secret and makes it difficult to prove a leak. |
|
Responsibilities of the recipient |
«The recipient is obliged to: (a) keep the information confidential; (b) use it exclusively for the purpose specified in the agreement; (c) restrict access only to those employees who need it». |
Clear boundaries of use and access reduce the risk of information leakage or misuse. |
|
Duration |
«The confidentiality obligations are valid for ___ years after the termination of cooperation between the parties». |
Establishing a specific term makes the agreement enforceable and avoids court disputes due to excessive abstraction («indefinitely»). |
|
Exceptions |
«The restrictions do not apply to information that: (a) was known to the party prior to receipt; (b) became public through no fault of the recipient; (c) was lawfully received from a third party without restriction». |
Clear exemptions help to avoid absurd claims for information that is already public or has been legally obtained. |
|
Return or destruction of data |
«Upon termination of the cooperation, the recipient shall return or destroy all media containing confidential information within 10 days and confirm the fulfillment in writing». |
Setting a deadline and a written confirmation ensures that the data will not remain with the partner and will not be used after the end of the cooperation. |
|
The right to injunctive relief |
«In the event of a breach of the contract, the disclosing party has the right to seek an injunction without the need to prove actual damages». |
It allows you to quickly stop the violation of the NDA without having to wait for lengthy procedures to confirm damages. |
|
Penalties |
«For breach of obligations, the parties shall pay a fine of ___, as well as compensate for documented losses». |
A specific fine and compensation mechanism motivate compliance with the terms of the agreement and make it practically applicable. |
How to negotiate an NDA when presenting an idea to an investor or potential partner
When presenting a business idea to an investor or potential partner, a non-disclosure agreement becomes an important tool for protection. However, improperly negotiating or requesting an NDA at the wrong time can complicate negotiations or even scare off a potential investor. To protect yourself and not lose the chance for funding or partnership, you should follow a few rules and a logical sequence of actions.
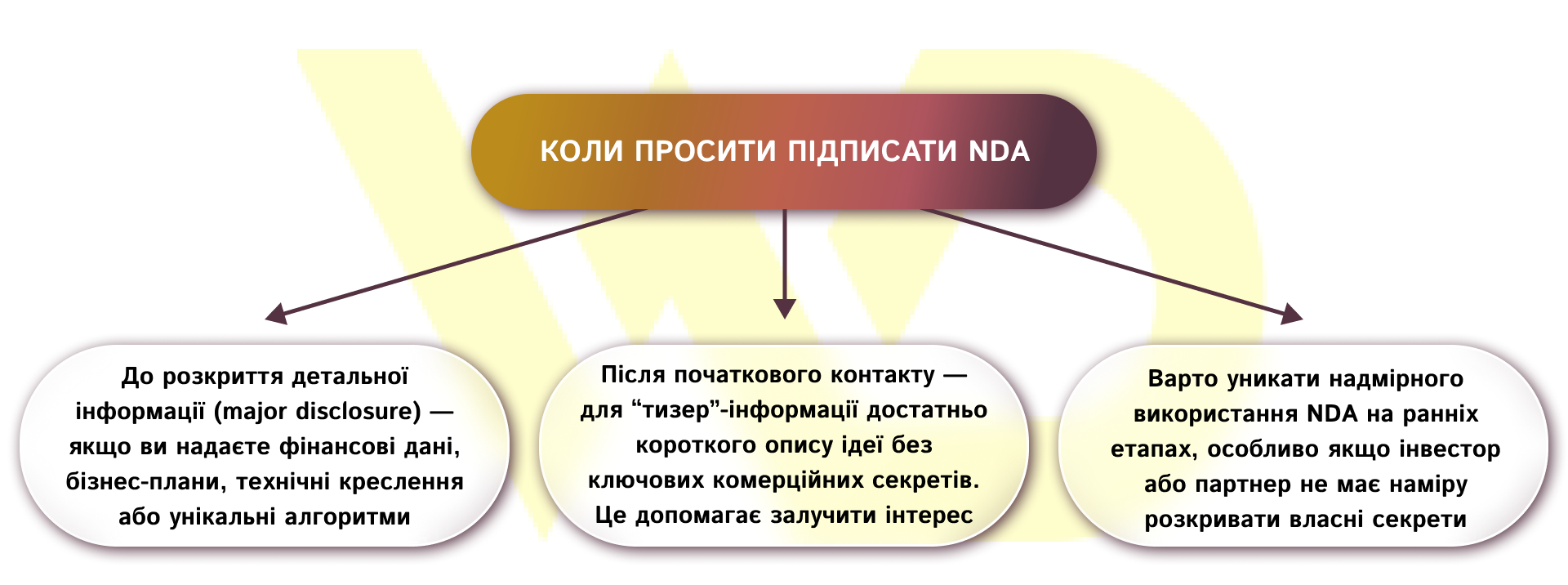
Before signing an NDA, you should disclose only the general principles of the product or service, briefly describe the market and target audience, avoiding specific revenue figures or detailed data on customer bases. You can also share concepts or unique ideas, but without technical details and financial forecasts, so as not to expose yourself to the risk of commercial information leakage.
The presentation should be as concise and clear as possible, emphasizing the value and potential of the business, but without revealing key secrets. This approach allows you to interest an investor or potential partner without disclosing confidential details and at the same time demonstrating the commercial attractiveness of the project.
An example of a teaser letter wording:
«We have developed a platform that automates key business processes and reduces the time to complete tasks by an average of 70%. To discuss a potential investment, we can sign an NDA and provide detailed financial forecasts and technical documentation».
Example of a short agreement before disclosure of detailed information
- The parties agree that any information provided during the negotiations is confidential.
- The recipient undertakes not to disclose the information to third parties and to use it only to assess the possibility of cooperation.
- The confidentiality period is set for 2-3 years.
- The mechanism for returning or destroying the provided materials is prescribed upon completion of negotiations.
This approach allows you to combine the security of commercial data and the tactical flexibility of negotiations without creating unnecessary obstacles for a potential investor or partner.
What to do if the NDA is breached: operational steps and legal options
Breach of an NDA is a situation that requires a quick and systematic response to minimize business losses and maintain control over confidential information. Actions are divided into operational measures and legal mechanisms that complement each other.
Operational steps
First of all, it is important to record the fact of the breach. To do this, you should
- document all the circumstances of the disclosure or misuse of information;
- immediately take measures to stop further dissemination (e.g., restrict access to materials, suspend communications)
- preserve all evidence of the violation – emails, screenshots, files, records of negotiations;
- send a formal written request to the infringer to cease disclosure and comply with the terms of the NDA.
These actions help preserve the evidence base and reduce the risk of further use of information by third parties.
Legal mechanisms of protection
In parallel, you can use legal instruments:
- a claim for damages;
- application of a temporary restraining order to prohibit further disclosure or use of information;
- in cases stipulated by the Criminal Code of Ukraine or the Code of Administrative Offenses, administrative or criminal liability of the offender is possible.
The right combination of operational actions and legal mechanisms allows businesses to respond quickly to NDA violations, minimize the risks of losing commercial information, and at the same time maintain their reputation in the business environment.
Organizational and technical measures alongside NDA
An NDA is an important tool for protecting commercial information, but it is not a panacea in itself. To effectively mitigate the risk of data breaches, businesses need to combine legal mechanisms with organizational and technical measures that provide real control over information flows.

These measures reflect the recommendations of the World Intellectual Property Organization on trade secret management and organization of confidential information protection in business processes.
Remember. When planning to work with partners or investors, you should take an integrated approach and prepare the appropriate documents and procedures in advance to minimize the risks of confidential information leakage.







 06/10/2025
06/10/2025  1524
1524


