Content of the article
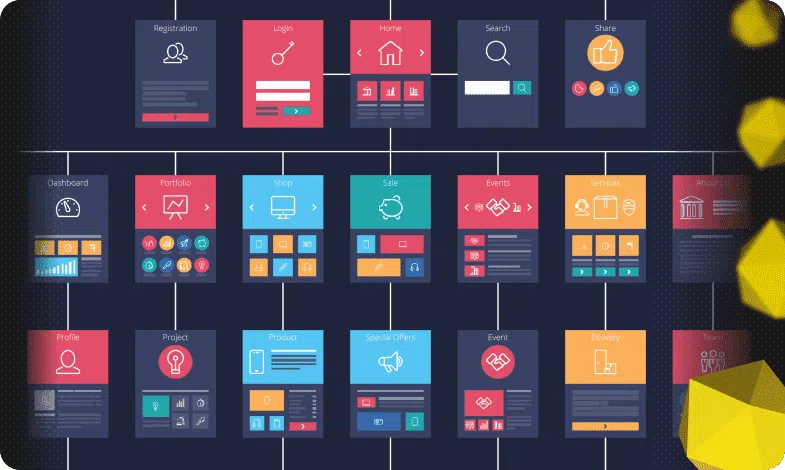
Many website owners rarely pay due attention to the issue of creating the correct structure of their resource at the development stage. Often, all the attention is paid to a variety of functional issues, design preferences, product or content additions, and other details. And the development budget does not always include the services of an SEO specialist.
As a result, it turns out that even the most visually beautiful and technically advanced website, full of products and content, simply does not generate profit.
Why this happens and what role the structure plays in this will be discussed in detail in this article.
What is the site structure?
The structure of a site is a navigational and logical connection of all pages of an Internet resource. If we consider the structure as a diagram, then we can add that it also defines the principles of interaction between various elements of the resource.
We also propose to dwell in detail on what types of structure there are.
Types of site structure
There are several standard structure options for different types of sites. Next, we will consider each of them in detail.
Single level structure
Often found on corporate websites. Such sites are distinguished by the equidistance of all pages from the main page. Thus, the maximum nesting on such sites is no more than 1. This is what it looks like in the diagram:
Linear structure
A rather outdated version of the structure, which is now used quite rarely. Used in some business card sites, presentations or resources aimed at selling 1 product or service.
This structure looks like a regular chain sequence of elements.
You can also find a slightly modified version of the linear structure, for example with alternative options or branches:

Hierarchical (tree) structure
When it comes to large commercial sites, they are always based on a hierarchical architecture model. As the name suggests, all elements of this structure are subject to a strict hierarchy, at the head of which is the main page.
This is what the basic hierarchical structure looks like:
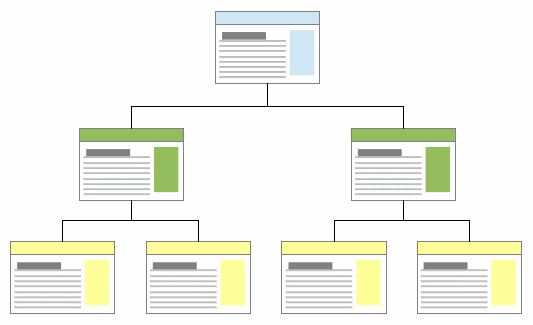
However, in 2022, the classic tree structure is used only in small online stores. Larger representatives use modified versions of this type of architecture.
Silo structure is the most commonly used variation. This organization of pages helps to focus on thematic groups and the pages that are included in these groups.
A relatively new vector in the development of silo architecture is the concept of semantic cocoons. Its essence is in constructing pages according to meaning, and not according to thematic affiliation.

The author of the idea is considered to be French web researcher Laurent Bourelly. Although it became popular in the homeland of the author of the concept back in 2013, outside of France it began to gain popularity only in 2020.
We will return to various aspects of the tree structure several times throughout the article, but for now we will formulate what requirements and recommendations are voiced by search engines for creating the structure.
Requirements for the site structure

We tried to collect all the requirements and recommendations that can be found on the official information channels of search engines:
- Logic of structure. It is required to highlight the main categories and subcategories, where each document located in them should logically belong to its groups
- Each article or product must be on its own page with its own unique address
- Use intuitive navigation. This can be a human-readable URL, where the nesting of pages or a block with breadcrumbs is clearly visible
- The site must have a clear link structure. A prerequisite is the ability to access any other page from the main page. We would like to note that we do not mean direct access like: “Home – final page”, but a similar option: “Home – page No. 1 – page No. 2 -… – final page”. This allows search robots to correctly index the site
- Availability of the most relevant pages for individual search queries. Some products may have several parameters at once, by which they are often searched for at the same time, so it is recommended to create corresponding pages where product cards are grouped according to different characteristics.
How to create a website structure
Now let’s move on to the practical part of the question and figure out how to create a structure.
First stage
At the first stage, it is necessary to collect semantics for the goods and services presented on the site, as well as cluster them.
The semantic core is a list of all the keywords by which your site can be searched in search engines. Typically, it should also include appropriate frequencies to determine user demand for each individual key.
To study this stage in more detail, we wrote a separate article about collection of semantics.
Second phase
As a second step, we recommend analyzing the structure of competing sites from the top search results. To do this, it will be enough to identify about 4-5 of the most promising competitors and study the following parameters:
1. Maximum site depth
You need to evaluate what is the highest level of nesting used on similar sites.
2. Number and types of nested subcategories in the highest priority categories
This step will help you double-check how well the semantic core was collected and clustered. At this stage, it is sometimes possible to expand your own semantics with additional non-obvious key options.
3. Availability of SEO filters
If most competitors use similar filters, this is a sure sign that you should think about this element yourself. The obvious advantage of such filters is the creation of a huge number of pages even for the lowest frequency keywords, thus significantly increasing the reach of impressions.
Third stage
Once more specific outlines of the structure have been formed, first sketches can be created.
You can start visualizing the structure after collecting the semantics. Then, when analyzing competitors, edits to the sketch will be made in real time.
To create a schematic structure of a website, you can use various paid and free services and programs. We have about 2-3 permanent tools in our own arsenal, so for more extensive information we turned to the guys from Habr:
Services for creating a website structure
-
-
- X-Mind
- do
- Gloomaps
- Flowmap
- Draftium
- Writemaps
- Rarchy
- Visual Sitemaps
- Slickplan
- Dynamapper
- Visual Site Mapper
- Creatively
-
They have a detailed analysis of each service, we recommend you read: https://habr.com/ru/post/467625/.
Errors when creating a site structure
Now that we have dealt with all the stages of creating a structure, I propose to study the most common mistakes.
Duplicate pages
The most common mistake when developing a structure for large sites. When planning a large number of branching elements, repetitions of the same content or product groups are possible.
Another characteristic feature of duplicates is the addition of the same products to different logical groups. Example:

In fact, if a product has several characteristics for which you want to promote queries, the product cards themselves should be added only to the parent category, and in the subgroups themselves you need to create links to it in the form of product previews:

Here is an example of what it looks like on the website of one of the market leaders in this topic:

As you can see, when you hover over a product, it has a completely different path (link No. 2) than the address of the current page (link No. 1).
According to the logic of the classical hierarchical structure, the product should be located at:
https://*store name*/ua/catalog/muzhskaya_obuv/brand-adidas-good_type-krossovki-podvid-krossovki-dlya-trenirovok/*product address*
a in fact, it has the address: https://*store name*/ua/product/sneakers-adidas-4874925
This way you can avoid duplicates of the product and at the same time demonstrate it in all suitable groups using the links that are posted in the photo.
Garbage pages
This error is typical when working with SEO filters. Incorrect configuration of the latter leads to the fact that in addition to useful pages with low- and ultra-low-frequency keys, completely non-target pages are generated that only harm the site.
Example:

At the intersection of these parameters there are no products (starting from the first 2 characteristics), but pages are generated and appear in the search results.
It is also important to note that separate product categories, which include 1-2 units of goods, also belong to junk pages. Often such pages are created so that the site covers a larger volume of keywords, but in fact they simply do not have the corresponding product.
Such pages are of little use and harm the promotion of the site. This is official information from Google representatives.
Insufficient product segmentation
If you observe that in your structure too many product groups contain a combination of different subgroups, this is a sure sign that the structure can and should be scaled: The exceptions are:
- ultra-low-frequency keys that make no sense to split
- parent categories that include more relevant subgroups
- small website volumes and low range of products
- marketplaces (more on this below)
If the product is not well segmented into groups, this will cause low relevance of landing pages.
Features of creating a structure for marketplaces
The structure of a store on marketplaces has one significant drawback – the store owner can display the product only in 1 actual group, without being able to create additional subgroups with links to the same products (as in the example with the sneaker store above).
For example, if the assortment includes all the same sports shoes, then they will be shown in search results only for one group of keywords (as a rule, these are high-frequency queries), missing all low- and mid-frequency keyword options.

Considering that young online stores receive all their traffic from low- and medium-frequency keywords, store owners on marketplaces should not count on organic traffic and can only rely on advertising.
To summarize
Structure is the skeleton of your website. Don’t rush through this stage, think through every nuance and study the experience of your competitors. An error at this stage can have serious consequences for the further development of the site, so be careful.
If you are not confident in your own abilities, contact specialists. We will always help with creating a well-thought-out website structure, which will certainly serve as an excellent foundation for the further promotion of your resource.






 30/04/2021
30/04/2021  2424
2424