Content of the article


Today, along with the digitalization of channels, fluctuations in demand, and rising costs of customer acquisition, the right marketing mix is becoming a critical factor in a successful product launch. In this article, we will consider why a company needs a marketing mix, what the main goal is, the basic concept and classic elements of the 4Ps, and compare popular model options. Separately, will focus on tools and metrics that allow you to monitor the effectiveness of solutions, because without this, all previous efforts may be in vain.
What is a marketing mix?
A marketing mix is an integrated set of solutions and tools that a company uses to bring a product to market, communicate its value to the target audience, and achieve commercial results. It is a systematic operating model in which each element is subordinated to a common business goal.
In practice, the complex simultaneously answers four questions that form the customer journey from the first contact to the repeat purchase:

These answers set customer expectations and determine their behavior.
The main feature of the complex is interconnection: a change in one parameter inevitably affects the others.
For example, a price reduction may require a revision of positioning and changes in the message, while a new sales channel may require adaptation of logistics and service. Therefore, decisions are made in the context of the entire complex and are accompanied by metrics and feedback mechanisms.
The basic concept of integrated marketing
The concept of the marketing mix is that the success of a product is determined not by individual tactical actions, but by their interaction in a single, customer-oriented system. In other words, a marketing mix is a mechanism that adapts to market needs and business goals and is regularly adjusted based on data.
Let’s look at the key components of the basic KM concept.
- Customer centricity as a starting point.
Solutions within the complex begin with an understanding of the target audience: its tasks, motivations, barriers, and the context of product use. Not «what do we want to sell» but «what problem does the client want to solve» is the guideline. This determines the choice of channels, the tone of communication, the format of the offer, and even the technical solutions in the product.
Practical implications: audience segmentation and the formation of a customer profile before making any serious marketing decisions.
- Systematic and interdependent elements.
Product, price, place, and promotion do not work independently of each other. Changing one element requires revising the others, as we have already mentioned above.
Practical implication: implement changes through coordination meetings (product + sales + marketing + operations) and evaluate the impact systematically, not locally.
- Clear Value Proposition
The value proposition is the central node of the concept. It answers the question «why should the client choose us?» and should be expressed simply, unambiguously, and measurably. Without a clear VP, all elements of the complex lose focus.
The practical implication is that every advertising message, price offer, and product featured should directly reflect aspects of the VP.
- Channel orchestration as an ecosystem.
Channels are not competitors to each other, but components of the ecosystem of influence: organic search, paid advertising, email, social networks, partners, retail. The concept involves defining the role of each channel in the funnel and synchronizing communication between them.
Practical implication: build a channel map with a role (awareness / consideration / conversion / retention) and KPIs for each channel.
- Product life cycle and complex adaptation.
KM is not static – it changes with the product. At the introduction stage, priorities are different than during scaling or maturity. The concept includes adaptability, and tactics and resource reinforcement are switched according to the stage of the life cycle.
Practical implication: be prepared to change the ratio of marketing budgets and channels depending on the phase (test → scale → optimization).
- Testing, analysis, and iteration.
The key part of the concept is hypotheses + controlled experiments. Each change in the 4Ps should be accompanied by a metric, a hypothesis, and a test plan. Scaling decisions are made based on statistically significant results.
Practical implications: use A/B testing, canal launches, segment pilots, and standardized decision-making criteria (e.g., ROI threshold, minimum conversion rate).
- Measurability and operational reporting.
The marketing complex should be «transparent» for the business: each activity has its own metric, and all metrics have a place on a single dashboard. This allows you to quickly identify deviations, adjust tactics, and reasonably allocate resources.
Practical implication: aggregate key indicators (CAC, LTV, funnel conversions, ROMI) in one dashboard and update them regularly.
- Balance of long-term and short-term goals.
The concept involves simultaneous work for the brand and direct sales. Part of the budget is spent on building trust and recognition, and part on tactical channels that give quick results. Ignoring one of the areas leads to inefficiency.
Practical implication: create a portfolio of initiatives with a distribution by horizons: urgent (0-3 months), medium-term (3-12 months), long-term (>12 months).
A practical example
Imagine a B2B SaaS product: you reduce the price of a subscription. By concept, it’s not just a number. You need to:
- Reconsider the positioning (why is the product cheaper now? Has the premium been retained or lost?)
- change the messages in the promo (from «exclusive» to «optimal price/value»);
- check channels (lower price can stimulate paid advertising for the mass segment);
- adjust the sales process (faster conversion, different script).
If any of these steps are skipped, the increase in sales may be short-lived or unprofitable.
Adherence to the basic concept ensures that the marketing mix works as a single system – predictably, scalably, and focused on business results. It is integrated thinking that distinguishes effective launches from scattered tactical activities.
KM elements: the classic 4P
The classic 4P model is worth knowing as a basic operational map.
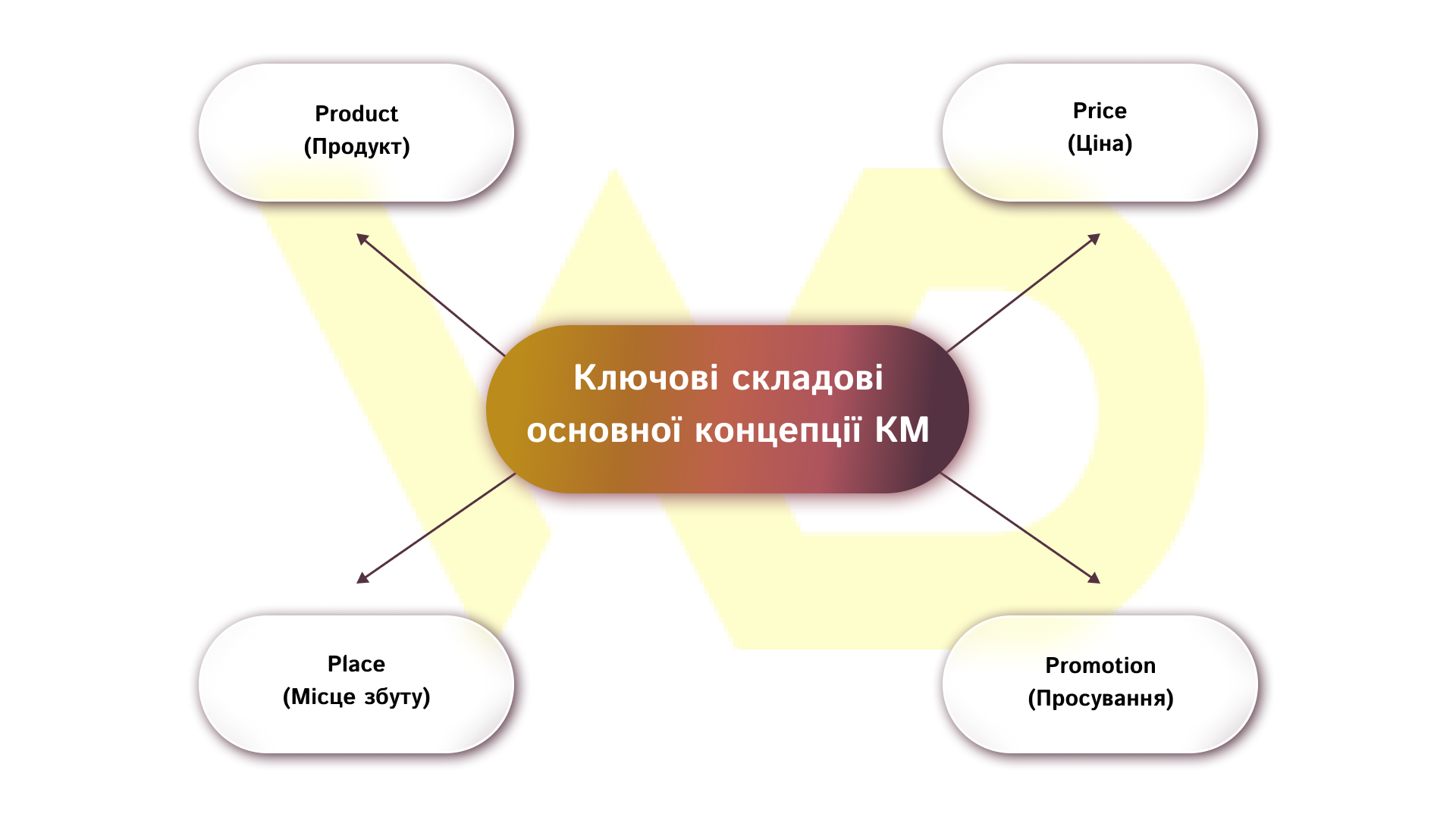
Let’s look at the practical importance of each element during a launch.
Product
The product includes not only the product or service itself, but also the packaging, assortment, service level, and support. When launching, it’s important to clearly articulate what problem the product solves, what its unique selling points (USPs) are, and what the minimum expected performance (MVP) will be.
Price
Pricing should take into account positioning, cost, competition, and elasticity of demand. At the launch stage, fixed experiments are often used: testing different price offers (A/B) or packaging offers.
Place
Channels include distribution, logistics, and customer contact points. Make a decision: directly to the consumer or through intermediaries; online or offline priority; necessary partners. For MVPs, it is better to start with several channels and optimize them consistently.
Promotion
Promotion is the message, channels, and tactics that drive traffic and conversions. It’s important to define a key message for each stage of the funnel and choose tools: content, PPC, PR, email, social media. At the launch stage, the priority is to quickly test message hypotheses and creatives.
Promotion that supports all elements
The WEDEX team takes care of comprehensive marketing: content, SEO, contextual and targeted advertising — so that your product quickly finds its audience and starts selling.
When working with the 4Ps, keep the rules simple: start with a clear value proposition, test changes locally, measure their impact on key metrics, and adjust other elements of the complex in unison. It is this coordinated work that turns the 4Ps from a theoretical scheme into an operational decision-making map.
KM models: options and extensions
The classic 4Ps are just a starting point. Depending on the product, market, and complexity of customer interaction, the marketing mix model is expanded with additional elements or changes in emphasis.
5P (People or Process add-on)
In different interpretations, the fifth element can mean People or Process. When it comes to People, attention shifts to the staff who directly affect the customer experience. If it is Process, the importance of well-established business procedures for the stability of the service is emphasized. Choose the interpretation depending on what is more critical in your business: the human factor or the operational discipline.
6P (People + Process)
The sixth position actually combines both approaches: the role of personnel and the quality of processes are simultaneously recorded. This makes the model useful for organizations with complex operational logistics and intensive customer interaction (e.g., service chains, retail with a service component).
7P (People, Process, Physical evidence)
The full version for the service sector adds a third «amplifier» – Physical evidence: certificates, branded materials, point of contact design, etc. The 7Ps are used where the experience of interaction forms the majority of the value – medicine, HoReCa, consulting, professional services.
SIVA (Solution, Information, Value, Access)
SIVA changes the perspective: instead of «what we sell,» it is «what problem we solve and how we inform about it.»
- Solution responds to a need, not a product;
- Information replaces the promotional focus on informing the customer;
- Value emphasizes the value (not just the price);
- Access – ease of access and purchase.
This model promotes a focus on customer experience and is especially useful for innovative products, digital services, and entering new markets.
Choose a model based on the «problem – tool» principle:
- If your product is a standard product, start with 4Ps;
- if it is a service, use the 7Ps;
- if you need to think from the customer’s point of view or work with innovations, test SIVA.
Don’t try to use all models at the same time without promoting hypotheses: the choice of model should reflect real points of influence on value and have clear KPIs to check.
Always start with one adapted model, conduct controlled experiments, and scale those elements of the complex that demonstrate a positive impact on key business metrics.
Tools and metrics to control the marketing mix
The next step is to ensure that the marketing mix model is working properly through tools and metrics. Without a clear set of technologies and a dashboard, decisions will remain declarations, but with them, they turn into controlled experiments.
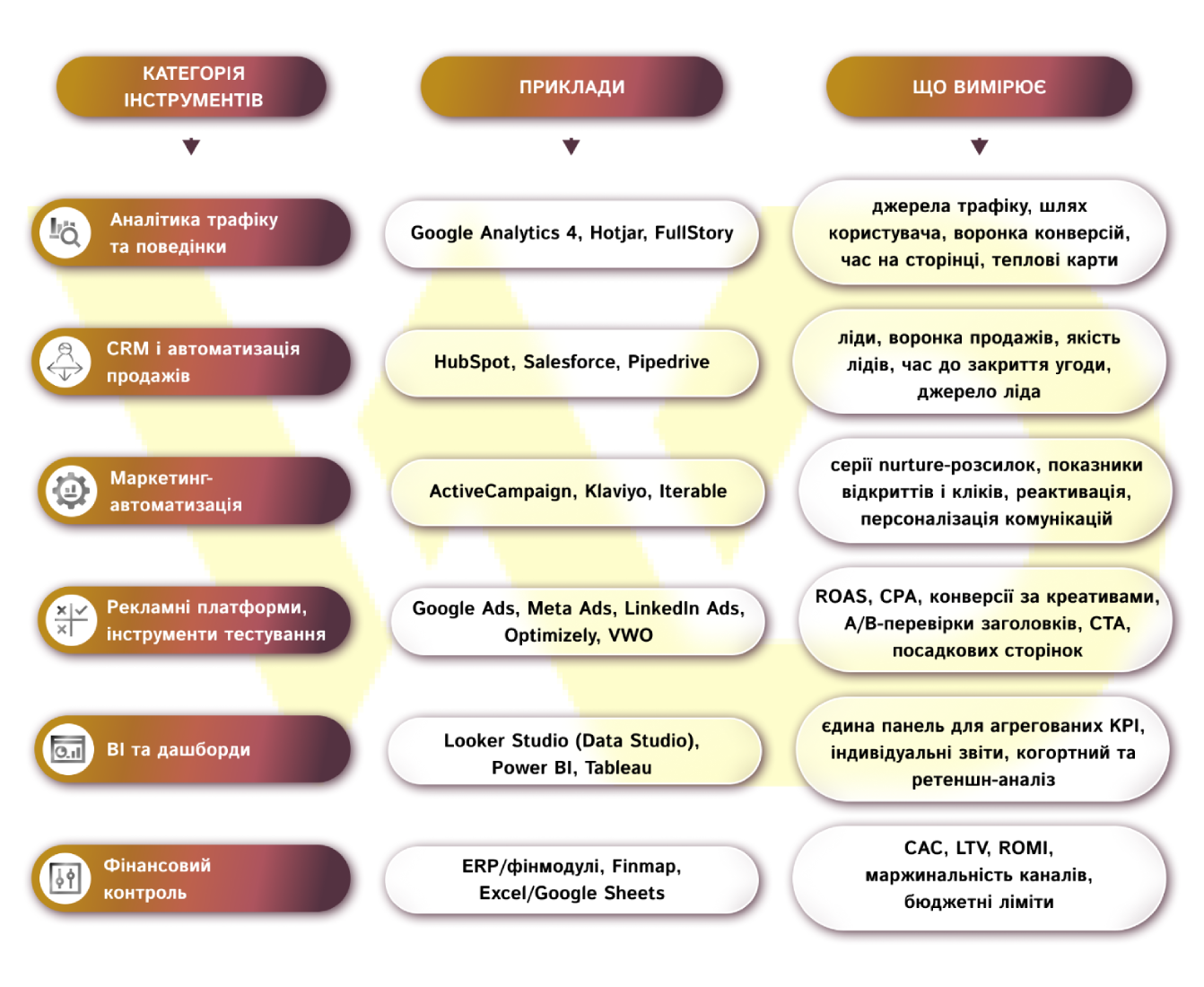
For the tools to work synchronously, it is important to establish data transfer: event tracking, UTM tags, CRM-analytics-advertising platform integrations. This allows you to track the customer journey from click to check and correlate marketing actions with financial results.
Thus, the implementation of a marketing complex is a process of continuous management. The implementation of KM, system analytics, and regular monitoring allow you to get better results over time: increase cost efficiency, reduce decision-making time, and scale those solutions that have a positive impact on profits.





 16/12/2025
16/12/2025  1349
1349


