Content of the article

Filters are not just a tool that a buyer needs to search for products in sometimes very large catalogs; their configuration is one of the key factors affecting the performance and efficiency of an online store. Three quarters of users who do not find the desired product within 20 seconds leave the web resource and look for a more convenient one. The presence of a “smart” product filter improves the site’s user experience statistics, while its absence leads to its deterioration.
The implementation and optimization of SEO filters has a significant impact on the search engine promotion of the site due to the creation of a large number of landing pages optimized for low-frequency key phrases, therefore increasing the semantic coverage for the catalog and the site in general.
How do filter pages differ from online store category pages?
Category pages and filter pages are two different pages on a website with different purposes and functions. The purpose of this category is to show the user all the products belonging to a certain category, and the filter page is to help the user filter products based on certain parameters such as size, color, material, etc. A category page usually has more complex navigation to navigate between different subcategories. The filter page has simpler navigation, usually in the form of checkboxes, radio buttons and other elements. Category pages can be more SEO optimized because they contain more content and keywords. Filter pages have less content, but can be more useful to users who are looking for products with certain parameters. Filters provide the user with a list of only those products that he needs: a certain size, color or price.
Depending on the diversity of the product range on the site, it is possible to implement both basic filters and a wider list of filters for more convenient navigation. That is, some categories of goods may have unique properties that are not related to goods in other categories, in contrast to characteristics such as “price” or “size”.
For such categories, the set of product filter parameters must be unique; it is recommended to use filters based on the list of characteristics included in the product description.
Using filters or tags, you can significantly expand the reach of your target audience, thanks to a separate landing page for each group of queries. For example, in a shoe store there is a category “Women’s sneaker”.
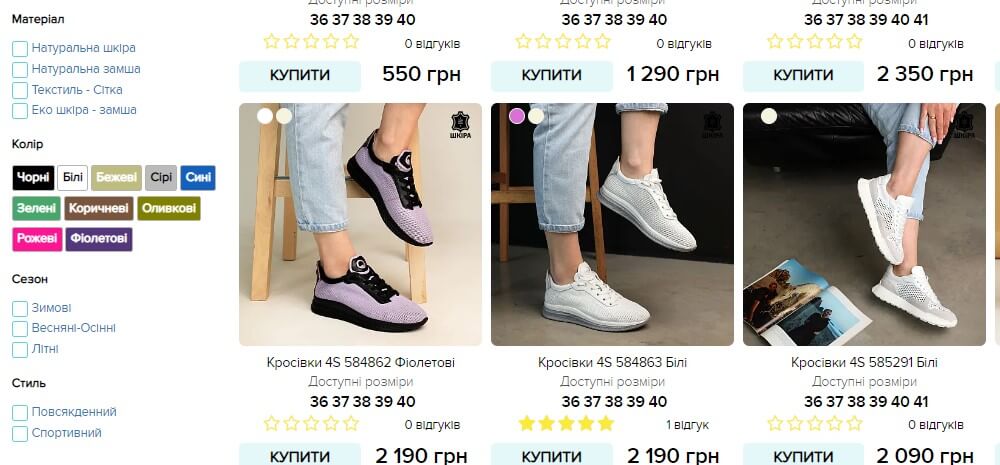
In the category you can choose sports sneakers, summer sneakers, gray sneakers and so on. Optimizing filter pages involves creating a separate landing page for separate groups of requests to receive targeted traffic for these requests to the relevant pages, and not to the main category.
Product filter menu design
The display of the filter menu is usually implemented by a vertical “tree” of traits in the catalog sidebar.
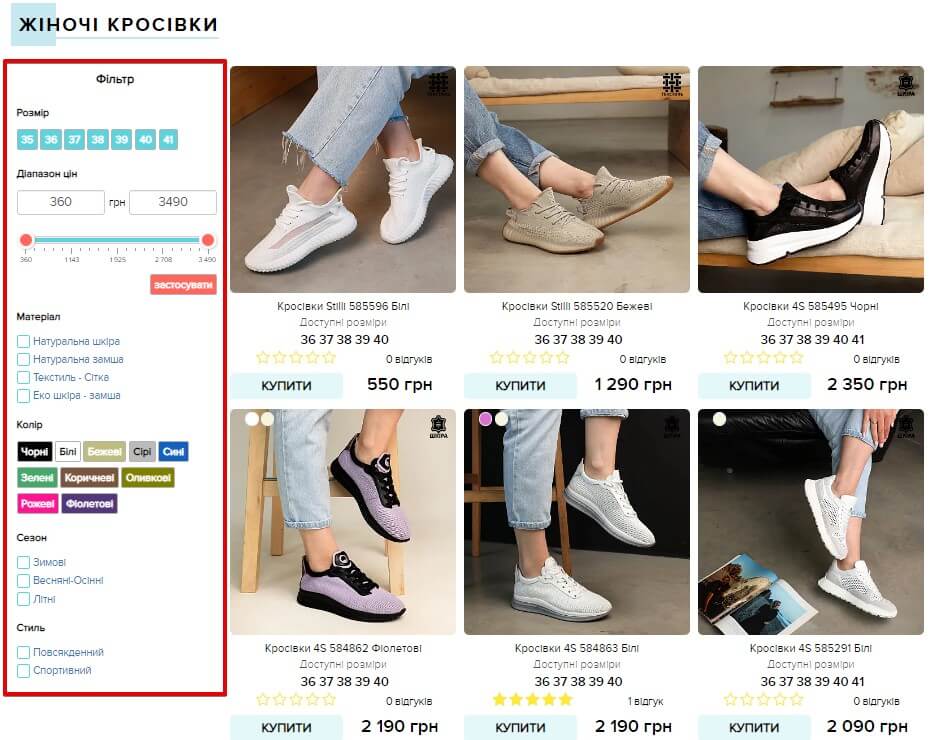
However, in recent years, horizontal display of menus has become increasingly popular, the disadvantage of which is that the screen width limits the space for expanding search categories.
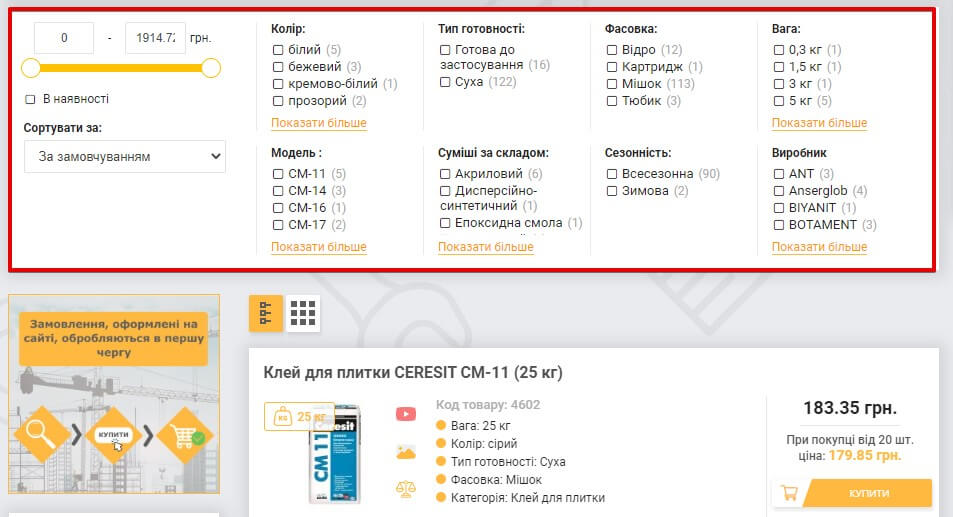
It is possible to use a combined display that combines two approaches for maximum ease of use.
It is useful to provide a display of applied filters – this will help the visitor to better navigate and, for example, cancel unnecessary filtering parameters.

How to optimize filter pages?
Most CMS generate product filter pages that are not optimized for search engines. They don’t have CNC URLs by default, have non-unique meta tags, and don’t have enough internal links, making them difficult for search bots to crawl. This determines the low probability of indexing filter pages by search engines.
Next, we will consider the activities necessary for SEO optimization of product filters, which should best be performed at the site development stage.
- Researching keywords and collecting a semantic core for a product category.
- Based on competitor analysis and search engine results, cluster, group the semantic core and form the desired site structure. You must select groups of search queries that correspond to subcategory pages and filters.
- The goal of optimizing filter pages is to get them into the search engine index:
Ensure the possibility of their indexing – setting up the robots.txt file and the “robots” tag, inclusion in the sitemap
- Customizing CNC URLs for filter pages – using a URL (for example: the main product category with the addition of the name and value of the filter parameter
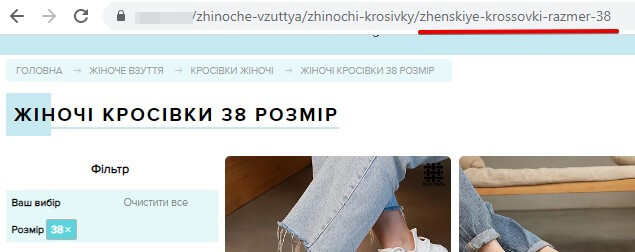
Using the results of semantic research, create goal-relevant Title, Description tags and H1 headings of pages, separately for each or by setting up auto-generation templates
In order for filter pages to receive sufficient weight, it is necessary to take care of internal linking: for example, using anchor links from the filter options menu or by characteristics in the product card.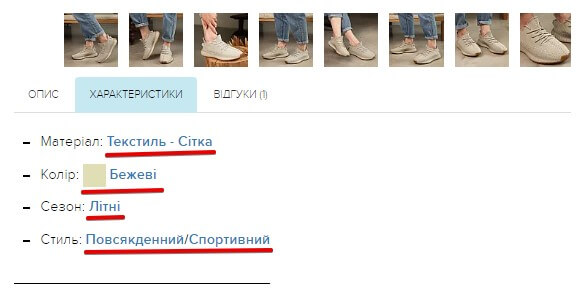
Before creating and optimizing filter pages, you need to discuss with the customer the availability of a sufficient range of products: search engines prefer resources that can satisfy the needs of visitors, so the number of products is one of the ranking factors.
The benefits of filter optimization
By creating and optimizing product filter pages that are relevant to low-frequency search queries, the online store significantly narrows the range of competitors in search results. Not all online directories create the structure correctly and do not have the necessary landing pages, so the number of competitors for such requests is much smaller.
Optimized search filters also help with contextual advertising. If a visitor goes to the main page of a category using the query “white sneakers,” he will be forced to apply a filter to get the desired group of products. If there is a page relevant to such a request, you can proceed to selecting a product without additional “manipulations” with the filter, and such pages can be used by contextual advertising specialists. Consequently, having separate optimized pages for each group of queries will lead to an increase in quality score and a decrease in the cost per click.
The use of filters in an online store is not just a convenient product search functionality, it helps demonstrate the diversity of the assortment, better semantic coverage and more flexible settings for contextual advertising.






 12/05/2023
12/05/2023  3387
3387


