Content of the article

Spam and targeted phishing emails remain one of the most common channels for spreading fraud and malware, as well as the main cause of account compromise and data loss. Today, when a part of business processes and critical communications are carried out via email, the ability to distinguish between the types of threats and respond quickly is key for any organization.
In this article, we will analyze the classification of spam emails, describe how email systems detect them, and provide practical, proven recommendations for end users, IT teams, and marketing senders.
What types of spam are there?
Spam is not homogeneous: the term hides a number of different threats, from intrusive ads to targeted fraudulent attacks. Here are the main types of spam.
- Advertising or marketing spam.
These are mass emails offering goods or services that the user did not expect to receive. For example, an email with a «special offer» from an unlicensed online store.

- Phishing.
Emails that masquerade as banks, services, or colleagues and are aimed at stealing logins and passwords through fake websites. An example is a message «from the bank» demanding urgent confirmation of data.

- Business email compromise (BEC, Business Email Compromise) or fraud on behalf of a manager.
Social engineering on a corporate scale: fake or hacked business emails are used to initiate payments or extract confidential information. An example is «letters from the director» with instructions to transfer funds.

- Malicious mailing (sending malware).
Emails with executable files or archives that run malicious code when opened. For example, an «invoice» in a .zip file with an .exe inside.

- Domain spoofing and impersonation.
Sending emails with a fake «From» field or using domains that look similar to yours (typographical substitutions).

- Technical and scalable techniques (mass mailing to many IPs, spam replies, botnet spam).
Attacks that distribute emails to a large number of IPs or use infected machines to avoid blocking. ISPs counteract them through reputation databases and blocklists, but such methods are still difficult to cut off instantly.

Each of these types of spam has its own characteristics and different consequences, but the main rule is not to act impulsively.
How email systems recognize spam
Modern email systems don’t rely on a single signal. They perform many successive checks, and the result of each is added to the final decision to deliver, quarantine, or reject the email. Often, this is perceived as «layers» of protection, which we will discuss.
Sender reputation (IP and domain)
The first filter is the «who is sending» check. The recipient’s server compares the sender’s IP and domain with reputation databases. If the IP is on known blacklists (for example, due to mass mailings or botnet activity), the email may be immediately marked as spam or even discarded.
For the sender, this means: monitor the reputation of your IPs and respond to blocklist warnings in time.
For the administrator: check the IP through reputation services; if it is blacklisted, perform an investigation (source of massive traffic, hacked accounts) and go through the procedure of removal from the list.
Domain authentication: SPF, DKIM, DMARC
These mechanisms signal to the email «can we trust that the email is really from this domain».
- SPF (DNS record) indicates which servers are authorized to send mail on behalf of the domain.
- DKIM adds a cryptographic signature to email headers that the recipient can verify.
- DMARC allows the domain owner to specify a policy for emails that fail SPF/DKIM verification and receive reports.
A practical example: if an email fails SPF and DKIM, DMARC can instruct the recipient’s server to quarantine or reject it, depending on the policy configured. The sender should understand that the correct configuration of these records increases trust and improves delivery.
Content analysis: signatures, heuristics, rules
This is a set of content-level checks: searching for known signatures of malicious emails, analyzing headers, text-to-attachment ratio, and suspicious links or keywords. Heuristic rules provide a quick «suspicious/not suspicious» assessment based on patterns.
An example of a heuristic: an email with a large number of recipients, a short message, and a link to a domain that is not related to the sender and receives a higher «spam rating».
Machine learning (ML) and behavioral analysis
ML models are trained on a large number of examples and are able to find non-trivial signs of spam: unusual sending patterns, changes in the style of correspondence, and anomalies in headers. Unlike strict rules, models adapt and reduce false positives over time. This means that ML helps to detect new phishing campaigns that do not yet have signatures, for example, when an attacker changes the texts but maintains a similar email structure.
Behavioral signals and feedback
Providers also take into account user actions: how many people marked the email as spam, the complaint rate, and the bounce rate. These metrics influence the sender’s reputation and further filter decisions.
Now that we understand how and on the basis of what signals the email system identifies spam, let’s look at practical steps to protect your business.
Protecting your organization: policies, technical settings, and incident response
Effective email infrastructure protection in an organization combines three components.

Below are practical recommendations and specific steps for each of these elements.
- Setting up the mail gateway.
Implement multi-level policies at the mail gateway level:
-
- quarantine / spam thresholds. Define thresholds (spam scores) for automatically moving emails to quarantine and marking them as spam. Set up regular quarantine reviews by responsible persons.
- Fast automatic deletion. Enable modes that allow you to quickly remove mass threats (Zero-hour auto purge), but with a log and the ability to roll back false positives.
- Attachment handling: Isolate, clean, and reconstruct content for documents with macros.
- Manage allowed and banned addresses. Maintain a centralized registry of allowed and banned domains with clear rules for updating and reviewing.
- Quarantine review process. Determine who is responsible for quarantine review, SLAs for response, and keep a log of actions.
It is worth setting up quarantine and automatic attachment analysis, creating a daily or weekly checklist for the quarantine moderator.
- SPF / DKIM / DMARC is a mandatory authentication base.
Building strong security starts with setting up SPF (Sender Policy Framework), which clearly defines the list of allowed senders, and enabling DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) for all mail servers and services. The next step is to implement DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) in p=none mode to collect statistics and analyze summary and advanced reports. Only then can you gradually tighten the policy, first moving it to p=quarantine and then to p=reject.
To increase reliability, you should use DKIM key rotation and keep documentation of all allowed email services, including third-party mailing platforms. It is also advisable to set up policies at the subdomain level: transactional email and marketing campaigns should work with different policies so that errors in mailings do not damage the reputation of the main domain.
It is recommended that you leave DMARC in monitoring mode for at least 30 days to get a complete picture and identify sources of inconsistencies before moving to stricter policies.
- Blacklists, reputation, and deliverability.
To monitor your reputation, regularly check your IP and domain against popular blacklists (e.g., Spamhaus) and other similar services. Set up alerts when the level of complaints or the undeliverability rate of your emails increases.
If you are blacklisted:
-
- Pause bulk email campaigns;
- identify the source (infected accounts, vulnerable scripts)
- eliminate the cause;
- contact the list with evidence of the fix;
- conduct test email campaigns to check if your reputation has been restored.
When using new IPs, it is recommended to gradually increase the volume of emails and clearly separate transactional email from marketing campaigns. To ensure reliability, set up continuous monitoring of undeliverable emails and complaints with appropriate notifications, and appoint a responsible person to oversee blacklist removal procedures.
- Incident response (detailed action plan).
In the event of a suspected phishing, BEC, or mass compromise, follow a clear sequence of actions and adhere to roles.
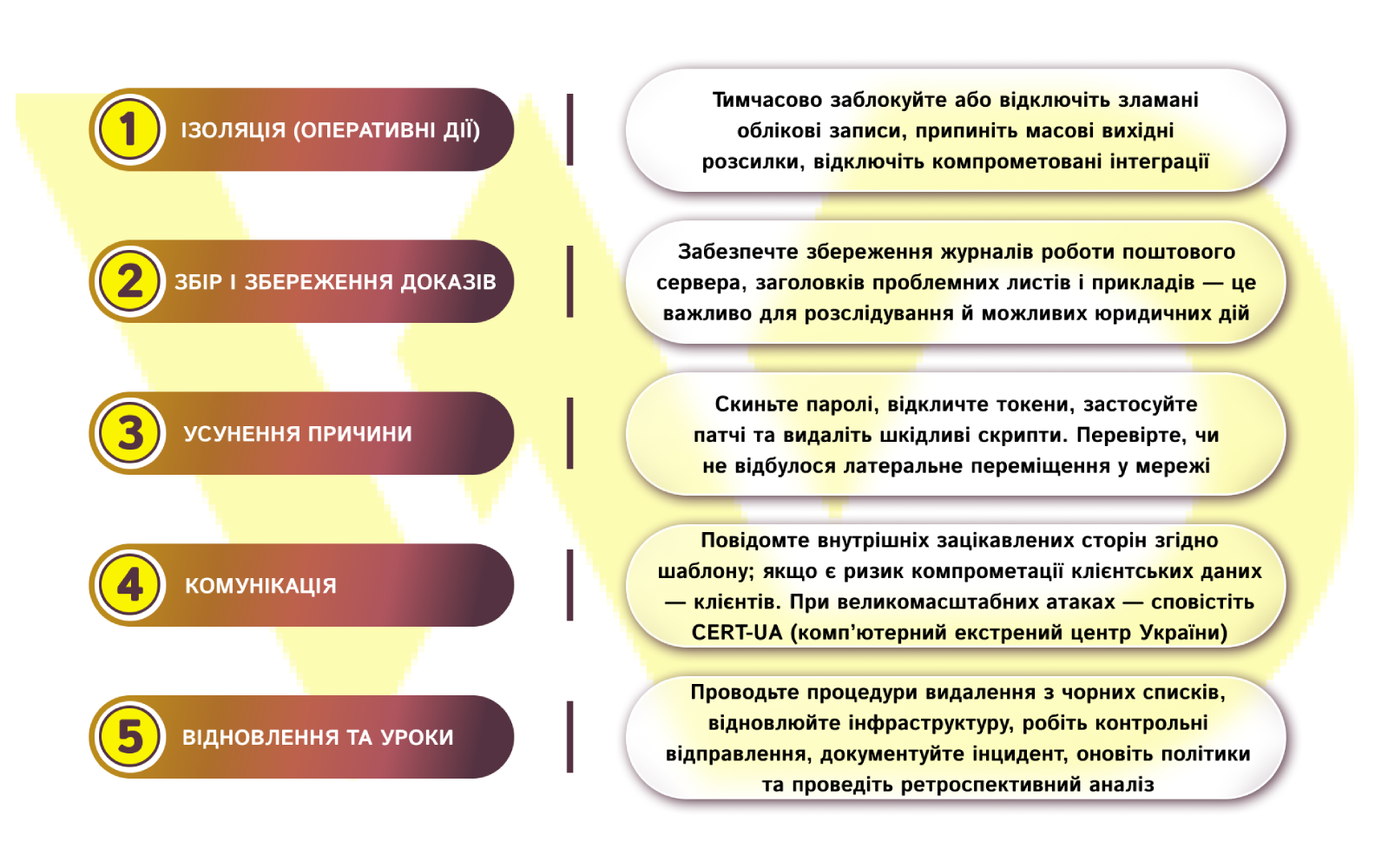
For effective work, assign people responsible for each action. Also, introduce annual tabletop training (scenario simulation) and test the action plan at least twice a year.
- Monitoring, metrics, and SLAs.
To maintain high delivery, it is important to define key indicators and acceptable thresholds. The complaint rate in marketing emails should remain below 0.1%, otherwise, you should automatically reduce the activity. The bounce rate should be tracked separately for hard bounces and soft bounces: exceeding the normal level is a signal for immediate database cleanup. Particular attention should be paid to spam traps – their number should remain zero, and any detection requires immediate investigation.
In addition, you should develop an internal service level agreement (SLA): for example, the initial response to an incident and its isolation should take place within a few hours, and the implementation of this standard should be constantly monitored. A good practice is to create a delivery dashboard and set up alerts for critical indicators.
For example, a request to be removed from the list might look like this:
«We have identified and eliminated the reason for being on the list (infected accounts/script). We have reset passwords, updated the software, and suspended mass emails. Please consider an application for removal from the list. Contacts: IT manager – name, phone number, email. Evidence and event logs are available upon request».
- Preventive measures and training.
A stable email infrastructure requires preventive measures and continuous development of team skills. The security base is to regularly clean the database of inactive contacts and use double opt-in confirmation, which reduces the risk of complaints and improves the quality of the audience.
It is also important to separate traffic: transactional and marketing emails should be sent from different IP addresses or subdomains to avoid mutual influence on reputation. Training and simulations play a significant role: regular exercises with phishing scenarios help employees better recognize attacks, and the results should be documented and re-trained for those who fail. A clear access policy should also be in place, limiting the rights to send mass emails and controlling any changes to templates or scripts.
An example of what an internal message to customers might look like:
«Dear customers, we have detected an unauthorized mailing from our domain. The cause has been eliminated and no signs of unauthorized access to payment data have been found. If you have received a suspicious email, do not click on it and notify us at support@…»
The combination of clear policies, competent technical settings, and a well-developed response plan creates a basic framework of protection. This does not guarantee the complete absence of incidents, but it ensures predictability of the team’s actions and minimizes risks to the business even in critical situations.
Local context: Ukrainian threats and response
In Ukraine, CERT-UA regularly warns about massive phishing campaigns, fake service messages, and suspicious documents. It’s important for Ukrainian organizations to synchronize their internal response processes with these recommendations to quickly block threats.
Attackers often disguise attacks as government agencies, banks, or popular online services, as well as local delivery services or registries. Therefore, it is important to constantly update security policies, check domain reputation, implement multi-factor authentication, and conduct training simulations for employees.
If large-scale suspicious activity is detected, contacting CERT-UA or regulators helps to quickly assess risks and coordinate actions. Sharing information with other companies through professional communities further enhances preparedness against attacks.
By integrating local threat data with internal procedures, the organization forms a reliable shield against spam and phishing, maintaining stable business operations even in crisis situations.






 04/11/2025
04/11/2025  1303
1303


