Content of the article


Links are the foundation of any website. They form the navigation for users, transfer the weight of pages in SEO, and determine how search engines crawl your resource. In this article, we will analyze in detail what absolute and relative links are, how browsers and search engines interpret them, what practical risks relative links pose, and how to reduce technical risks and preserve the SEO value of your site.
What is a link?
A link (URL) is a unique address of a resource on the Internet. For business, it is important to understand not only «where» the page is located, but also «how» to correctly indicate it in internal menus, marketing newsletters, external publications, and in the code of website templates. Incorrect link organization can lead to loss of traffic, problems during migrations, and additional costs for fixing errors.
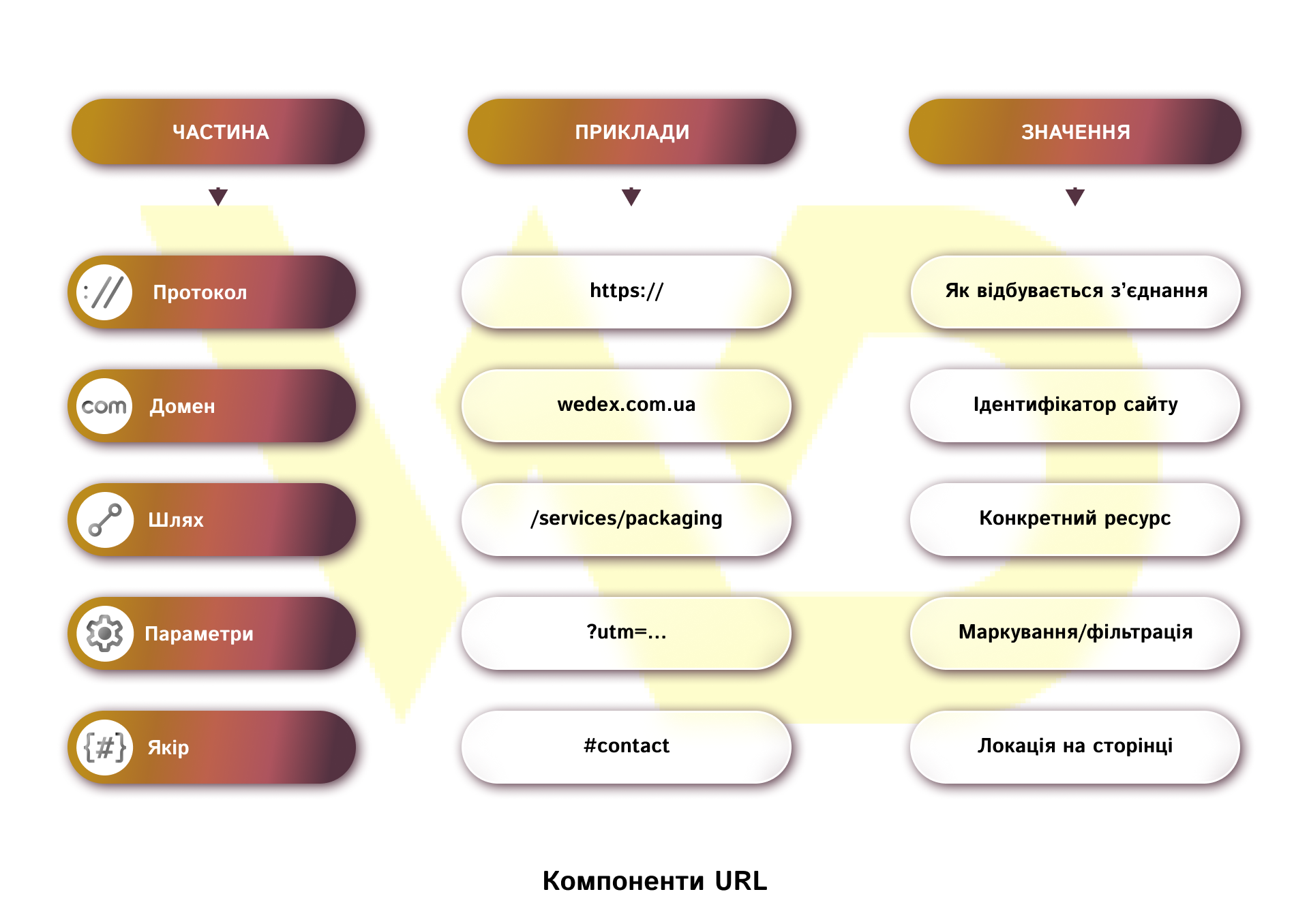
How absolute links work
An absolute link always contains the full address: protocol, domain, and path. This makes it independent of the current page or directory structure.
Why it is important for business
Absolute references are of practical importance for business because they ensure predictable and consistent behavior of a resource across all workflow bodies.
- When copying or archiving pages, absolute URLs remain correct no matter where the files are moved. They always point to the same domain, so links to images, styles, or internal pages won’t break when content is moved to other directories or backup media. This reduces operational risks and saves developers and content managers time on fixing broken links.
- In marketing materials (newsletters, press releases, or affiliate emails), absolute URLs ensure that recipients will land on the page you intended. Links in emails should work correctly in any environment – regardless of the email client, device type, or network restrictions. That’s why using full, absolute URLs is critical to the stability of your email campaigns. Absolute URLs reduce the risk of false or incorrect clicks and ensure that links behave the same way for all recipients. This means fewer complaints and better conversion rates.
- When integrating with third-party services (analytics, CRM, ad platforms, or CDNs), absolute URLs ensure unambiguous addresses. This is necessary for the correct collection, transmission, and analysis of data. Third-party systems often store and reuse transmitted URLs, and if they are incomplete or depend on the context of the page, this leads to incorrect data aggregation, errors in reports, and incorrect traffic routing. Therefore, to preserve data integrity and ensure the correct operation of automated processes, it is better to use absolute addresses where it is important to guarantee access to a specific resource.
Absolute addresses increase the reliability of the infrastructure, improve the performance of marketing campaigns, and ensure the accuracy of integrations, which directly affects operating costs and the quality of the customer experience.
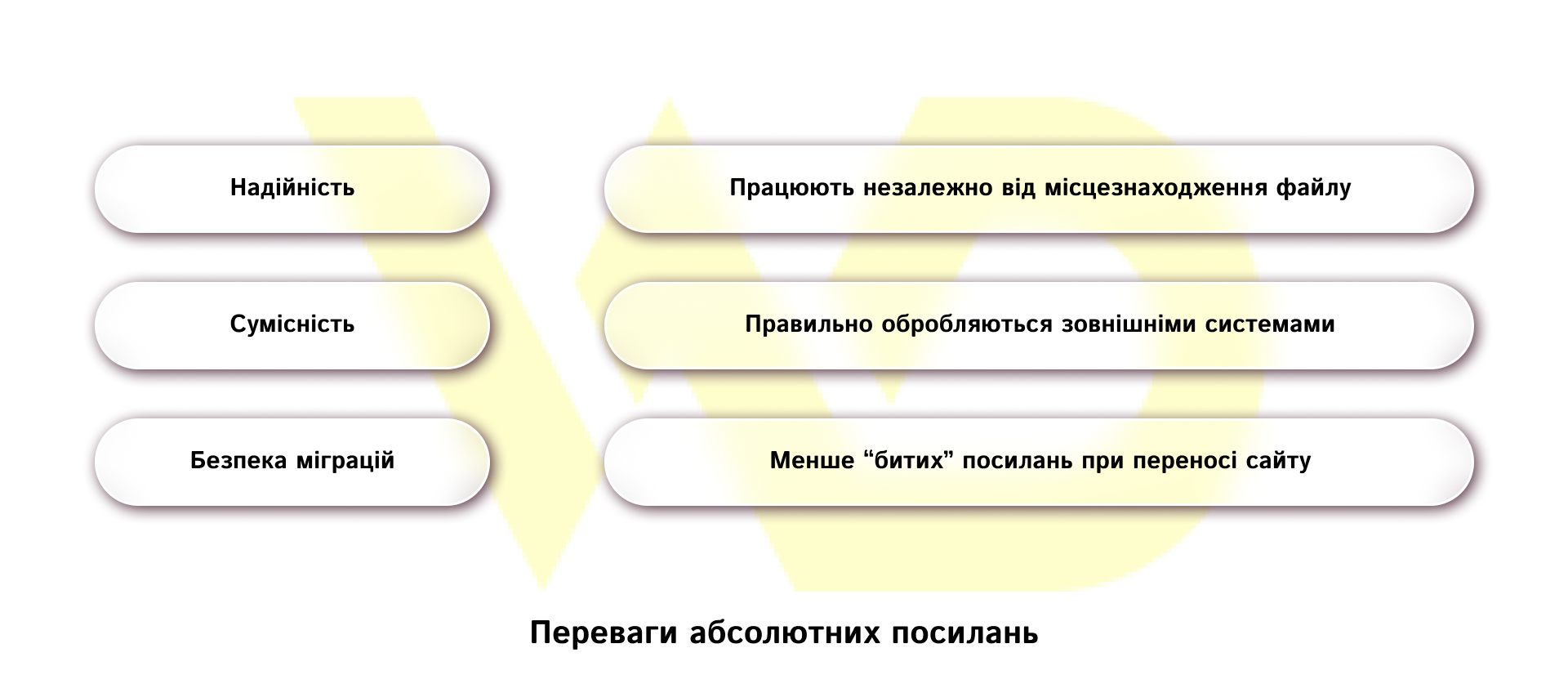
Relative links and their types
Relative links are URLs that do not contain the full site address and define the path to the resource relative to the current page or domain root. Unlike absolute links, they «work in context» – the browser calculates the final address each time based on where the document is located. It is this feature of that makes relative links convenient to develop, but at the same time requires a more careful approach to their use.
There are three types of relative links, each of which has its own peculiarities.
Root-relative links
Root-relative links begin with a slash (/) and are always counted from the root of the domain. No matter what page the user is on, the browser substitutes this path directly to the domain name.
For example:
<a href=”/services/packaging”>Packaging to order</a>
This format is often used in internal navigation: menus, footers, breadcrumbs, buttons to switch between sections. It is easy to read, does not depend on the depth of nesting of pages, and allows you to maintain a uniform link structure across website templates. At the same time, root-relative links are tied to the root of the domain, so when working with copies of the site in subdirectories or test environments, their behavior needs to be additionally checked.
Path-relative links
Path-relative links are formed relative to the current location of the document in the file structure. They do not start with / and can contain directory navigation elements, such as ../ to go to a higher level.
For example:
<if the page is located at /blog/2025/post.html>
<a href=”../services/packaging”>Packaging services</a>
In this case, the browser first determines the path of the current page, and then «adds» the specified relative route to it. This approach is often used for local blocks or modules that are saved and moved along with the entire folder. At the same time, path-relative references are the most sensitive to structure changes. That is, any movement of the file can change the final address and lead to incorrect transitions.
Protocol-relative links
Protocol-neutral references begin with a double slash (//) and do not explicitly indicate the protocol.
For example:
<a href=”//wedex.com.ua/poslugy/kontekstna-reklama-ppc”>Example of protocol-relative</a>
Previously, this format was used to automatically adjust to HTTP or HTTPS. Today, it is considered outdated, as most sites operate exclusively over HTTPS, and explicitly specifying the protocol is a security standard. The use of protocol-relative links can cause ambiguous behavior in some environments and contradict modern requirements for content security policies.
How the browser handles relative links
When a browser encounters a relative link, it takes the full address of the current page and applies URL rules to it. If the path starts with /, it is substituted for the domain, and if not, it is added to the directory of the current file. You should also take into account the <base href=”…”> tag in the page code: it sets the base address for all relative links and can radically change their behavior.
Thus, relative links are a flexible tool, but they require a clear understanding of the site structure and the rules for their calculation. It is the correct choice of the type of relative link that determines the stability of navigation, correctness of transitions, and the absence of technical errors in the future.
The main differences
Let’s summarize all the key differences between absolute and relative links. This will help you understand in which situations which approach is more relevant.
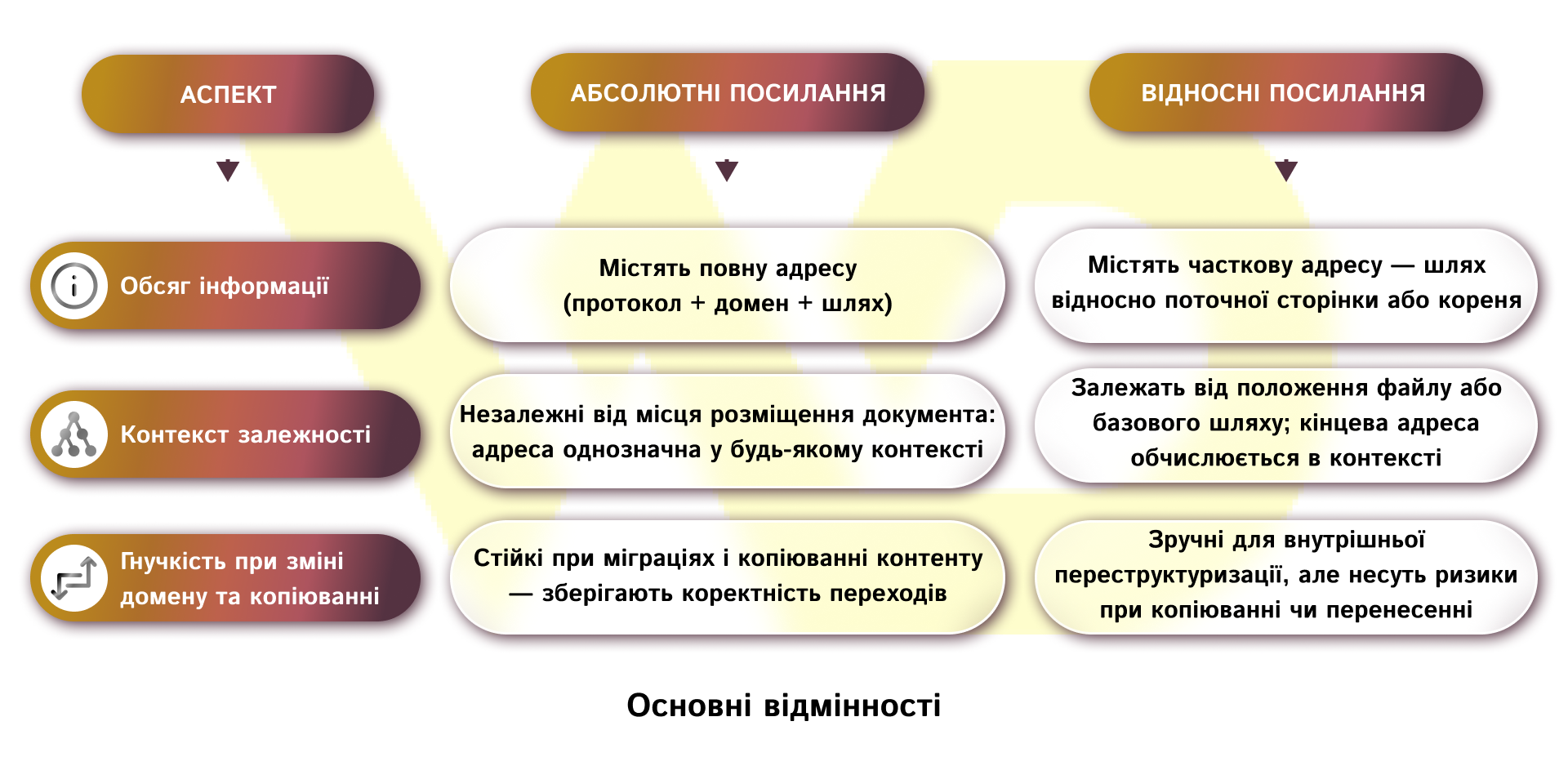
So, absolute links provide predictable and stable behavior in the context of integrations and migrations, while relative links provide convenience and compactness in the local context, but require more careful control when changing the structure or moving content.
Why relative links pose risks
Relative links are easy to develop and allow you to write compact templates, but they require conscious control. If used incorrectly or when the site structure is changed, these links can cause technical errors, worsen indexing, and complicate operation. So, the key risks are as follows.
- Insecurity during downloading and backup.
Relative paths that link to resources in other directories may stop working when copying or archiving a website. This applies both to offline archives and to transferring parts of the site to another environment (for example, for demonstration or backup). To prevent this, when exporting or backing up, you need to perform automatic resource checks, and for archiving, use tools that make absolute links or correctly package dependencies.
- The risk of duplicate content.
If the same page becomes available through different URLs – through a mixture of relative and absolute links or through different domains and/or subdomains – search engines may index duplicates. This dilutes the SEO authority of the page and lowers its rankings, as the link weight and internal signals are distributed among multiple URLs. Therefore, you need to set <link rel=”canonical”> on pages where there is a risk of duplication, and in case of copying content, set up 301 redirects from old addresses. In templates, clearly define the link format for different blocks.
- Deterioration of internal linking.
Incorrect relative paths often lead to 404 errors, especially in global components (menu, footer). This disrupts the transfer of internal PageRank, makes navigation more difficult for users, and makes parts of the site less visible to search engines.
For example, after the catalog is reorganized, some path-relative links no longer lead to landing pages, which causes complaints from users and a decrease in behavioral indicators.
To prevent this risk, it is worth fixing the rules for link formation in code standards, testing global components after structure changes, and automating 404 checks in CI/CD.
- Complication of scanning and determining the canonical domain.
On large projects with multiple environments, CDNs, or subdomains, the lack of reference unification complicates the work of crawlers and analytics. Search robots can get confused by URL variants, leading to incomplete or duplicate indexing. For businesses, this means unpredictable changes in visibility and difficulties in tracking performance.
It is recommended to unify link policies (e.g., absolute for external integrations and root-relative for internal menus), document the use of <base> if applicable, and test crawler behavior after changes.
Relative links remain a useful tool, but for businesses, their use should be controlled: rules, tests, and automation are needed to reduce risks to SEO, user experience, and operational stability.
To summarize, the smartest strategy for a business owner is a combined approach. Absolute references provide stability and better predictability during migrations and external integrations, root-relative references are convenient for managing resources within a stable domain, and path-relative references should be used sparingly and only where the context is precisely controlled.





 19/01/2026
19/01/2026  894
894



