Content of the article


A drop in traffic or the sudden disappearance of a website from search results is painful for a business. Often, the problem is related to Google’s actions: from algorithmic adjustments to manual sanctions (bans). In this article, we will analyze what a ban is, how to distinguish it from other problems, and what quick and in-depth checks you can do on your own. And also a practical recovery plan.
What is a Google website ban?
A ban is the most severe form of sanction when a search engine removes a website from the search results in whole or in part. In practice, this means that users can no longer find the resource by any queries, even by direct branded ones. This status is a signal that Google considers a website to be dangerous, manipulative, or in violation of the rules.
The ban status can take different forms.
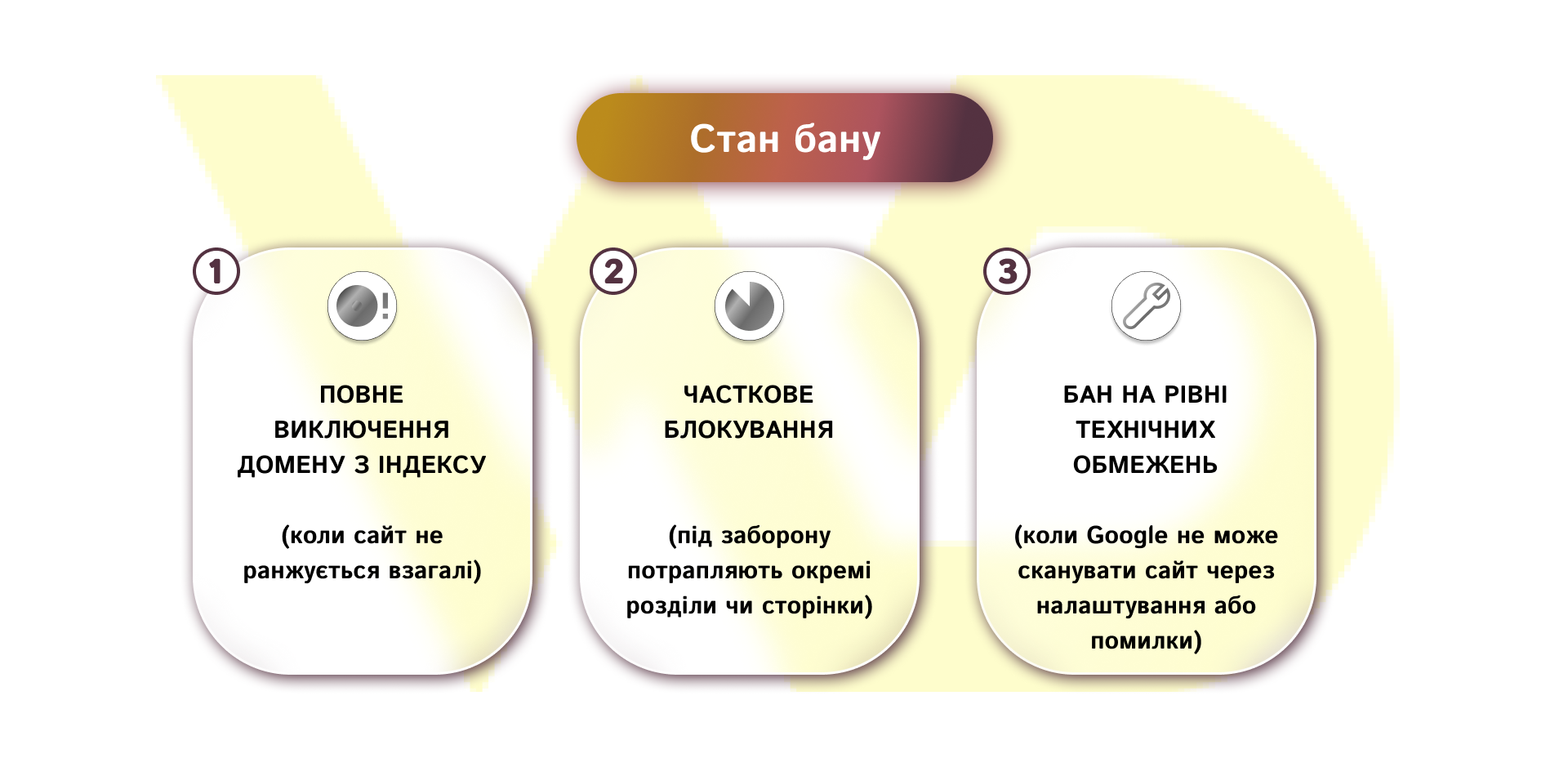
As a result, a website loses organic traffic, commercial requests, keyword rankings, and algorithmic trust. Therefore, it is important not only to state the fact of sanctions but also to understand their nature, which affects the way to get out of the penalty.
The difference between sanctions and bans
The terms «sanction» and «ban» are often used interchangeably, but for practical work with a website, it is important to understand their differences in scale, source, and consequences.
A penalty is a general term that covers any visibility or ranking restrictions imposed by a search engine. It can be either manual, when a Google engineer or moderator applies a measure to a specific resource, or algorithmic, as a result of ranking updates.
And a ban is a more radical phenomenon: complete or almost complete exclusion of a resource from the index, when the site stops appearing in the search results even for branded queries.
The main differences are also:
- The source of the decision.
Manual sanctions have a «human trail» and are usually accompanied by a notification in Google Search Console. They give clear clues about the reason. Algorithmic sanctions are more subtle: the site loses positions due to algorithmic changes, and sometimes you have to compare the dates of the drop with Google updates to understand the reason. A ban is usually associated with serious violations or technical problems (for example, detected malware or complete blocking of indexing), and its consequences are more extensive and long-term.
- The level of intervention for recovery.
With manual sanctions, the remediation process is usually formalized: detect the problem → fix it → request a re-examination. Algorithmic cases require systematic work on the quality of content, links, and UX, and the results appear gradually – after the next update. In the case of a ban, especially due to hacking or malware, you need to urgently restore security, clean up the site, and show Google that the threat has been eliminated.
- Scale of influence.
A sanction can reduce the visibility of individual pages or sections, while a ban usually affects the entire domain or its main part. The priority of actions also depends on this: with partial sanctions, they start with certain sections, while with a ban, they start with the entire website infrastructure.
- Timeframe and forecast.
Manual sanctions can be appealed and the result can be obtained fairly quickly if corrected – from several days to several weeks. Algorithmic restoration often requires months of system work and repeated updates. Fixing the consequences of a ban can be the most difficult and require the simultaneous work of technical specialists, SEO specialists, and platform support.
Understanding the differences between a sanction and a ban helps to prioritize actions correctly: a quick technical response and restoration of accessibility are critical in case of a ban, while algorithmic drawdowns require systematic work on the quality of content and links.
How to check a website for a ban
Initial diagnostics help to quickly understand whether a website has a serious problem with indexing or sanctions and determine a further action plan.

Let’s take a closer look at how to find out if a website domain is banned.
Check visibility in search
Start with the standard site:yourdomain.com query. If Google returns no results or shows only a few pages, this is the first reason for concern. Next, check if there is a cache in the search results for several key pages. The absence of cache may indicate that the pages are not being indexed. Also, do a brand name query: if the site is not found even for the exact brand name query, the likelihood of a complete blocking or a serious drop in visibility increases significantly.
Google Search Console overview
Google Search Console is the main tool for detecting manual penalties and technical issues. First, you should check the Manual actions section – the presence of a notification immediately makes it clear what the cause and scope of the violation is. Next, check the Coverage report, which will indicate indexing errors, noindex pages, 404s, and server 5xx errors. Also, check the security section – if Google has detected malware or hacking, a warning will appear there. Data from GSC allows you to accurately localize the problem and prioritize steps.
Analysis of traffic and time trends
Compare organic traffic in Google Analytics (GA/GA4) by date: a sharp drop in a short period (for example, 50-100%) often correlates with algorithm updates or manual actions. It is important to see if only organic traffic has fallen or if all channels have been affected. If the decline only affects organic traffic, it is a signal of SEO problems, and if all sources are affected, it may be a technical or server malfunction. Analyzing the time frame will help you compare the drop with known Google updates and determine whether it is worth looking for an algorithmic cause.
Check server availability and logs
Check the saved access logs: whether Googlebot visited the site, what HTTP responses it received, and whether there were numerous 5xx or 403 errors for bots in the logs. If Googlebot receives errors or does not visit pages at all, the problem may be at the level of hosting or server configuration. Checking the logs helps to distinguish technical unavailability from sanctions, because technical failures are visible in the behavior of bots and response codes.
Analyze the robots.txt file and indexing meta tags
Examine https://yourdomain.com/robots.txt for accidental or intentional blocking (Disallow: /) and check if the noindex meta tag is present on critical pages. Sometimes changes in templates or CMS configuration can lead to global indexing blocking. In such cases, the fix is technically simple but urgent. Also make sure that HTTP headers do not contain directives that prohibit caching or indexing.
Evaluate the link profile
A quick look at the link mass will show you if there has been a sudden influx of «toxic» donors or massive link buying, which could have caused an algorithmic drop or manual penalty. Use the tools to build a list of suspicious donors and evaluate the anchor profile. If you find a high proportion of low-quality links, start the removal process or prepare a file for disavowal as part of your recovery plan.
Check for hacking and malicious code
Examine your site for any third-party code, redirects to suspicious resources, or unusual template insertions. Google responds quickly to malware detection and may restrict the display of pages that threaten users. If you suspect a hack, use security scanners and start cleaning immediately. Restore backups, update all passwords, and remove infected files.
Check the indexing of individual URLs
If the problem does not affect the entire domain, check the indexing of specific URLs like site:yourdomain.com/page-url. If one page is not included, it may be due to its meta data, parameters, or content errors. This approach allows you to localize the problem and avoid unnecessary global changes.
For deeper diagnostics, it is advisable to connect external analytics and security services: Ahrefs, SEMrush, Sistrix, or Moz will show you the history of visibility and loss of positions, and tools such as Sucuri or VirusTotal will show you the presence of malicious code. Checking the WHOIS and domain status will help to eliminate problems with the registration period or unforeseen redirects.
Once the technical and analytical picture is gathered, the next logical step is to understand the reasons why the site might have been banned.
Why you can get banned
Search engines impose penalties when a website violates quality, security, or good behavior requirements. The most common reasons can be divided into several groups.
- Manipulative schemes with links. This category includes purchased links, PBN networks, uncontrolled directory placements, and other methods of artificially building a link profile. Search engines consider such activity as an attempt to influence rankings, which often leads to manual penalties or a significant decrease in visibility.
- Low-quality or duplicate content. Penalties are possible in cases where texts are created not for the user, but exclusively for search robots. This applies to pages with excessive optimization, automatically generated content, weak rewrites, and duplicate content. Such pages have no value, so search engines reduce their presence in the results.
- Hiding. This refers to situations when users and robots are shown different content. This practice is considered intentional manipulation, as it distorts the assessment of the page’s relevance.
- Malicious code or website hacking. If a resource contains malware, phishing elements, or other dangerous code, it poses a threat to users. In such cases, the site instantly loses the trust of search engines and may be marked as «unsafe».
- Automation schemes. Mass creation of similar pages, automated content, spam in comments, or aggressive bot traffic also form a signal of unnatural activity. This can lead to both filters and stricter sanctions.
- Intentional violation of the rules. Attempts to hack competitors, manipulate ratings, carry out technical attacks, or implement prohibited promotion methods are considered critical violations with corresponding consequences.
Regular audits, timely maintenance, and adherence to basic SEO principles in most cases help to avoid these risks and maintain a stable website position.
Recovery plan after sanctions
Of course, you need to put your website back in order after a ban or sanction as soon as possible. How to do it:
- record the fact of the problem;
- determine the type of sanction;
- promptly fix technical errors;
- conduct a content audit;
- conduct an audit of the link profile;
- if manual sanctions are applied, prepare a detailed report on the work done and provide Google with a clear plan for further work;
- submit a request for reconsideration in the Search Console;
- check notifications in GSC, monitor changes in traffic and website behavior. Google’s response time can vary from a few days to several weeks, so it is important to continue improving content and links even during the waiting period.
In complex or large-scale cases, it is advisable to involve technical SEO specialists or an agency, as recovery from serious sanctions requires accurate analysis, comprehensive solutions, and experience in dealing with such situations.
But the most important thing to remember is that recovery from sanctions is not a one-time action, but a strategic process. It is important not only to return the website to the search results, but also to create conditions under which the risk of repeated problems will be minimal. Regular technical audits and algorithm monitoring are key to this.






 12/01/2026
12/01/2026  1077
1077



