Content of the article


In digital marketing, link weight is one of the main factors that affects the visibility of a website in search engines. And for business, this is not an abstract technical detail. A part of organic traffic, search engine rankings, and, ultimately, the number of sales and leads depends on understanding and controlling this indicator.
In this article, we will look at what link weight means, how it is formed, what types of link weight exist, what tools are used to measure it, and what practical steps can be taken to increase page weight and protect against its loss.
What is link weight?
Link weight is a conditional measure of the value that a hyperlink transfers to a page on the web. In simple terms, when one site links to another, it is as if it recommends it, and search engines take these recommendations into account and increase the credibility of the page. The weight depends not only on the number of links, but also on the quality of the donors (authority of the resources), the type of links (dofollow or nofollow), the context, and the anchor text. The internal linking of the site also plays an important role: the correct structure helps to distribute the available weight among the key pages. In practical work, weight is estimated using a set of metrics, i.e. PageRank analogues in various services, and is used to make decisions about link building and optimization of the site structure.
Types of link weight
It is important to understand the difference between the types of link weight because each of them has a different impact on the page ranking and requires different optimization tactics. Let’s analyze the main types of weight and why they are important for SEO decision-making.
Static weight (analogous to PageRank)
Static weight reflects the «average» amount of authority that a page receives from inbound links within a website or a network of external donors. In the traditional PageRank model, each outbound link divides a portion of the page’s authority between the sites it points to, so pages with a large number of high-quality donors accumulate more static weight. In practice, this means that if your landing page has strong external links and favorable internal linking, it will receive stable basic ranking support.
Dynamic (behavioral) weight
Dynamic weight is formed based on real user behavior: link clicks, time spent on the landing page, bounce rate, and other interaction signals. If users actively click on a link and interact with the content, search engines can interpret this as an additional signal of relevance, which increases the effective weight of the link in a particular context. Therefore, it is important not only to get links, but also to make them visible and useful to the audience.
External weight
External weight is the strength that backlinks from other domains give to a page. It depends on the authority of the donors, thematic relevance, and the number of unique referral domains. Links from thematically related, authoritative resources have a much higher external weight than mass mentions from low-quality sites. It is the external weight that is most often the decisive factor in increasing positions in competitive queries.
Internal weight
Internal weight occurs within your site and is determined by the linking structure. That is, how many internal links lead to a page, from which sections, and how close it is to the main sources of authority, such as the main page or categories. Reasonably designed internal linking allows you to redistribute existing authority in the direction of commercial landing and key sections without additional external costs.
Anchor weight
Anchor weight depends on the link text – the anchor. Relevant, informative anchors strengthen the semantic correctness of the link and the signals for ranking for specific keyword phrases. However, excessive or artificial saturation of anchors with optimized keys can raise suspicion among search engines, so a balance between branded, neutral, and keyword anchors is important.
The influence of link attributes: dofollow vs nofollow
Link attributes determine whether weight is transferred. Links with the rel=”nofollow” attribute or implemented through scripts and redirects often do not pass the classic link weight, although search engines may sometimes interpret them differently in the context of the overall picture. This means that in order to transfer weight, you should focus on dofollow links from authoritative sources as the main link building tool, and use nofollow as an additional traffic channel.
After we have understood the types of links, we need to understand what tools are used to measure these types of links.
How to measure link weight
Since Google no longer shows PageRank, page weight is determined directly through SEO services and special programs. The main tools are as follows:
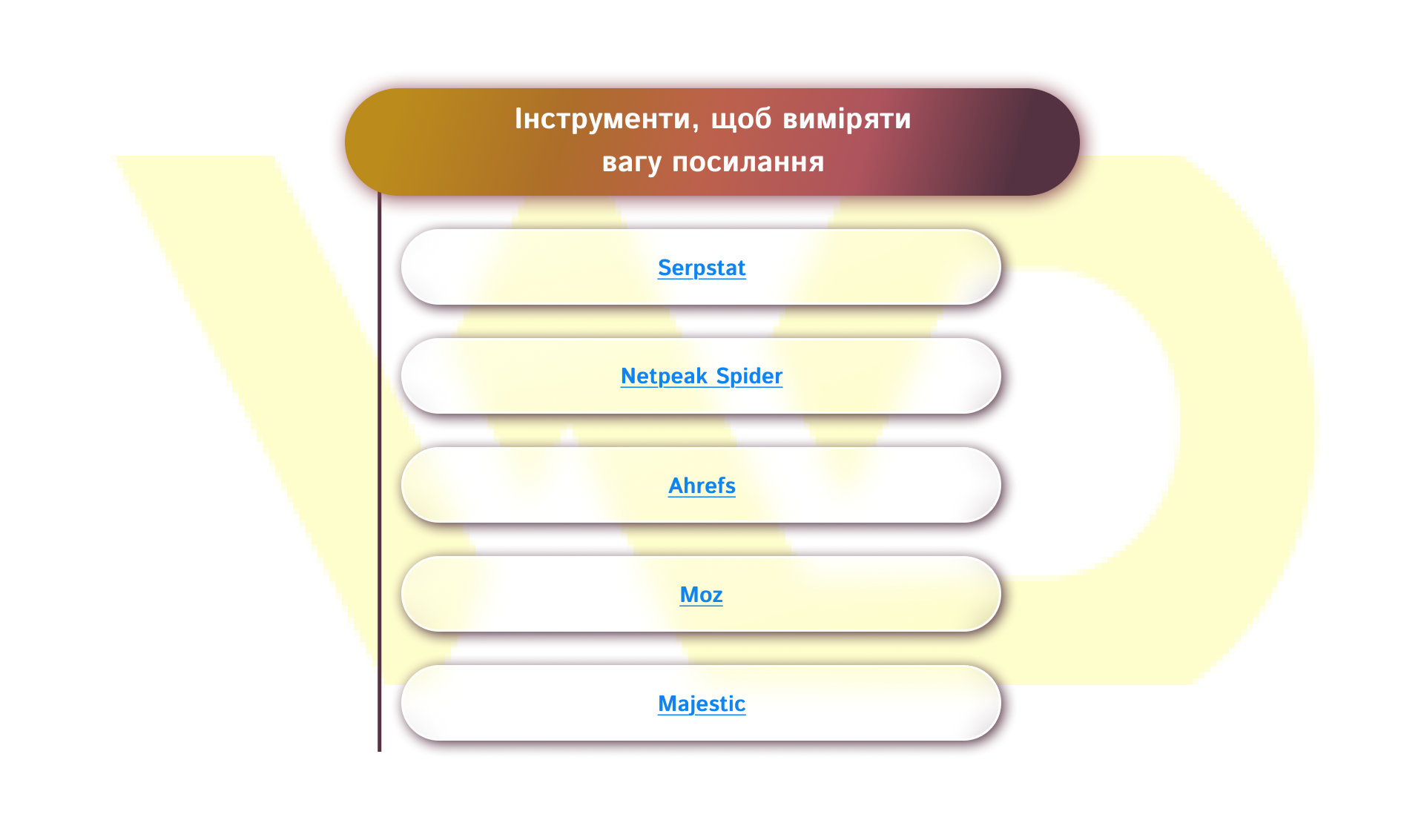
- Serpstat is a cloud-based SEO platform that gives you a quick overview of the link picture of a domain or a specific page. Main metrics:
-
- domain authority score (similar to a 0-100 ranking;
- number of referring domains;
- follow/nofollow ratio;
- donor topics.
To use the tool, add the URL to the Link Analysis module, filter the donors by authority, and select those that are thematically relevant. Based on this, you can create a list of potential partners for guest posts or PR placements. The advantage for business is a quick panorama and convenient reports suitable for making decisions at the marketing level.
- Netpeak Spider is a desktop site scanner that conveniently decomposes the internal structure and shows how the weight moves within the site. The main results are:
-
- internal PageRank;
- internal link map;
- a list of pages with a large number of outbound links or dead-end nodes (dangling).
Use Netpeak Spider to crawl your site, find pages that have poor internal weight, optimize linking in favor of commercial landing pages, and close gaps in the structure. This tool allows you to improve visibility without using external backlinks.
- Ahrefs is one of the most powerful tools for analyzing external links. Main metrics:
-
- URL Rating (UR) for a specific page;
- Domain Rating (DR) for a domain;
- full list of backlinks with dates of appearance and anchors.
To use it, analyze which donors bring the most weight, track new and lost links, compare your profile with competitors, and form a link building strategy. This tool is useful for business because it provides in-depth analytics and helps to find real opportunities to strengthen the authority of the site.
- Moz offers a couple of easy-to-understand metrics: Domain Authority (DA) and Page Authority (PA). They show the relative strength of a domain and a page. The tool is convenient for quick comparison with competitors: if a potential donor has a higher DA than yours, the link from it is more valuable. Moz is recommended for prioritizing sites in outreach campaigns and for monitoring changes in link profiles. The advantage of this tool for the user is simple indicators that are easy to interpret and a user-friendly interface that does not require special technical knowledge.
- Majestic focuses on the quality aspects of backlinks through the Trust Flow and Citation Flow metrics. Trust Flow shows how reliable the sites that link to you are. This is a metric that evaluates the quality of sources. Citation Flow displays the total volume of links without taking into account their reliability. In practice, you should focus on donors with a high Trust Flow – they provide real value. If Citation Flow is high and Trust Flow is low, this is a sign of a large number of weak or irrelevant links. For businesses, Majestic is valuable because it allows you to evaluate not only the quantity but also the quality of potential platforms for placement.
Start with one or two tools, such as Serpstat for a general panorama and Netpeak Spider for internal optimization. Then connect Ahrefs, Majestic, or Moz for deeper donor analysis. Comparing data from several sources gives you the most objective picture – don’t rely on one metric, evaluate the quantity, quality, and internal structure of the site.
Ways to increase page weight
Increasing page weight is not a single action, but a set of measures at the level of website structure, content, and external links. Let’s take a look at the following ways to increase page weight:
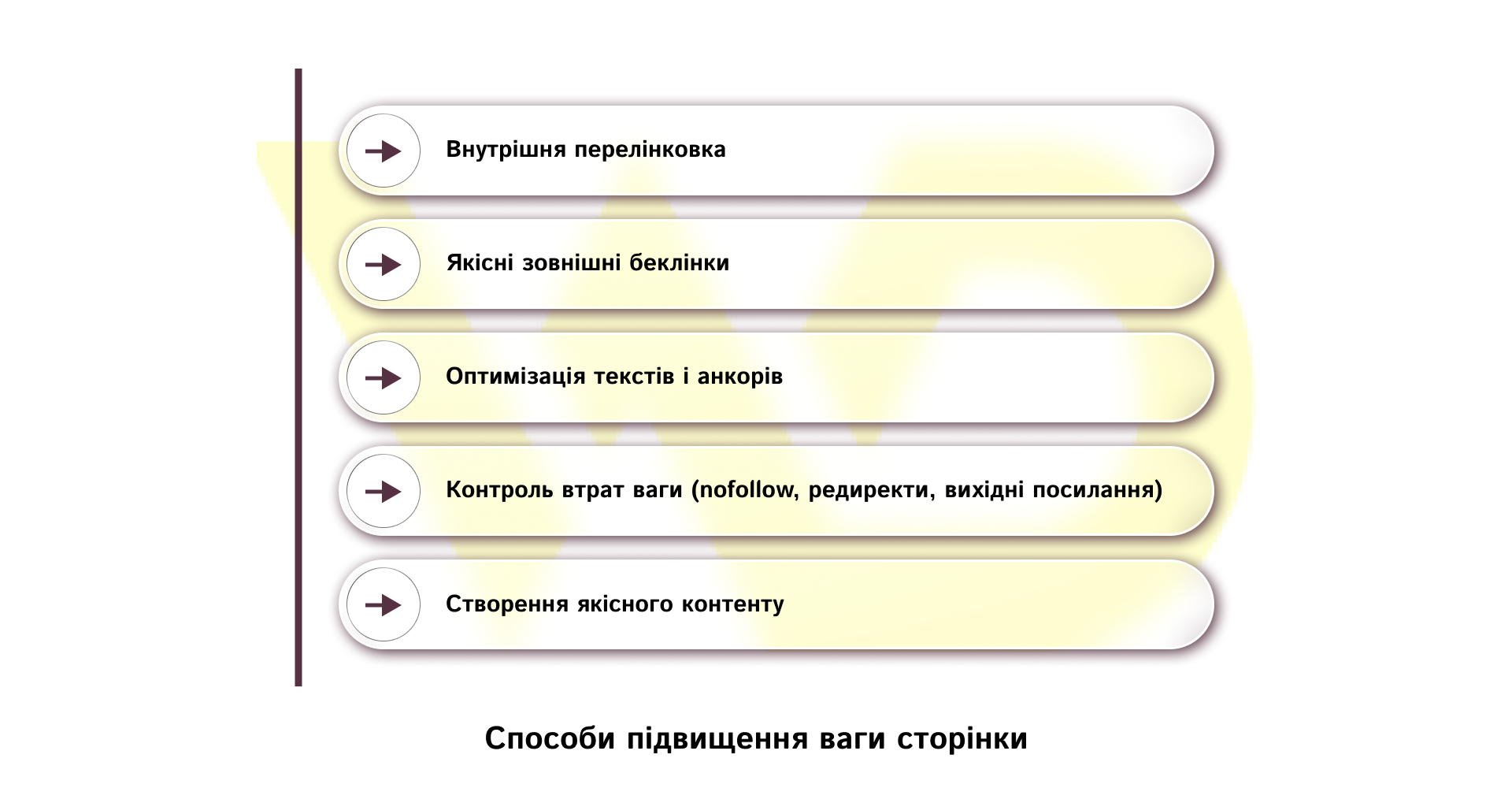
Internal linking is the first and most affordable step that does not require additional investments. The right internal linking network directs the authority of the site to commercial or priority pages. The main page and categories accumulate the most weight, which is logically passed on to the links. In other words, you need to make sure that an important landing page is no more than 2-3 clicks away from the main page. It’s also important to avoid a chaotic grid of links, where all pages link equally, because in this case, the weight is evenly dispersed and loses its effectiveness.
High-quality external backlinks are the second most important mechanism of link growth. Do not strive for quantity at any cost: it is much more useful to get a few links from thematic and authoritative resources than hundreds from little-known sites. Focus on the relevance of donors and such working formats as guest posts on related sites, thematic PR publications, and affiliate mentions that naturally weave links into useful content.
Optimization of texts and anchors helps search engines to correctly interpret what topics a page should be ranked for. Anchors should be informative and natural. You should combine branded phrases, neutral wording, and a moderate number of keywords. Make sure that important links are in visible places in the material and, if possible, closer to the beginning of the text – such links are more likely to be noticed and followed.
The next point is weight loss control. This is the technical hygiene of the site. Make sure that important donors provide dofollow links, eliminate unnecessary or low-quality outbound links that take away weight, monitor the correctness of redirects so that the power is not lost in redirects, and regularly find and fix broken pages that interrupt the logic of authority transfer. When one page has too many external links or no internal exits, it reduces its ability to effectively transfer or accumulate weight.
Quality content is the basis of all the previous measures. Unique, useful, and structured content captures the attention of users and stimulates natural mentions and links. Update your content, add practical cases, infographics, and answers to audience questions – this increases the time spent on the page, the number of shares, and the chance to get external backlinks organically.
After implementing these steps, it is recommended to measure the result and set priorities: start with internal optimization and content improvement, while working on high-quality external links and technical cleanliness of the site.
Delegate SEO to professionals
We comprehensively optimize your website: from structure and content to high-quality external links and technical optimization. You get controlled growth, not chaotic experiments.
Internal linking schemes
A well-designed internal linking scheme is the key to making the existing weight of your website work for your business goals. You may have high-quality content and external links, but without a logical site structure, these resources are dissipated, and important landing pages do not receive the necessary support. Let’s look at four example linking schemes, their strengths and weaknesses.
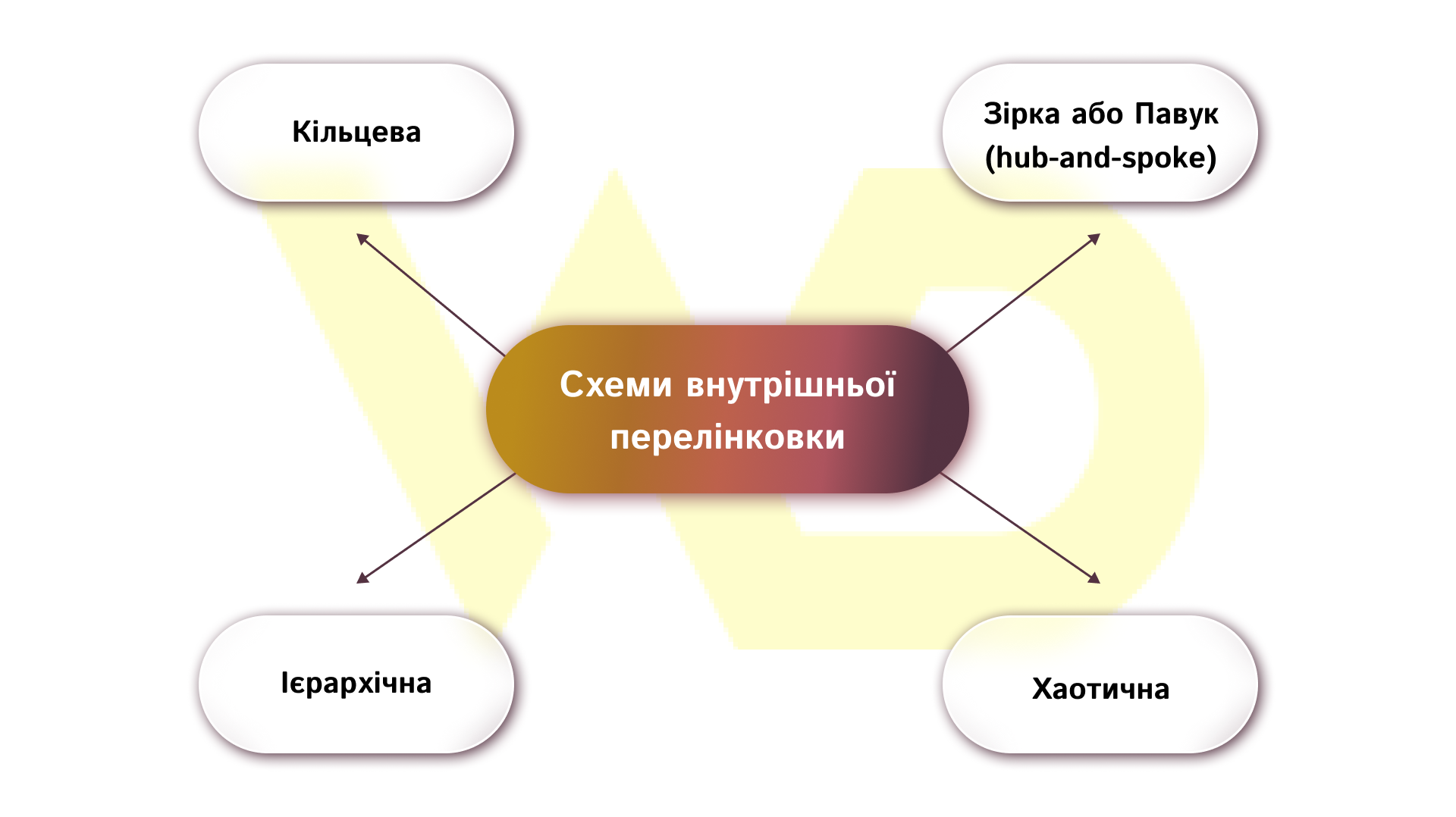
Circular
A ring schema is a closed chain of pages that link to each other in a circular pattern (A → B → C → A). This structure is easy to implement and helps to distribute the internal weight evenly among the participants of the ring. At the same time, it should be used with caution for groups of thematically related materials (for example, a series of articles or product selections), because if used incorrectly, the weight can «loop» inside the ring and not reach the key landing pages.
It is best to use the ring as an addition to the hierarchical structure – to link related materials, but be sure to add outbound links to the central pages of the site.
Star
The «Star» or «Spider» (hub-and-spoke) scheme is built around a central hub page that is pointed to by many «rays» – child materials. This configuration concentrates weight on the hub and is great for landing pages, categories, or key products. The advantage of using it is a quick concentration of authority, and the risk is that if the hub has too many outputs, the effect can be blurred.
Make the hub informative, minimize unnecessary outbound links from it, and support the hub with relevant internal articles to make the scheme work well.
Hierarchical
A hierarchical scheme is a classic tree structure: main → categories → subcategories → pages. It naturally reflects the logic of the site and allows you to clearly distribute weight from top to bottom. This model works well for online stores, large portals, and sites with a complex content structure. The main principle is to ensure that important landing pages are within close reach of the main page, no more than 2-3 clicks away. To get the effect, think carefully about the categorization and avoid «empty» levels that only disperse weight.
Chaotic
A chaotic scheme is the absence of clear logic. Pages are linked without a system, often chaotically. This approach is common on websites without a well-thought-out structure and leads to an even but inefficient weight distribution. As a result, important pages do not receive sufficient support, and it is difficult for the search engine to prioritize them. Therefore, if chaos is detected on your site, the first priority is to reorganize the linking into one of the above schemes.
Whichever scheme you use, the goal is to optimally distribute the available weight among the key pages. The choice of a particular model depends on the size of the site, the type of content, and the business goals:
- for stores and a large catalog, a hierarchy is better;
- for content projects, a combination of a star and a ring.
After building the scheme, be sure to measure the changes using internal PageRank calculations and traffic analytics, and adjust the structure based on the results. This is the cycle that ensures sustainable improvements in visibility and conversions.
How to disable weight transfer
Sometimes businesses need to intentionally block weight transfer from certain links or pages. This is relevant in cases where:
- there are paid or affiliate links that should not affect SEO;
- the page is of a technical nature (account, filters, shopping cart) and should not accumulate weight;
- you need to minimize the «leakage» of authority to external resources.
The easiest way is to use the rel:
- nofollow – for links that do not transfer weight;
- sponsored – for advertising and affiliate materials;
- ugc – for comments and user-generated content.
If the entire page should not carry weight, use noindex, nofollow. This means that it is not indexed and does not share authority. This method should be used carefully – close only the sections that are not necessary for SEO.
It is important to remember that the main goal is control, not complete blocking. Weight transfer should be prohibited selectively so as not to harm the internal structure of the site. Properly configured attributes and an understanding of when to apply them allow you to keep weight where it is really needed.
When link weight decreases
Weight is not always transferred in full. There are several situations when a link loses some of its strength. If there are too many outbound links on a page, each of them gets a smaller percentage of weight. This weakens the impact of even useful links. Also, a page that does not link to anything can lose weight. Such pages are called «hanging pages». They receive links but do not pass on authority, violating the logic of internal weight distribution.
You should also take into account the factor of changes on the source page. If a donor loses its position, gets hit by filters, or is deleted, the weight it transfers also decreases. Another case is getting links from irrelevant or low-quality websites. Such links may not only fail to bring weight, but also reduce the overall credibility of the page. Thematic relevance and credibility of donors remain key.
Link weight is a key indicator that directly affects the visibility of a business in search. The higher the link strength, the higher the chances that the page will get better rankings and drive organic traffic without additional advertising costs. Understanding the mechanism of weight transfer and regular analysis of the link profile help to increase the authority of key pages in a targeted manner. And competent internal linking and obtaining high-quality external links strengthen the position of the resource, reduce the time to reach the TOP and ensure a steady flow of potential customers.





 06/01/2026
06/01/2026  983
983


