Content of the article


Longread is not a format for the sake of format. For businesses, it’s a tool for positioning, funneling, and trust. A well-written long-form article does not scare the reader away, but leads them from the problem to the solution, increases the company’s expertise, and works for SEO. In this article, we will analyze what a longread is, why a business needs it, what types there are, how to prepare and promote such texts, and where to avoid common mistakes.
What is a longread and when should you make one?
A longread is a detailed material that provides an in-depth disclosure of a topic: analytics, case studies, instructions, interviews, or combined content. The main thing is not the volume itself, but the value: a longread should answer complex questions of the reader.
For business, longreads are justified when the topic requires context and argumentation. That is, when a short post is not enough to build trust or make a decision.
Longreads bring business results when written with a clear purpose.

- To show expertise.
In-depth material demonstrates not only knowledge, but also the company’s thought process: the methodology, approaches, and techniques you use in practice. The client sees not abstract promises, but an evidence base – data, arguments, and real cases. This increases trust and makes the brand a natural choice in a competitive environment.
- Increase traffic and improve SEO.
Longreads cover a wide pool of related key phrases and answer complex information requests. Such materials rank better for long-tail queries, keep users on the page longer, and increase the number of internal links. The result is stable organic traffic growth and a lower cost per lead over time.
- Make leads «warmer».
When a reader spends time with detailed material, they get context and understand your approach. This shortens the decision-making cycle: the potential client comes already informed – with clearer expectations and questions that are much easier to translate into a commercial conversation.
- Increase content for marketing.
One longread is a source for dozens of micro-contents: quotes, visuals, social media carousels, excerpts for email newsletters and presentations. Such a content pool saves resources and ensures consistent brand communication across different channels.
- To support sales.
The longread serves as an argumentative guide for the sales team: it contains figures, implementation examples, profitability calculations, and answers to common objections. By using the longread in negotiations, managers build trust and move to a deal faster.
So, longreads are an investment in the long-term value of a brand. Strategically planned and executed material returns the investment through increased expertise, organic traffic, and better lead-to-customer conversion.
Types of longreads
There are several working types of materials, each of which solves a specific business problem. When choosing a format, be guided by your goal: positioning, lead generation, sales support, or SEO growth. Let’s analyze each type, when to use it, what blocks to include, and what results to expect.
Analytical research
An analytical longread is suitable when you have data or insights that should be systematized and presented to the market in a reasoned manner. Such material works to position the company as an opinion leader: it demonstrates a deep understanding of trends, data collection methodology, and business conclusions that can be immediately used in decisions. To be as useful as possible, an article should contain the following elements
- methodology;
- visualizations (graphs or charts);
- interpretation of figures;
- practical recommendations;
- key conclusions.
Invest in high-quality visualizations and a thoughtful introduction to increase credibility and build citations and backlinks.
Step-by-step guides (How-to texts)
A step-by-step guide is intended for a reader who is looking for specific actions: from setting up a process to implementing a solution. Such a longread should be practical, with executable steps and materials that the reader can take and apply. This is a high-intent format, meaning it brings in targeted users and increases conversion. Recommended basic structure:
- an introduction with an objective;
- a list of expected results;
- step-by-step instructions;
- checklist or templates;
- common mistakes.
Adding ready-made templates or short tools will significantly increase the practical value of the guide.
Case studies
A case study is a story about a real result: the client’s context, the solution applied, and the quantitative effects. For B2B sales, this is one of the most convincing formats because a case study with specific metrics reduces doubts and speeds up decision-making. For a case study to be effective in sales, you should include the following blocks
- context and client goals;
- approach and solution;
- KPIs before/after;
- experience gained;
- customer feedback.
Do not forget about visual evidence (such as graphs or screens) and the client’s official permission to publish.
Interviews and reports
Interviews provide a voice for the industry: expert opinions make the material authentic and help expand the discussion around the brand. Reports are useful when you need to show an event, trend, or practice «from the field.» The interview format works well in combination with a summary – the reader gets both the expert’s opinion and the author’s own conclusions.
The main components of a quality interview:
- a brief introduction;
- introduction of the expert;
- Q&A or thematic blocks»
- highlighted quotes;
- summary insights.
Prepare questions in advance, but leave room for unexpected thoughts. They often provide value.
Combined longreads
The combined format combines data, a case study, and practical steps in one material. This approach is suitable for complex topics that require context, evidence, and implementation instructions. The combined longread is useful because simultaneously meets the needs of different audiences: analysts, practitioners, and managers, as long as you clearly mark the structure. Recommended set of blocks:
- a brief synthesis;
- a block with data and/or trends;
- a case study with results;
- practical how-to section;
- final action plan.
Label sections and add «quick navigation» links at the top. This will help different readers find the right part quickly.
The choice of format should be based on your business goal, resources, and audience type. The main thing is a clear structure and a well-thought-out promotion plan: without this, even the best longread will not realize its potential.
How to prepare a high-quality longread: a step-by-step plan
Work on a longread begins long before it is written. It’s not just a big text, but a well-thought-out information product that has to fulfill a specific business function. To make the material work, you need a systematic approach:
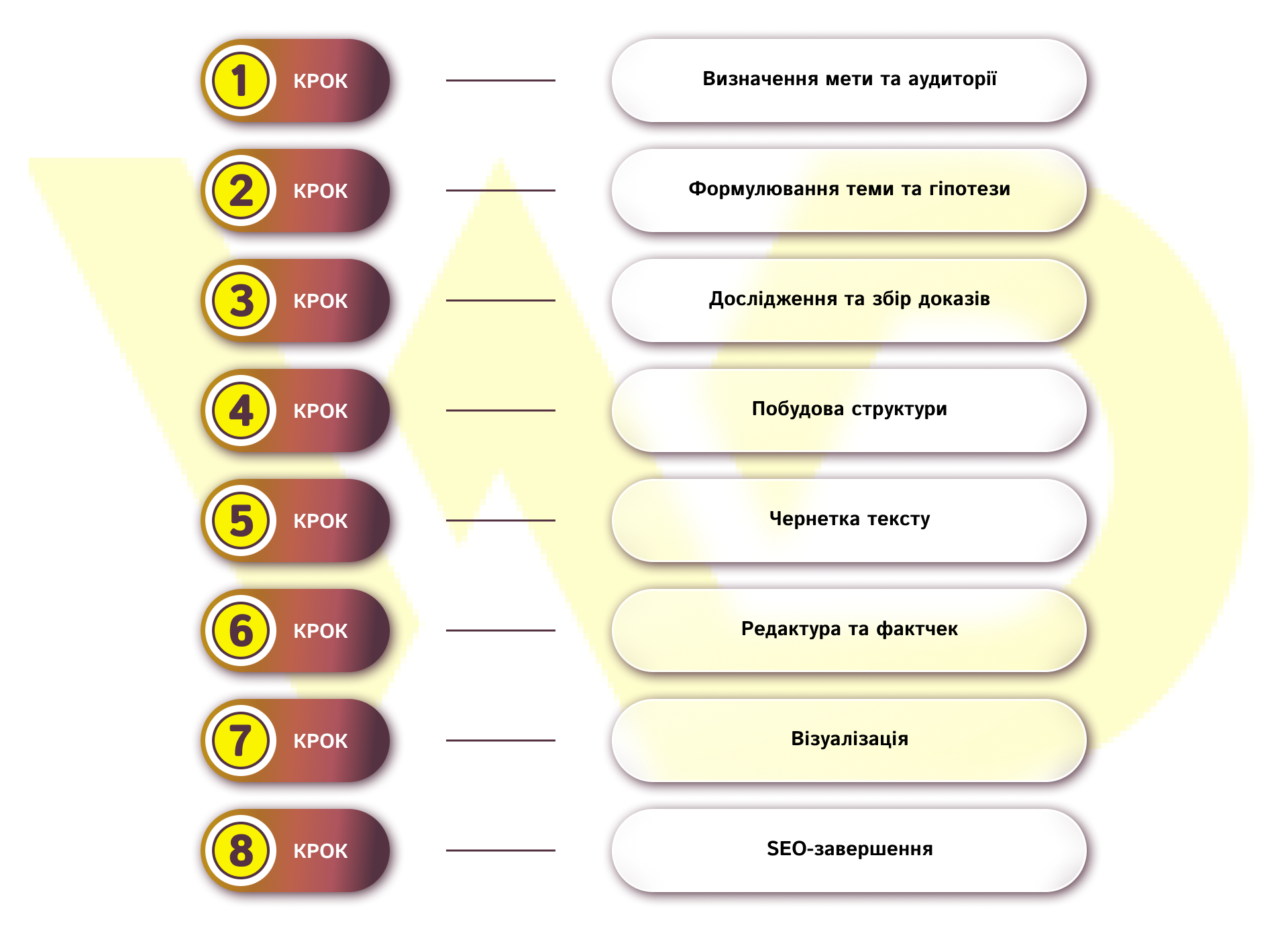
STEP 1: Define the goal and audience
Before setting the topic, you need to clearly understand who the reader will be and what decision you want to encourage them to make: leave a contact, subscribe, consider a purchase, or dive deeper into the product. It is this intention that determines the tone, format, and depth of disclosure.
STEP 2. Formulate the topic and hypothesis
Choose one clear angle and formulate a hypothesis – a thesis that you will prove with the material. It keeps the focus and protects the text from unnecessary branches. The hypothesis answers the question: «What will the reader learn from this material?»
STEP 3. Research and gathering evidence
This stage is the foundation of trust. You collect internal data (your own cases, statistics, unique insights), external sources (research, market trends, authoritative assessments), and expert opinions. The stronger the evidence block, the higher the chance of maintaining attention to the end of the text.
STEP 4. Building the structure
A longread should be structured: the logic of moving from the problem to the solution should be transparent even when skimming through it.
Introduction → context → arguments → examples → conclusions/practical part.
At this stage, think about subheadings, transitions between sections, and places where visual blocks will be appropriate.
STEP 5. First draft (draft text)
The first version of the text is written not for «perfection» but for content and logical cohesion. It is important to keep the rhythm of reading: short paragraphs, clear wording, change of pace through examples, quotes, blocks with conclusions. The longread should lead the reader, not force them to go back to understand the meaning.
STEP 6. Editing and fact-checking
When the framework is ready, the text needs to be cleared of unnecessary things, the wording needs to be clarified, sources and figures need to be checked. At this stage, the logic is also tested: whether all the statements are proved, whether there are no missed transitions.
STEP 7. Visualization
A good longread always contains visual support: infographics, process maps, comparative blocks, case screens, highlighted quotes. This is not a «decor» but a way to reduce cognitive load and keep attention.
STEP 8. SEO completion
The final touch is to prepare the text for long-term life: correct headings, search intent reinforced by subheadings, internal links, meta description, convenient URLs, and markup. Thanks to this, the longread continues to work as a source of traffic for months and even years after publication.
Consistent implementation of each stage ensures not just the publication of the text, but the creation of a tool that brings the audience, keeps attention, and pushes them to action. Therefore, the quality of a longread is not born at the moment of writing – it is built step by step even before the first paragraph appears.
Useful tools for working with longreads
A high-quality longread cannot be based on a clear plan, so it’s important to think about a working tool stack right away. In practice, business teams use four groups of tools – and each is responsible for its own stage of work:
|
Stage |
What is it for |
Examples of tools |
What it does |
|
Researching the topic |
Analysis of user intent and search demand |
Google Trends, Also Asked, Ahrefs, SEMrush |
A clear understanding of what exactly «hurts» the target audience and what issues need to be addressed |
|
Writing and collaboration |
Drafting, comments, approval |
Notion, Google Docs |
Transparent editing process, saving time on task transfer |
|
Visualization |
Infographics, flowcharts, graphs, quotes |
Figma, Canva, Miro |
Ease of perception, greater depth of reading |
|
Publication and SEO analytics |
Optimization, internal links, metrics |
WordPress + RankMath, Yoast, Webflow, GA4, Search Console |
Long-term search visibility and data for further improvement |
It’s important to remember that tools don’t replace content, but they do ensure consistent quality and reproducibility of the result. Thanks to this, longreads cease to be «one-off projects» and become a scalable format in the content strategy.
How to ensure the reach and long-term return on longreads
Publishing is only the first step. For a longread to work for a long time, you need systematic promotion and support after the launch.
- Distribution plan.
Start with the basic coverage: email newsletters, series of posts on social media, native promotional platforms, and targeted advertising for key segments. This creates the first «wave» of engagement and helps the audience discover the material.
- Internal links.
Link the longread to other pages on the site (case studies, blogs, services). This way, you increase the time spent on the site, improve SEO, and strengthen the position of the main material through internal linking.
- Content remarketing.
Create a «content ecosystem» out of longreads: short excerpts for social media, infographics, visual quotes, carousels, short videos, or digests. This provides a steady flow of traffic from various channels and increases the longevity of the material.
- Support from sales and PR.
The sales team can use the longread as an authoritative proof of expertise in negotiations. And the PR team can use it as a reason for expert mentions in specialized media or participation in discussions.
- Analytics and optimization.
Keep track of key signals: time on page, bounce rate, traffic sources, viewership, conversions. If the data sags, test the headline, introduction, visuals, or CTA. Timely edits strengthen the material without re-development.
Longread is a tool that works for trust, traffic, and sales, but only if it is created systematically and receives regular attention after publication. When you start with the goal and audience, keep the focus on the main idea, support your conclusions with data, case studies, and provide thoughtful promotions, longreads cease to be just text – they become a business asset that consistently brings results in the long run.






 16/12/2025
16/12/2025  1183
1183



