Content of the article

Regular SEO audits allow you to control the visibility of your website in search engines.
An SEO audit can reveal technical issues such as broken links, duplicate content, poor site structure, and other issues that can negatively impact search engine rankings. An SEO audit usually covers areas such as:
- Indexing and accessibility for search engines
- User Experience
- Site architecture
- Comparison with competitors
- Keyword Research
- Page SEO
- Backlink Profile
This is essentially a general “health check” of the website.
SEO Audit Tools
We suggest using various tools to check elements on a page, such as title tags, meta descriptions, title tags, and keyword usage:
Google Structured Data Testing Tool
Ahrefs (or Ahrefs Webmaster Tools)
Screaming Frog SEO Spider
Let’s take a closer look at how to conduct an SEO audit using these tools.
Check for indexing problems
Pages that are not indexed are not in Google’s database, so Google cannot rank them.
To see if your pages are indexed, check for issues directly in Google Search Console.
Highlight the Pages report under Index in the left menu. Here you can see a graph of all pages based on their indexing status.
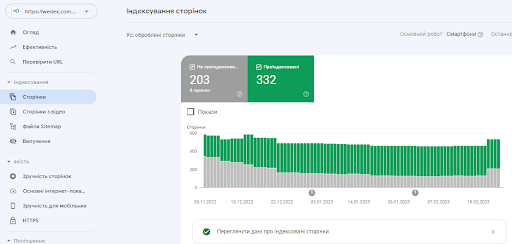
Below you will see a list of reasons why pages were not indexed.
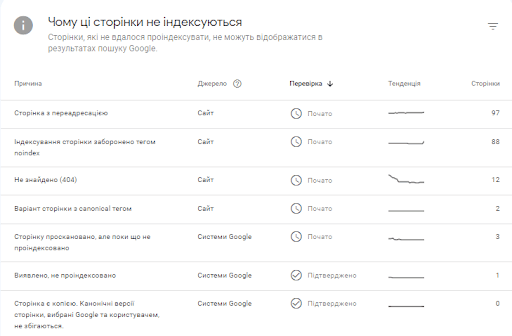
Go through each of the above reasons one by one. Check out the pages that fall under these reasons.
Remember that not all pages need to be indexed, only the ones you want to rank high in the SERPs. Therefore, it is quite normal if some URLs are not indexed. Here are some examples of URLs that do not need to be indexed:
- Pages with redirects
- Admin Pages
- Alternate pages with canonical tags
- News feed pages
If you find a page that should be indexed but isn’t, follow Google’s instructions to fix it. Then click the “Confirm Fix” button.
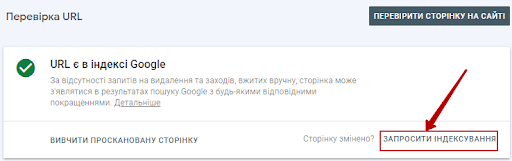
Alternatively, you can simply grab a specific URL and enter it into the top search bar in the Google Search Console toolbar.
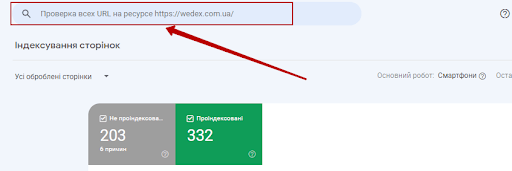
You will see the URL status. You can also ask Google to index the URL by clicking the “Invite Indexing” link.
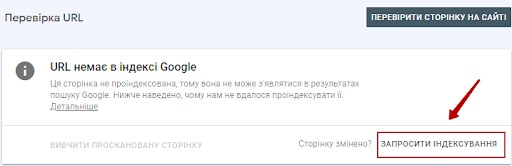
If you have changed the page significantly, you can resubmit your index request. Even if the page is already indexed.
Check for duplicate versions of your site
It’s important to make sure Google only indexes one version of your site.
Your site may be hosted on different versions of the URL (depending on whether the domain is WWW and whether your site uses HTTPS).
For a search engine, these are all different versions of the site:
If your site is running on more than one of these URL versions, this can cause a lot of crawling, indexing and ranking problems because Google will treat them as duplicates. Additionally, having multiple versions of your site can dilute PageRank, which can also have a negative impact on your ranking.
You can check this very simply by entering all versions of your site in your web browser. You should be automatically redirected to the desired version. For example, if your desired version of the URL is https://wedex.com.ua, you should be redirected to it if you enter any other version in the browser.
If you can access your site through different versions, use a 301 redirect for other versions.
Checking manual measures
If your site violates Google’s spam policy, Google may take manual action against it.
In practice, a manual action means that your site’s ranking will decline until Google reverses the action. This action can be either at the page level or at the level of the entire site.
Some reasons why you might have received a manual action include the following:
- Keyword overload
- Unnatural links (both to and from your site)
- Different types of spam
- Thin content with little or no added value
You can check if you have received manual actions in Google Search Console. At the bottom of the left side menu, you will see a “Security and Manual Actions” section, and in it there is a “Manual Actions” link.
Click on it and you will be taken to a page where you will see the status.
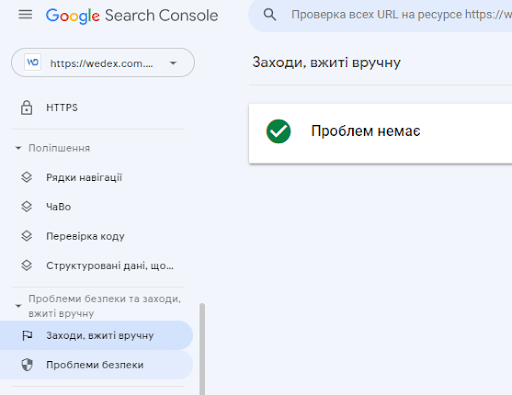
Hopefully you’ll see a green check mark, which means no problems were found.
If your site has been subject to manual actions, you will need to correct the issues and request a re-review. For more information check out manual “Manual Actions” from Google.
For example, if you receive a manual action as a result of buying backlinks (“Unnatural links to your site”), you need to get rid of those links by contacting the webmasters or opting out.
Check for mobile responsiveness issues
We live in a mobile-first world, and if your site isn’t mobile responsive, there’s a good chance you’re not putting user experience first.
Mobile-friendliness is one of the main Page Experience signals for Google. In fact, it’s ranking factor since 2015. This means it can have a direct impact on your search rankings.
You can check for issues in the Mobile Experience report in Google Search Console. Just click “Mobile Friendly” under “Quality” in the left menu.
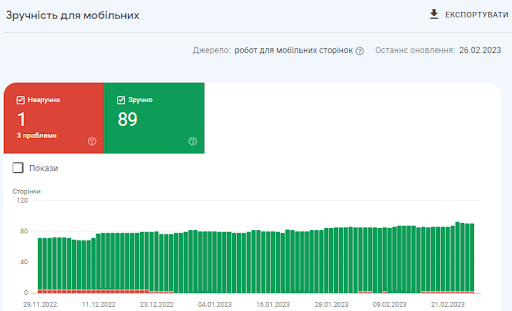
Here you will find a quick overview of the usability of your pages over time:
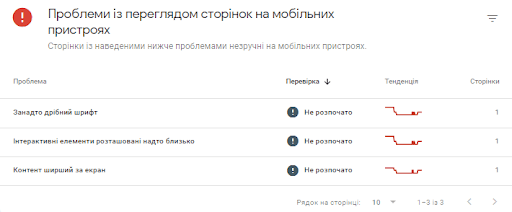
The report will list all mobility-related issues.
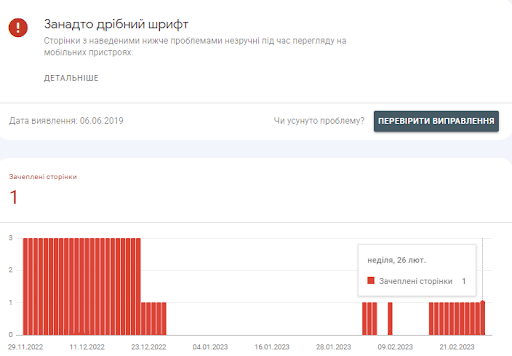
You can expand each issue to see all relevant pages.
After you fix it according to the instructions in the Google Search Console Help Center, you can confirm the fix to ensure that Google has re-verified the page and confirmed that the issue has been resolved.
Check page loading speed
Page speed has been a small ranking factor on desktop devices since 2010, and on mobile devices since 2018. However, there is no official page load speed threshold, but there are a large number of metrics that you can use as a proxy.
For example, a tool Google PageSpeed Insights shows all types of indicators:
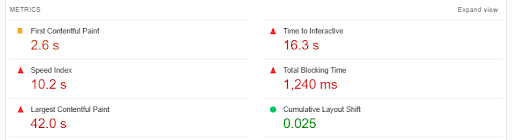
The downside of this tool is that you can only test one page at a time.
You can check your page speed metrics in the Key Internet Metrics report in Google Search Console:
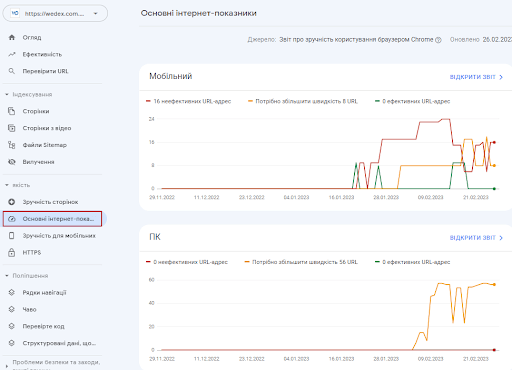
The downside of this tool is that you can only test one page at a time. You can check your page speed metrics in the Key Internet Metrics report in Google Search Console:
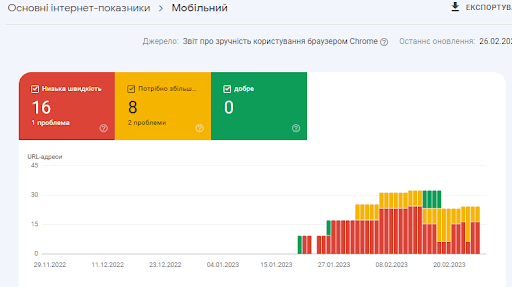
where there is information about the metrics that Google Search Console takes into account:
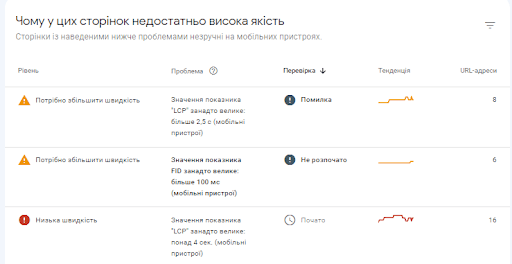
and problems that Google recommends fixing – working on improving page speed.

Check your organic traffic
Organic traffic is visitors who land on your site by clicking on unpaid (“organic”) search results. This is one of the most important indicators of your website’s success when it comes to SEO.
To see your organic traffic, go to Google Search Console and open the Search Results report under Performance in the menu.
There are four main metrics in the report. The most interesting metric in this context will be the “Total number of clicks” – how many times a user went to your site during a specified period of time.
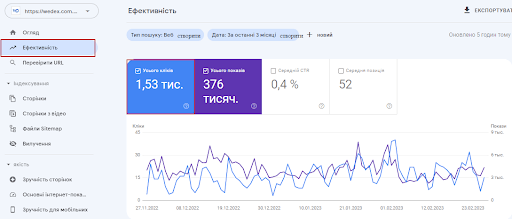
There are many ways to customize your report to see the data you need. For example, you can view results by query, page, device, and country:
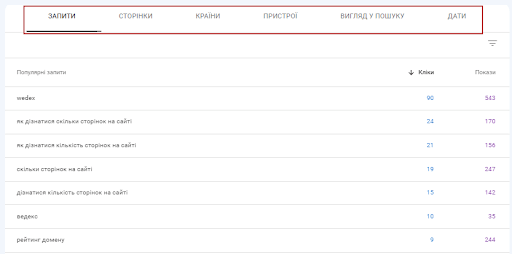
These reports will give you a lot of useful information about the organic traffic to your site. They will also help you set benchmarks and track your progress.
Comparison with competitors
A good SEO audit should also help you see where you stand compared to your competitors. To compare the performance of your site and competitors, you can use services such as Ahrefs, Serpsat or Similarweb.
The tools give you a comparison of key metrics across selected domains. This will give you a good idea of where you are falling behind and where you are outperforming your competitors. To get the best overview, focus on these metrics:
- Service Authority Rating: Shows the overall quality of a domain on a scale of 1 to 100 (based on its backlinks, search traffic and other factors)
- Organic Traffic: Shows how much organic traffic a domain receives
- Organic Keywords: Shows how many keywords a domain is ranking for
- Referring Domains: Shows how many different domains are linking to the domain being analyzed (this gives a better picture for comparison than the total number of backlinks).
Identify Content Gaps
Content gaps are topics that users are looking for information about that are not covered on your site. Filling content gaps provides a better experience and helps increase organic traffic.
You can detect gaps in content like this:
- Looking at content rankings: Your keywords may be ranking, but not as high as you’d like. Start with the basics: make sure the SEO fundamentals are in place and improve content where possible.
- Keyword Research: Your first step is to see what works, so check out high-performing keywords. Pay special attention to long-tail keywords as they often have lower competition, and also pay attention to related keywords.
- Competitor Analysis: What keywords are your competitors ranking for? Use them as inspiration for new theme ideas.
To speed up the process, you can automate it using a tool like Ahrefs.
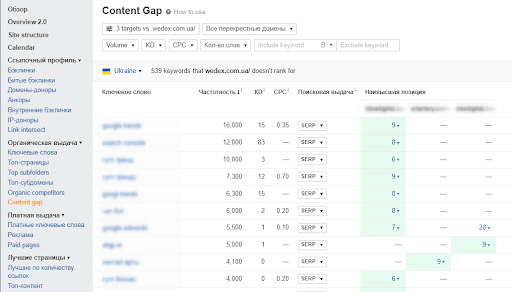
Enter your URL and the tool will show you which keywords your site is not ranking for. Ahrefs also allows you to find subtopics.
To summarize
It doesn’t matter how great your website looks – if it’s not performing at its optimal level, it won’t attract the visitors, leads, or conversions it needs to thrive.
A detailed SEO audit allows you to find and correct any potential problems, and provides the information you need to improve your site’s performance, rankings and visibility.
Although SEO may seem complicated, it has a powerful effect on your traffic. Many tools such as Serpstat, Ahrefs and Screaming Frog can help you get your site back on track.
Do you conduct regular SEO audits of your website? What are your favorite tools and strategies?







 19/04/2023
19/04/2023  3490
3490


