Content of the article
- /01 What is Google Search Console (GSC)?
- /02 How to get started with GSC?
- /03 How to prove ownership
- /04 How to add a sitemap to GSC?
- /05 Setting up users, owners and permissions
- /06 Indicators and metrics
- /07 Troubleshooting with GSC
- /08 Problems with indexing
- /09 Performance issues
- /10 Security issues and manual sanctions
- /11 5 Ways to Use GSC for SEO
- /12 To summarize

Google Search Console is an indispensable tool for SEO because it provides data on the organic performance of a site or page. Understanding how users search for products and services, measuring your site’s performance in search engines, and getting recommendations for improvements are essential for SEO. Originally known as Google Webmaster Tools, Google Search Console is an SEO tool that most SEO specialists use to obtain data on the performance and technical condition of the site.
What is Google Search Console (GSC)?
Google Search Console, also known as GSC, is a free service from Google that allows site owners to monitor the overall health and performance of their sites using data directly from Google.
Among many aspects, the GSC provides several valuable reports, including:
- impressions and clicks;
- indexing;
- link;
- manual sanctions;
- Core Web Vitals (CWV).
GSC also allows site owners to perform actions related to their sites, such as:
- Submitting a sitemap.
- Removing URLs from the index.
- Checking URLs for indexing issues.
In addition, GSC regularly sends email updates to verified owners and users indicating any scan errors, accessibility issues, or performance issues. Although data for GSC has been extended from 3 to 16 months, it only starts to be collected after you confirm your ownership of the site.
How to get started with GSC?
To get started with Google Search Console, you’ll need a work Google account – such as a Gmail account or email associated with Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) for business – and you’ll need to be able to add code to your website or update domain name servers at your hosting provider.
In this section, we will cover the following steps:
- How to confirm site ownership in GSC.
- How to add a sitemap to GSC.
- Setting up owners, users and permissions.
- Indicators and metrics.
How to prove ownership
Because the data provided and the processes available in GSC can be quite valuable to your competitors, Google requires site owners to take one of several available steps to prove ownership.
- Go to the Google Search Console page.
- Click Add Resource.
- Select the type of property you want to verify.
It’s important to stop here and discuss the two different types of properties you can confirm with GSC: Domain and URL Prefix.
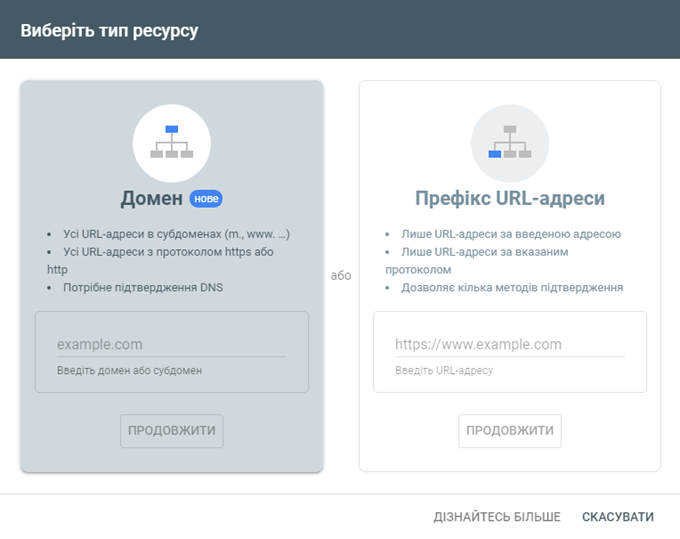
Domain
If you are verifying your domain with GSC for the first time, you should choose this ownership type because it will set verification for all subdomains, SSL templates (http:// or https://), and subfolders on your site.
There are two types of confirmations for this property type: TXT and CNAME. Both will require you or your programmer to have access to modify your site’s Domain Name System (DNS) records.
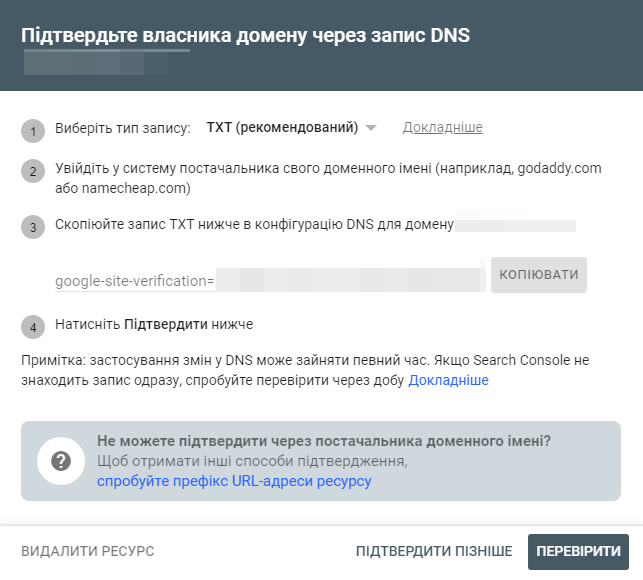
To verify using TXT (preferred method):
- Copy the text in the TXT record field.
- Create a new DNS record for your domain (usually from your hosting provider) with the TXT type set.
- Paste the TXT confirmation text from GSC into the entry field.
- Save the entry.
- Wait for the DNS record to update.
- Click Confirm in GSC to confirm that you have added a TXT record to your DNS.
- Since this change can take a few minutes to several days to register, you can click Verify Later if the change is not immediately verified.
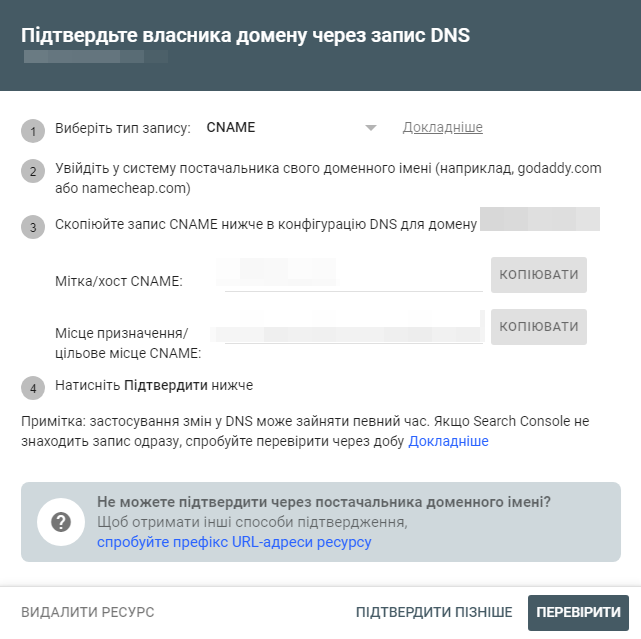
To verify using a CNAME:
- Copy the CNAME label and paste it into the “Name” field of the new CNAME record in your site’s DNS configuration.
- Copy the contents of the “Destination/Target” CNAME into the entry field in your DNS configuration.
- Save the entry.
- Wait for the DNS record to update.
- Click “Confirm” in GSC to confirm that you have added the CNAME record to your DNS.
- Because this change may take several minutes to several days to replicate, you can click Verify Later if the change is not immediately verified.
More details in the video from Google:
DNS record for site ownership verification – Google Search Console Training
After you verify your domain, you can verify additional properties for that domain using the URL Prefix property type.
URL prefix
This validation method is used when you cannot access your domain’s DNS records, or when you want to validate specific URL paths within an existing domain validation.
URL Prefix Verification allows you to verify:
- http:// and https:// separately (unless you’ve canonicalized your URLs).
- Subdomains such as m.domain.com or community.domain.com.
- Subdirectories such as www.domain.com/products or www.domain.com/articles.
- Any prefix with a set of URLs that match this pattern.
Note that this validation method will provide data that will only apply to the specified prefix.
While smaller websites may only need a single verification, larger sites may want to track site health and metrics for subdomains and subdirectories individually to get a more complete set of data.
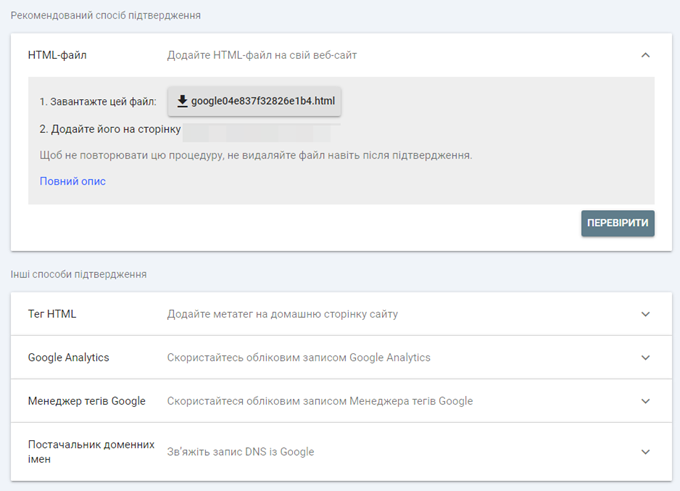
GSC offers five options for verifying your site or divisions using this method:
- HTML page – this method allows you to upload the .html file directly to the root directory of your site using a free FTP client or your hosting platform’s cPanel file manager.
- HTML tag – by adding the provided HTML tag to the <head> section of your home page, you validate your site. Many CMS platforms like WordPress and Wix allow you to add this tag through their interfaces.
- Google Analytics – if you have already verified your site in Google Analytics, you can use this verification to add your site to GSC.
- Google Tag Manager – similarly, if you already use the system Google Tag Manager, you can validate your site using the tags you’ve already set up.
- DNS configuration – if you have already verified your site using the TXT or CNAME methods described above, you can verify your site’s subdivisions using this verification method. Use this method to validate subdomains or subdirectories.
These verification methods can take anywhere from a few minutes to several days to sign up, so if you need to click the “Verify Later” button and come back later, you can find that site or segment under “Not Verified” under your account properties.
How to add a sitemap to GSC?
While Googlebot will likely find your XML sitemap over time, you can speed up the process by adding your sitemaps directly to GSC.
To add a sitemap to GSC, follow these steps:
- Go to the sitemap you want to add and copy the URL. The syntax of most XML sitemaps looks like this: https://www.domain.com/sitemap.xml. Sitemaps automatically generated by content management systems such as WordPress can have the following syntax: https://www.domain.com/sitemap_index.xml.
- In GSC, click on Sitemaps in the left column.
- Add your sitemap URL in the Add New Sitemap box at the top of the page and click Submit.
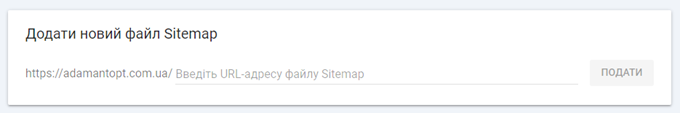
Note that you can add as many sitemaps as your site needs. Many sites have separate sitemaps for videos, articles, product pages, and images.
An added benefit of including your sitemaps in this interface is that you can compare the number of pages your site has submitted to Google with the number of pages indexed.
To see this comparison, click on the three vertical dots to the right of your sitemap and select View Page Indexing.
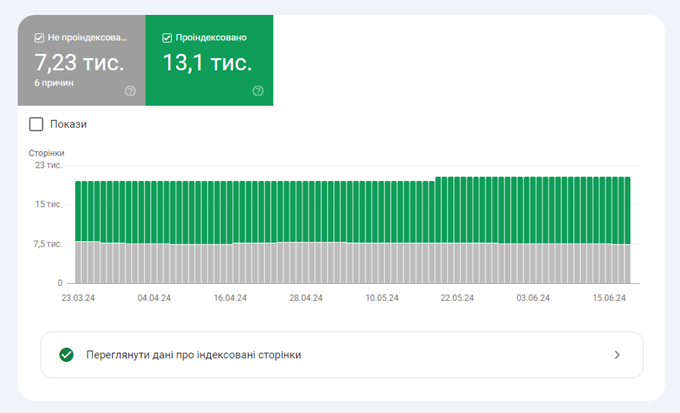
The next page will display the number of indexed pages (in green) and pages that are “not indexed” (in gray), along with a list of reasons why those pages were not indexed.
Setting up users, owners and permissions
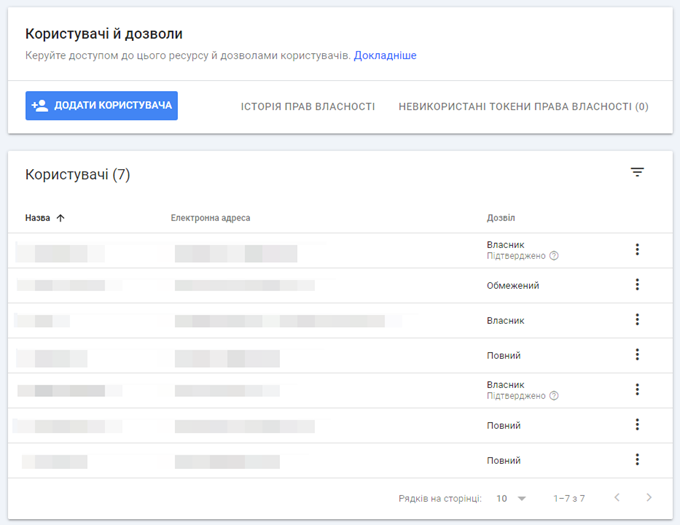
It is important to control who has access to data and functions in GSC. Some features, such as removal tools, can be very dangerous in the wrong hands.
Permission settings associated with user types restrict access to these parts of the GSC.
- Owner. There are two types of owners: a user who has verified their ownership through one of the verification steps above, or someone to whom the owner has delegated ownership. This user level has full control over the property until it is completely removed from GSC. To configure Google Indexing API exactly this form of ownership is needed.
- Full access. This type of user has access to almost all functions of the owner. However, if a user with full access deletes a property, they only delete it from their site list, not from GSC entirely.
- Limited access. This user can only view data in GSC. He cannot make any changes to the account.
It is important to note that Google recently increased the security of Search Console by introducing a new feature to manage ownership tokens under Settings – Users & Permissions – Unused Property Tokens.
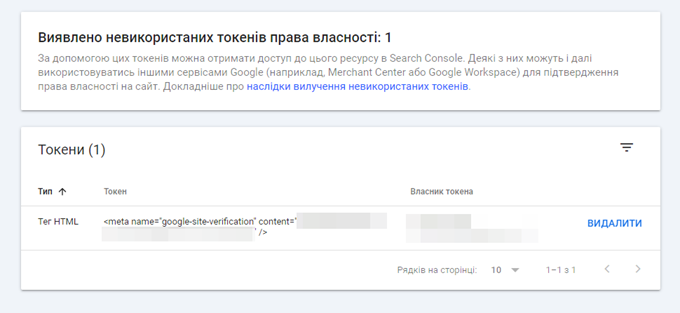
Tokens are those unique codes in HTML tags that you set in the <head> section, HTML files that you upload, or DNS TXT record values that you set when validating your website.
Imagine a situation where a website had multiple verified owners using an HTML tag download, and one of them left the company. If you delete that user from the search console, the problem is that the person can still regain access to the search console if you don’t delete their token from the unused property tokens page. This is an important feature, as website owners can now remove obsolete validation tokens to prevent unauthorized access by former owners.
Indicators and metrics
In Google Search Console, data is divided into indicators and metrics. You can use this data in reports to measure your site’s performance, from page indexing to ranking and traffic.
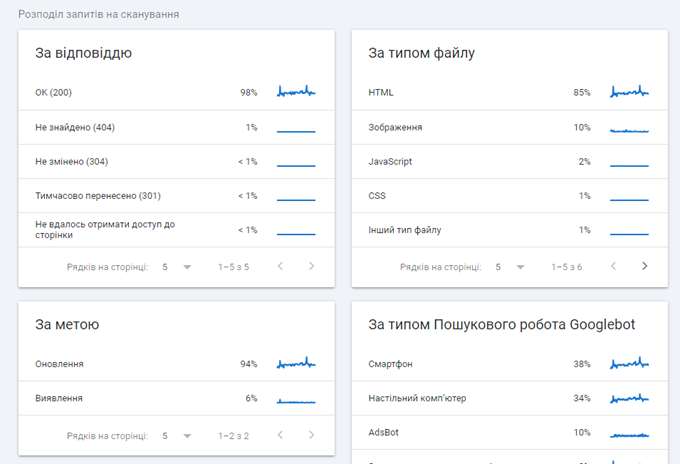
In the performance report, metrics group data into meaningful segments such as pages, queries, countries, and devices. Metrics include data such as impressions and clicks.
In the page report, the indicator will be the reasons why the pages were not indexed, while the metrics will include the number of pages that were affected.
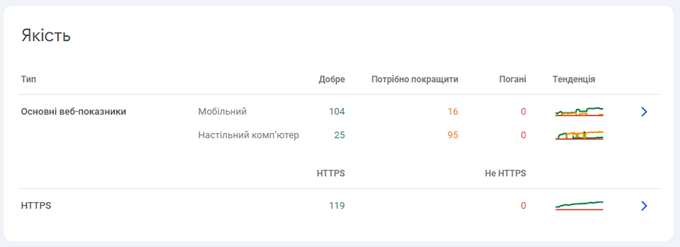
For Core Web Vitals, the metrics will be Poor, Needs Improvement, and Good. Metrics will include the number of pages that fall into each category.
Troubleshooting with GSC
GSC is a valuable tool for SEO professionals because it allows you to diagnose and rank pages from Google’s perspective. From indexing to page user experience, GSC offers a variety of tools to troubleshoot your site.
Scanning problems
Before a page can rank in search engines, it must be crawled and then indexed. A page must be open to indexing in order to be evaluated for search.
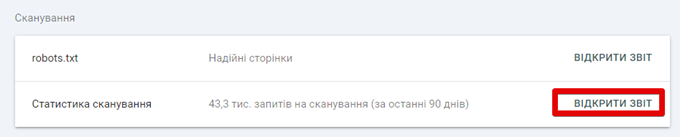
Whether you’re having trouble scanning or not, it’s a good idea to regularly check the Scan Statistics report in GSC. This report will let you know if there are any problems with:
- By uploading your robots.txt files.
- Your site’s DNS (Domain Name System) solution.
- By connecting to your servers.
To use this report:
- Click “Settings” in the left column of GSC.
- Click “Open Report” next to “Scan Statistics” in the “Scan” section of the settings page.
- Check the Hosts section of the page to see if your subdomains are having problems.
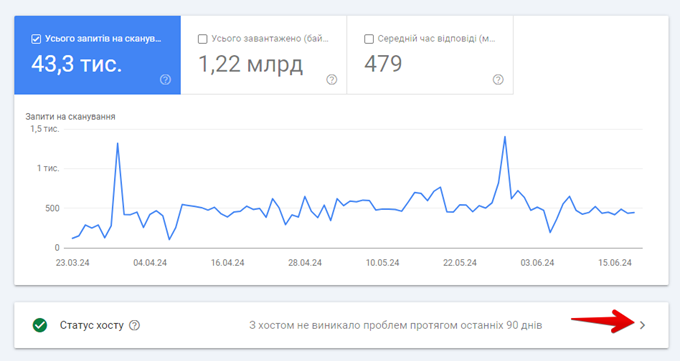
- If your host has had problems in the past, you will see a failure report.
- If there are any pages with 404 response codes, click Not Found to view those pages.
These steps will help you understand and fix crawling issues with your site, which is an important step in improving your site’s performance in search engines.
Problems with indexing
If your pages aren’t indexed, they can’t rank for your most important queries. There are several ways to see which pages on your site are not indexed by GSC.
The first place you can visit is the Page Report located in the left column of the GSC.
While you can get a lot of information about the pages on your site that are and aren’t indexed, this report can be a bit misleading.
The “Not Indexed” section of the report includes pages you may not have intentionally indexed, such as tag pages on your blog or pages you want to keep for logged-in users.
The best report to determine the true extent of your site’s indexing problems is in the “Files Sitemap“.
To get there:
- Click on Sitemaps in the left column of GSC.
- Click on the three vertical dots next to your site’s main sitemap.
- Select View page indexing.

This report is similar to the page report, but it focuses on the pages your site deems important enough to include in the sitemaps you’ve submitted to Google.
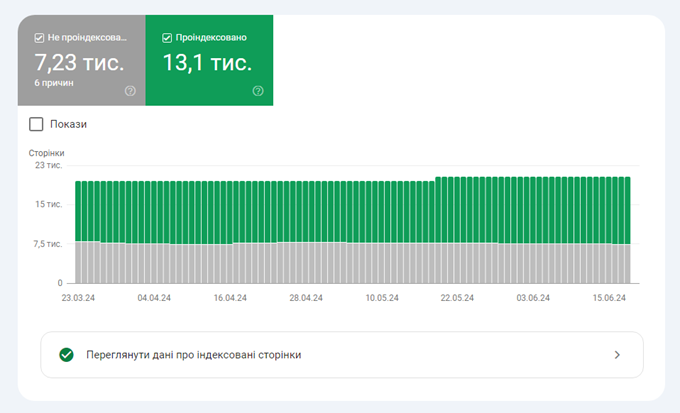
From here, you can view the Reasons columns in the Why pages are not indexed table.
For example, you may have several pages that have been crawled but are not currently being indexed. To rate one of these pages, do the following:
- Click on the row “Scanned – not currently indexed” to see a list of pages.
- Hover over one of the listed pages until three icons appear after the URL.
- Click on the “Verify URL” icon.
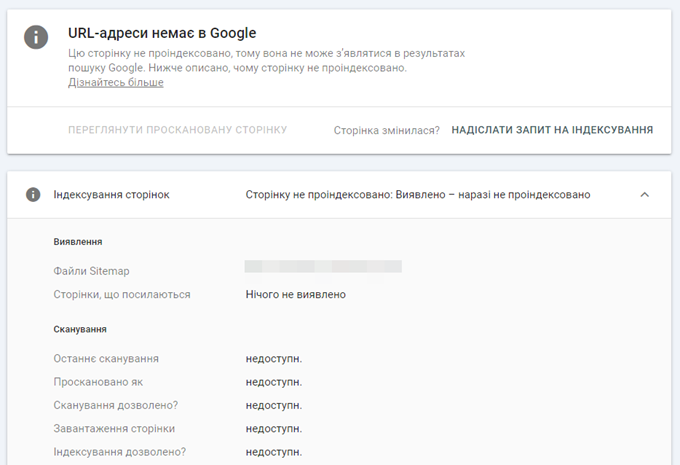
- On this page, you can manually request indexing.
- You can also click the “Verify Published URL” button on the right side of the page.
- The resulting page will show whether your page is available to Google.
- To view the test results for a page, click View Scanned Page.
The resulting pop-up window shows the HTML collected from the page, a rendering of the page on a smartphone, and “More Information” about the page, including any problems with the page’s resources or JavaScript console errors.
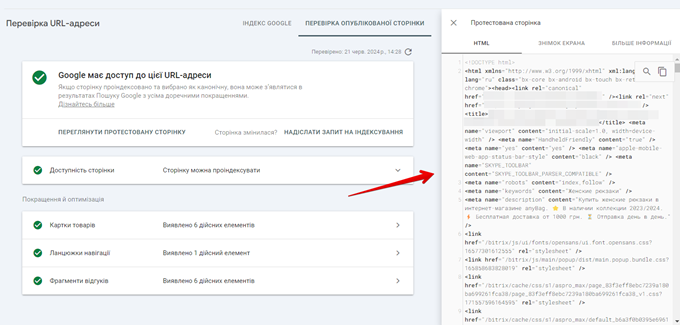
The HTML displayed in the validation tool shows that Googlebot could crawl and render, which is especially important for JavaScript-based sites where the content does not initially exist in static HTML, but is loaded via JavaScript (via REST API or AJAX). By checking the HTML, you can determine whether Googlebot was able to see your content correctly. If your content is missing, it means that Google has not been able to crawl your webpage effectively, which can negatively affect your rankings.
In the “Screenshot” tab, you can see how Google visually sees your page:
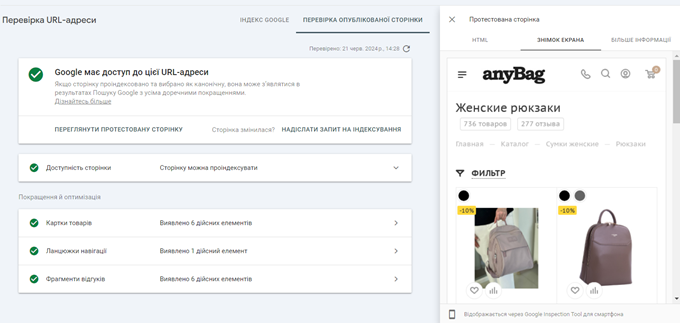
By checking the More Info tab, you can determine if Googlebot failed to load certain resources. For example, you can block certain JavaScript files that are responsible for loading content via robots.txt. If everything looks fine, click “Submit Indexing Request” on the URL Inspection main page. The box at the top of every page in GSC allows you to check any URL on your verified domain.
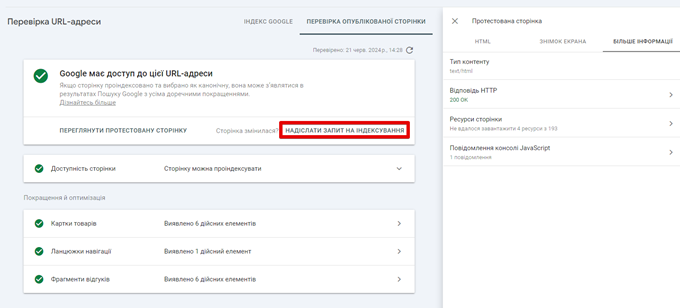
I also recommend making sure that Google has no problems crawling robots.txt under Settings – robots.txt. If you have a robots.txt and Google can’t load it (for example, because it’s blocked by a firewall), then Google will temporarily stop crawling your site for 12 hours. If the problem is not fixed, Google will act as if the robots.txt file does not exist.
Performance issues
If you’re having trouble indexing your pages in Google or ranking in search engines, it’s worth looking at your site’s Core Web Vitals (CWV). These are indicators of how your site performs for real users, using data from the Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX).
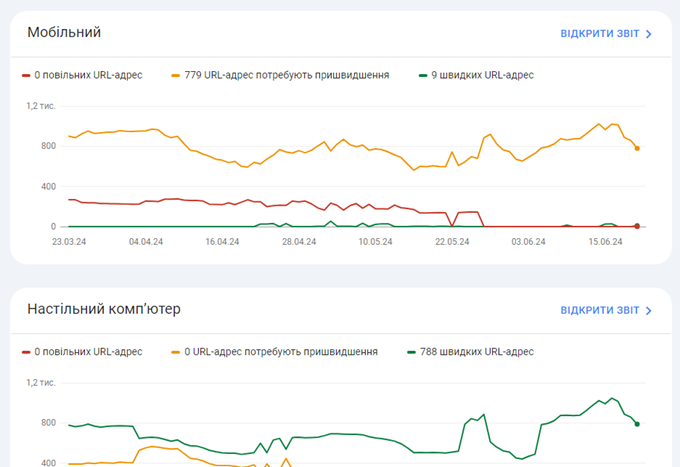
CWV measures three main usability indicators:
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures how much the position of elements on a page change as it loads. If the images shuffle and shift the text on your page when loading, it can lead to a poor user experience.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP), which replaced First Input Delay (FID), measures how long it takes for a page to respond after a user scrolls, clicks, or performs any action that loads additional content.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures how long it takes for the largest portion of content on your page to be fully rendered to the user.
GSC provides scores for both mobile and desktop, and pages are classified as Good, Needs Improvement, or Poor based on CWV scores.
To see issues with your pages:
- Click on “Basic Web Metrics” in the left column of GSC.
- Click “Open Report” in the Mobile or Desktop graphs.
- Click on one of the items in the “Why URLs are not considered good” table.
- Click on “URLs”.
- Click on the three vertical dots next to one of the application URLs in the pop-up window.
- Click on “Developer Resources – PageSpeed Insights”.
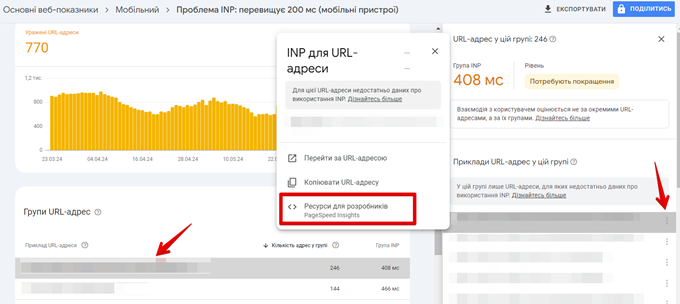
The resulting page will allow you to see Diagnostics of problems that may be affecting your CWVs.
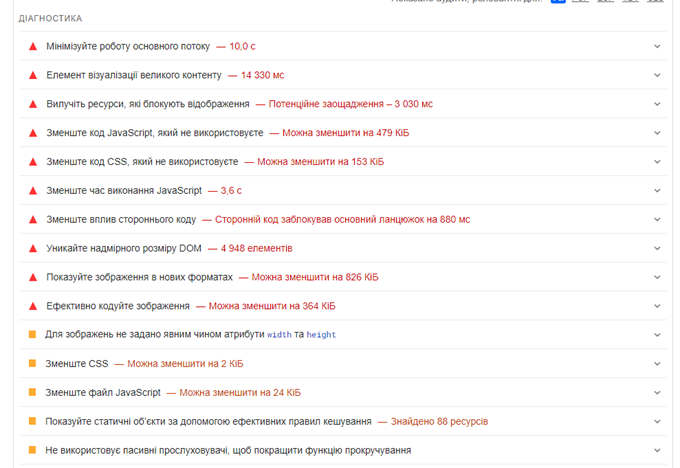
Use these diagnostics to inform your developers, designers, and programmers who can help you solve these problems.
Security issues and manual sanctions
If you’re having trouble indexing and ranking, Google may have detected a security issue or taken manual action against your site. GSC provides reports on both security issues and manual sanctions in the left column of the page.
If you have a problem with any of these issues, you’re indexing and ranking problems won’t go away until you fix them.
5 Ways to Use GSC for SEO
There are five ways to use GSC for SEO in your daily activities.
1. Measuring site performance
The top of the performance report in Search Console provides a lot of information about how the site is performing in search, including search features such as snippets.
Four types of searches can be explored in the performance report:
- web;
- image;
- video;
- news.
By default, Search Console shows the search type “Web”. You can change the displayed search type by clicking the Search Type button:
A useful feature is the ability to compare the performance of two types of searches within the graph.
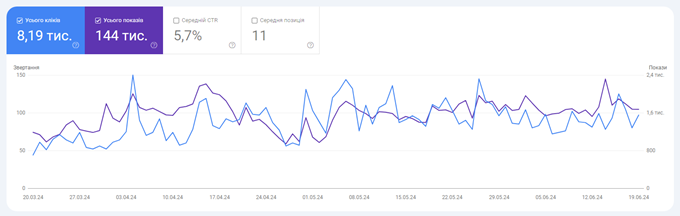
The four metrics that appear at the top of the performance report are:
- total number of clicks;
- total number of impressions;
- average CTR;
- middle position
By default, the Total Clicks and Total Impressions metrics are selected. By clicking on the tabs dedicated to each metric, you can choose to display those metrics on the graph.
Showings
Impressions are the number of times a site appears in search results. If the user does not have to click on the link to see the URL, it counts as an impression. Also, if the URL is at the bottom of the page and the user doesn’t scroll to that section of the search results, it still counts as an impression. High impressions are good because it means Google is showing the site in search results. Impression’s metrics gain importance through clicks and average position.
Clicks
Click-through metrics show how often users move from search results to a website. High clicks and high impressions are good. Low clicks and high impressions are less good, but not bad. This means that the site may need improvements to attract more traffic. Click metrics gain significance when combined with average CTR and average position.
Average CTR
Average CTR is a percentage that represents how often users move from the search results to the website. A low CTR means that something needs to be improved to increase traffic from search results, whether it’s changing the page title or updating the meta description. A higher CTR means that the site is performing well with users. These metric gains significance when combined with the average position.
Average position
The average position shows the average position in the search results in which the website appears.
An average position from 1 to 10 is great.
An average position in the range of 11-29 means that the result appears after the user scrolls through the search results, revealing more results. While this is not bad, it is not optimal. This may mean that the site needs more work to get into the top 10.
Average positions below 30 (overall) may indicate that pages need significant improvement.
It can also indicate that the site is ranking for a lot of low-ranking keywords and a few very good high-ranking keywords.
All four metrics (impressions, clicks, average CTR, and average position) taken together provide a meaningful overall picture of how a site is performing. The main thing to take away from the performance report is that it is a starting point for quickly understanding a site’s search performance. It is like a mirror that reflects whether the site is performing well or not.
Do you know how the average position in GSC is calculated? This is quite interesting! The average position is counted only if it was fixed for queries, which is logical, but there is a point here, namely “if the site was ranked by 100 queries, where part was in the TOP-10, part in the TOP-50, etc., then the average position will be , for example, 15. And for the next month, nothing has changed, but the site stopped being ranked by the part of requests that were in the TOP-50, then the average position will increase to 10.” Let’s give an example:
|
Request |
Position 10.05 |
Position 10.06 |
|
Request 1 |
5 |
5 |
|
Request 2 |
7 |
7 |
|
Request 3 |
12 |
12 |
|
Request 4 |
11 |
11 |
|
Request 5 |
4 |
4 |
|
Request 6 |
15 |
– |
|
Request 7 |
20 |
– |
|
Request 8 |
30 |
– |
|
Request 9 |
45 |
– |
|
Question 10 |
80 |
– |
|
Average position |
22.9 |
7.8 |
In May, the site was ranked by 10 queries and had an average position of 22.9, and in June the site was already ranked by 5 queries and had an average position of 7.8. It would seem that this is it, an “improvement”, but there is a nuance.
2. Search for keywords “on the edge of reach”
The search results report in the GSC performance section lets you see queries and their average position. While most of the queries for which many companies rank in the top three positions in the GSC are branded terms, the queries that are in positions 5-15 are considered “out of reach” queries. You can prioritize these queries based on impressions and update your content to include these queries in the language of those pages.
To find these terms:
- Click on “Search Results” in the left column of GSC.
- Click on “Search results”.
- By default, the “Total clicks” and “Total impressions” metrics are activated, so click on “Average position” to activate this metric as well.
- In the query table below, sort the columns by position and scroll until you reach positions 5 through 15.
- Collect queries that have higher impressions and use them to improve your content strategy.
3. Request for faster indexing of new pages
For many sites, Googlebot is very efficient at finding new pages quickly. However, if you have a priority page that needs to be indexed urgently, you can use the URL Checker tool to test the live URL and then request indexing.
To request indexing:
- Click “URL Validation” in the left column of GSC.
- Paste the URL of the page you want indexed into the top search box.
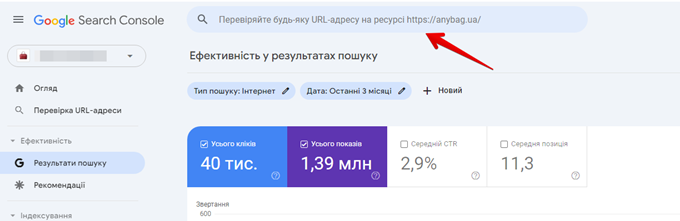
- Press “Enter”.
- On the next URL validation page, click Submit Indexing Request.
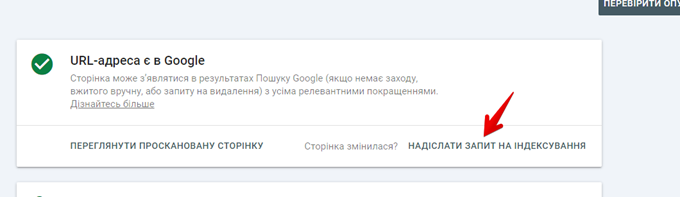
This process will add your URL to Googlebot’s priority queue for crawling and indexing, however, this process does not guarantee that Google will index the page. If your page is not indexed after this, further investigation will be necessary.
Note: Each verified property in GSC is limited to 50 indexing requests per day.
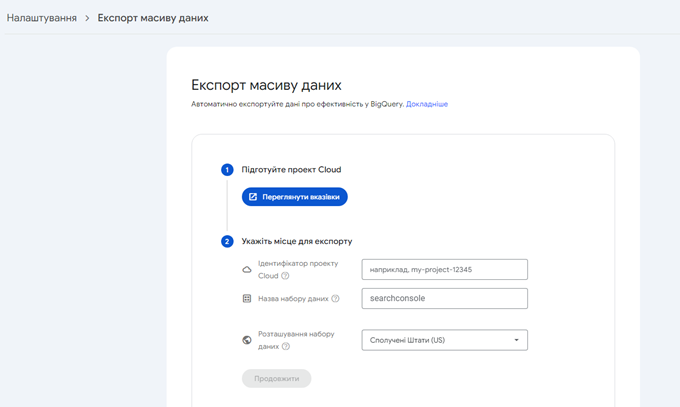
4. Mass export of data
GSC historical data is limited to a maximum of 16 months. Fortunately, you can overcome this problem by exporting GSC data to BigQuery, where it can be stored indefinitely. This allows you to access as much historical data as you need. Since this action is irreversible, you should start as soon as possible.
5. Integration with other SEO tools
While you can do a lot of things in GSC, the real magic happens when you integrate data from GSC into the many SEO tools and platforms available on the market. Integrating GSC into these tools gives you a clearer view of your site’s performance and potential.
From desktop crawlers like Screaming Frog and Sitebulb to enterprise server crawlers like Lumar and Botify, integrating GSC information can lead to a more thorough audit of your pages, including crawlability, accessibility, and user experience factors.
Integrating GSC into major SEO tools like Semrush and Ahrefs can provide more comprehensive ranking information, content ideas, and link data. In addition, the convenience of having all your data in one view cannot be underestimated. We all have limited time, so these options can make your job a lot easier.
To summarize
Google Search Console has evolved over its nearly two decades of existence. Since its release as Google Webmaster Tools, it has provided valuable information for SEO professionals and site owners.
If you haven’t yet integrated it into your daily activities, you will quickly realize how important this tool is to making the right decisions about optimizing your site in the future.






 02/07/2024
02/07/2024  3165
3165



