Content of the article
- /01 How a news site differs from others and how it affects promotion
- /02 How to build a website structure and navigation correctly
- /03 How to get into search as quickly as possible
- /04 Keywords and working with trends
- /05 The importance of mobile adaptation of the resource
- /06 Technical stability and speed of the website
- /07 Additional methods of promoting news sites


The competition for reader attention in the news space is fiercer than ever. The audience consumes information instantly, so a split second and the right headline often determine whether a user will stay on the site. This creates specific requirements for the promotion of a news resource: the speed of publication, technical readiness of the platform, adaptation to mobile channels, and at the same time maintaining editorial standards.
In this article, we will look at how to build a news website promotion with these requirements in mind. We’ll talk about the key differences between news portals, how they form an SEO strategy, and what you need to do first to ensure that your site systematically increases organic traffic and retains its audience.
How a news site differs from others and how it affects promotion
A news site operates in a fundamentally different dynamic than corporate, e-commerce, or service resources. Content is updated every hour, topics quickly lose their relevance, and competition for the top positions in the search results unfolds literally in real time. These features shape the requirements for SEO strategy, technical architecture, and editorial processes.
To build effective promotion, it is important to consider several key factors:

Fast news life cycle
Most news has a very short period of active demand. If the material is not found in search within the first hours after publication, its potential to attract organic traffic is significantly reduced. This places increased demands on website speed, sitemap correctness, and stable accessibility of the resource for search robots. At the same time, speed should not compromise quality – fact-checking and editorial standards remain critical to audience trust.
Large volume of pages and the risk of duplication
News portals accumulate thousands of materials: feeds, sections, tags, archives. Without a clear logic of structure, the same topic can have several similar pages, which compete with each other in the search results. This leads to cannibalization of traffic and unstable positions. To avoid this, you need a well-thought-out hierarchy of sections, the correct use of tags, canons, and internal linking.
The need for the fastest possible indexing
For news, it is crucial that search engines find new materials immediately after publication. This is achieved through dynamic XML sitemaps, RSS feeds, correct metadata, and structured data. This approach increases the chances of your content getting into newsgroups and aggregators and allows you to get the first traffic faster.
Behavioral factors and readability
Users consume news quickly: they look at the headline, introduction, and scan the text. If the page loads slowly, has an overloaded design or inconvenient navigation, bounce rates increase, and this negatively affects SEO. Readability, logical structure of the material, adaptation to mobile devices, and convenient access to related news directly affect the attraction and retention of the audience.
Combining breaking news and long-form content
Breaking news generates peak traffic, but analytical materials, explanatory articles, and thematic collections provide a steady flow of visitors. An effective strategy involves the development of both areas: quick coverage of events and systematic work with content that remains relevant in the long term.
Rapid response to trends and well-coordinated processes
In the news business, a delay of even a few hours can mean losing a significant share of traffic. That’s why it’s important to have trend monitoring tools and clear internal processes for interaction between the editorial staff, SEO specialists, and the technical team. This allows you to simultaneously ensure the speed of publication, correct optimization, and stable operation of the site.
This approach creates the basis for systematic growth of the news resource. In the next section, we’ll look at how to build a website structure and navigation to support content scaling and convenience for readers and search engines.
How to build a website structure and navigation correctly
To scale content without chaos, a website must have a clear information architecture. The reader should intuitively understand where to look for a topic, and the editorial staff should know where to post materials. So let’s look at the practical principles of building sections, the logic of URLs and breadcrumbs, the role of tags, working with search and filters, and organizing internal transitions.
- Heading hierarchy: simple levels, clear logic.
Start with a limited number of main sections (6-10) that reflect the information priorities of your audience. For each heading, allow only 1-2 levels of subheadings, because more depth makes navigation more difficult and content management more difficult for the editorial staff. For each section, define its role: a breaking news feed, an analytical hub, or a thematic selection. This helps to immediately determine where to place the material and what blocks to show on the section page (for example, TOP, latest, popular).
- URL and «breadcrumbs»: the obvious way for the user.
The URL should reflect the logic of the structure: site.com/heading/subheading/title. Such addresses are clear to the reader and make it easier to navigate. Breadcrumbs add context wherever the user may get lost: they return the reader to the section or subsection and encourage deeper browsing. Take care of the stability of page addresses – changes in URLs should be avoided or accompanied by correct redirects.
- Tags: labeling topics, but without chaos.
Tags are useful when they provide an accurate thematic context. But without tagging rules, they create hundreds of useless aggregator pages. Implement a clear policy: limiting the number of tags per article, standardized forms (e.g., trends-SEO-2026), regular review, and merging rarely used tags. A good tag page is not just a list of links, but a brief description of the topic and a selection of key materials.
- Internal transitions and hubs: direct the reader’s attention.
Offer relevant content at the end and within articles: «Read also», topic hubs, or series of publications. For serial topics, create hub pages with annotations and navigation by subtopics, as this helps to retain the reader and logically group materials. Avoid random «link noise»: every internal link should be useful to the reader.
- Search and filtering: a user retention tool.
Fast and relevant search with auto-suggestions increases the satisfaction of the site. Add easy-to-understand filters (date, region, heading, type of material, etc.) and save the state of the filters in the URL – this allows you to share filtered pages by link and quickly return to the desired results. Consider simple personalized options for registered users: subscriptions to topics, saved searches, and update notifications.
So, before scaling your content, do a basic cleanup of the structure: select the main headings, define the role of each, create simple tagging rules, implement breadcrumbs and a working search with auto-complete suggestions. This will give the editorial staff discipline and readers quick orientation. And it will greatly facilitate the further growth of the project.
How to get into search as quickly as possible
As we have already mentioned, news content should be visible immediately after publication – a delay in indexing often means losing readers. To ensure fast delivery of materials to search engines and aggregators, you need to set up several interconnected processes:
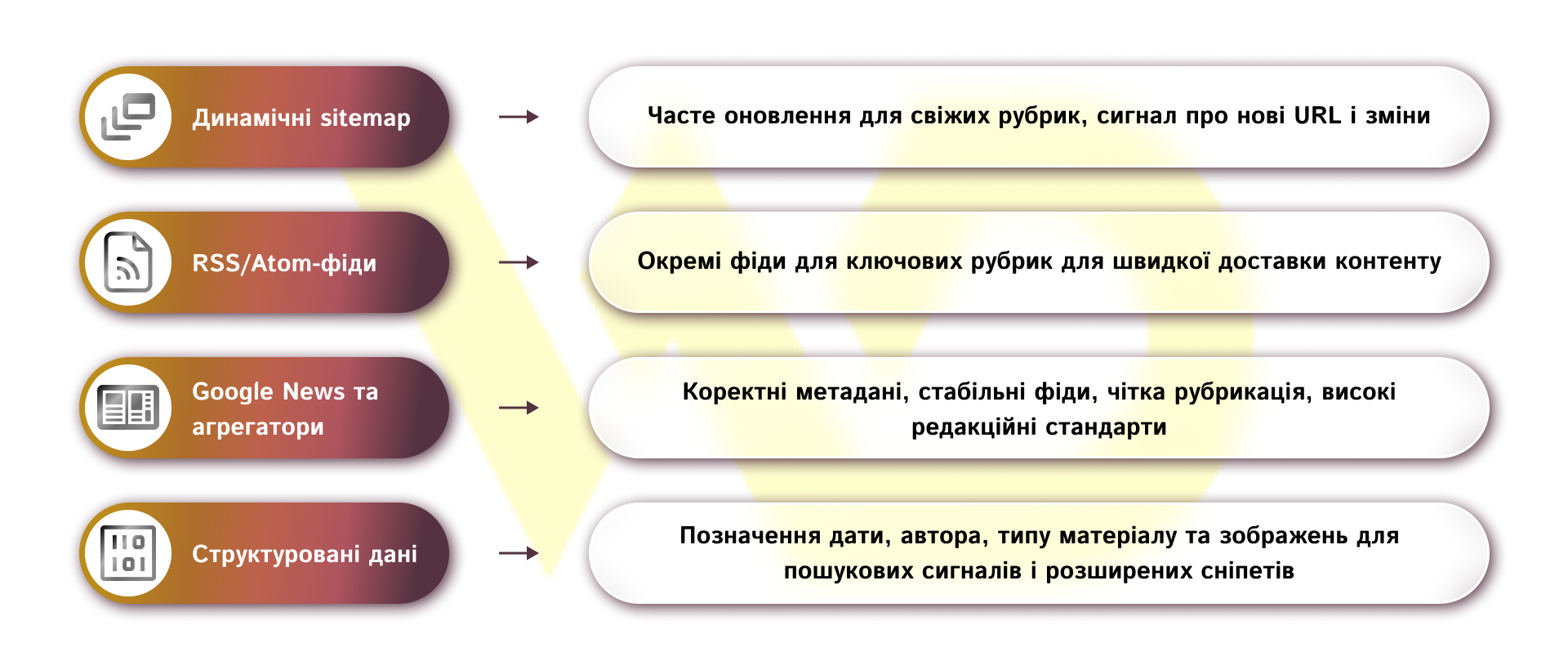
Firstly, dynamic sitemaps should reflect the real state of the feed: for fresh headings, frequent updates, for archives and special projects, separate maps. A dynamic sitemap is automatically updated when you publish or edit a piece of content and serves as a prompt signal to search engine crawlers about new URLs and changes on your site.
Secondly, RSS/Atom feeds remain the main content delivery channel for aggregators and services. It is worth setting up separate feeds for key sections or thematic streams, so that external services will pick up exactly the materials they need faster, without unnecessary «noise» from the general feed.
Thirdly, working with Google News and local aggregators requires compliance with their rules: correct metadata, stable feeds, no duplication, and high editorial standards. Having hub pages and a clear rubric simplifies moderation by aggregators and increases the chances of getting into thematic selections or carousels.
Finally, structured data is a technical, but at the same time understandable way for search engines to convey key information: date of publication, author, type of material, images. Correct tagging gives search engines additional signals and improves the likelihood of advanced snippets or getting into thematic sections of the SERP.
The fastest way to make your content visible in search engines and aggregators is to automate the updating of sitemaps and topical feeds, centrally control metadata for each publication, and make sure that new material is immediately placed in the appropriate feed.
Keywords and working with trends
In the news niche, semantics works in real time: you need to quickly identify and address «hot» queries, but also form a cluster structure around longer topics. Practical approaches to on-page SEO:
- Use several sources at the same time. Google Trends for search spikes, social media feeds and hashtags for instant feedback, and aggregators for local signals. Set up internal notifications for the newsroom.
- When a trend is detected, quickly formulate a set of key phrases (short and long queries) that should be used in headlines, subheadings, and meta descriptions. Create temporary page templates for events; with a clear H1, subheadings and an update block.
- In news, the headline plays two roles at once: to attract searchers and to accurately reflect the essence. Work with wording that balances accuracy and clickability, add the date and place, a key fact, and a unique angle. The meta description should complement the title and give a reason to click on your material.
For convenience, create a simple process to «catch the trend»: one operator monitors the signal, the editor generates a headline and a list of key phrases, and the technical team ensures quick publication. Such an organization will allow you to respond to events quickly and optimize the material correctly.
The importance of mobile adaptation of the resource
Most users read news on their phones, so the convenience of the mobile experience directly affects audience retention. Let’s take a look at the key UX solutions for mobile readers.
Mobile-first design of news pages
Design pages primarily for small screens. There should be concise headlines, short paragraphs, catchy CTAs, and simple menus. Consider responsive blocks that change the order of content depending on the screen (for example, the first block with the main fact and the «Read More» button).
Readability, navigation and scrolling convenience
Optimal font size, sufficient line spacing, and contrast ensure that text is scanned quickly. Avoid long embedded elements that force horizontal scrolling. Divide large text into subheadings and interactive inserts.
Appropriateness of AMP and PWA
AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) provides very fast content loading. Such pages are more easily included in some news carousels. At the same time, AMP has limitations in functionality and design, which reduces project flexibility. In turn, PWA (Progressive Web App) allows you to create the feeling of a full-fledged application right in the browser. The user gets quick access to the site, the ability to receive push notifications, and work with the content more stably. However, the implementation of PWA requires additional resources for development and support.
The choice depends on business priorities. If the key goal is to open articles instantly and maximize speed for the mobile audience, AMP may be the right solution. If interactivity, repeat visits, and user retention are important, then PWA is more promising.
Technical stability and speed of the website
The technical stability and speed of a website is the basis without which editorial and marketing investments do not yield the expected result. For a news resource, this means constant readiness for peak loads, predictable performance, and quality control of the user experience.
Reducing the time of content delivery to the reader is ensured by using a distributed CDN, and caching at the server and browser levels reduces the load on the infrastructure and stabilizes the site during traffic spikes. Particular attention should be paid to image optimization: the use of modern WebP or AVIF formats where supported, adaptive images for different screens, and delayed loading so as not to overload the first screen of the page.
For systematic quality control, it is necessary to define the basic Core Web Vitals metrics:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint, the speed of displaying the main content);
- FID (First Input Delay);
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift).
And set up continuous monitoring. This allows you to quickly detect degradation of indicators, prioritize technical corrections, and maintain a stable level of user experience even with active content updates.
A separate area is preparation for peak loads that inevitably occur during high-profile events or information waves. Planning for horizontal and vertical scaling, limiting excessive bot activity, using request queuing mechanisms and aggressive page caching reduce the risk of failures and speed drops. For critical materials, it is advisable to prepare static versions of pages in advance that can withstand high simultaneous traffic.
Additional methods of promoting news sites
The publication strategy is only the first part of the work. Next, the material needs to be further promoted and the user needs to be encouraged to make repeated visits.
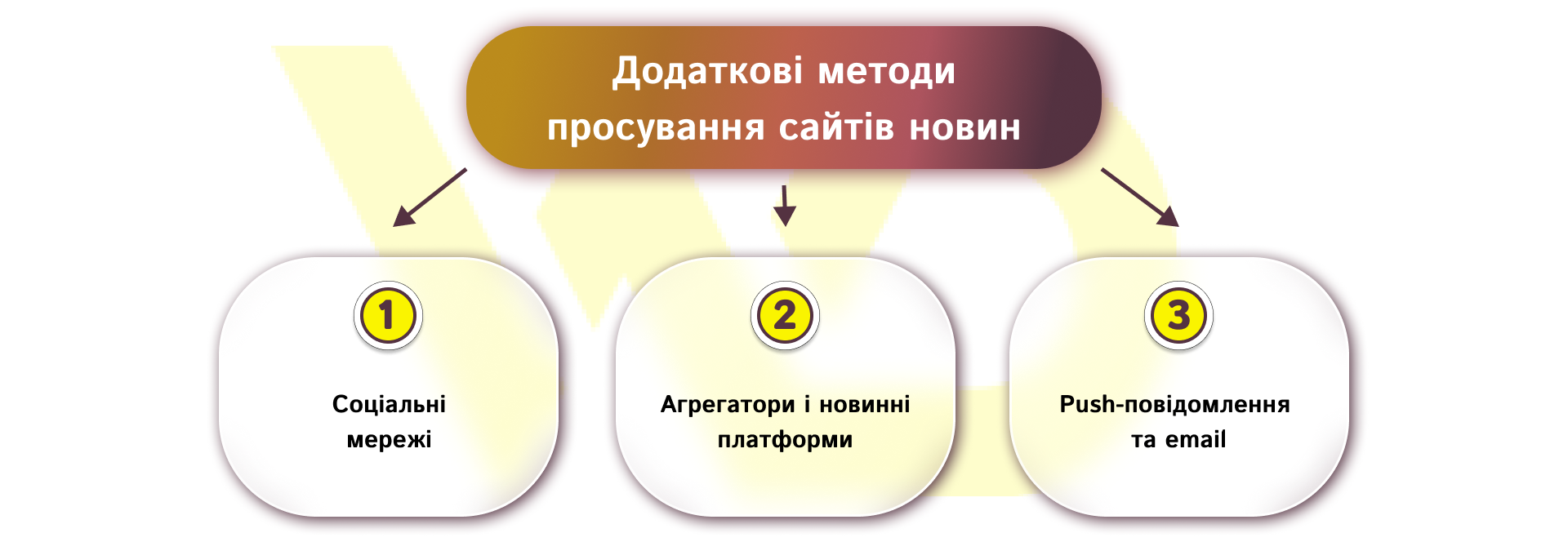
Social media as a traffic channel
For urgent topics, social media provides a quick boost, while for analytics, it works as a long-term channel. Choose a format, such as short reviews, carousels, or videos, adapt the headline to the platform, and use local groups and communities to expand your reach.
Aggregators and news platforms
Publishing in aggregators (Google News, local services) requires technical compliance and content quality. Set up feeds and follow aggregator policies – this can provide a stable additional traffic channel.
Push notifications and email as retention tools
Push notifications work for instant engagement during important events, and daily digest or themed email newsletters work for building loyalty. Be sure to segment your audience, test the timing and frequency of emails, as too aggressive emails can be off-putting.
Useful tip! Combine channels: fast public dispersal on social media and aggregators and personalized return mechanisms (email, push) provide the best balance between reach and retention.
In conclusion, to promote a news site, you need to start by improving the structure of the resource, automatic indexing, and readiness for mobile traffic. It’s also important to invest in step-by-step improvements, which will ensure steady growth and minimize the time spent on fixing critical errors.






 28/01/2026
28/01/2026  1046
1046



